Yunjing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ''Yunjing'' () is one of the two oldest existing examples of a
''Yunjing''
(page scans) at the
''Yunjing''
(page scans) at the
Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
rhyme table A rime table or rhyme table () is a Chinese phonological model, tabulating the syllables of the series of rime dictionaries beginning with the ''Qieyun'' (601) by their onsets, rhyme groups, tones and other properties. The method gave a significa ...
– a series of charts which arrange Chinese characters
Chinese characters () are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. In addition, they have been adapted to write other East Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as ''kanji' ...
in large tables according to their tone and syllable structures to indicate their proper pronunciations. Current versions of the ''Yunjing'' date to AD 1161 and 1203 editions published by Zhang Linzhi (張麟之).
The original author(s) and date of composition of the ''Yunjing'' are unknown. Some of its elements, such as certain choices in its ordering, reflect features particular to the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
, but no conclusive proof of an actual date of composition has yet been found.
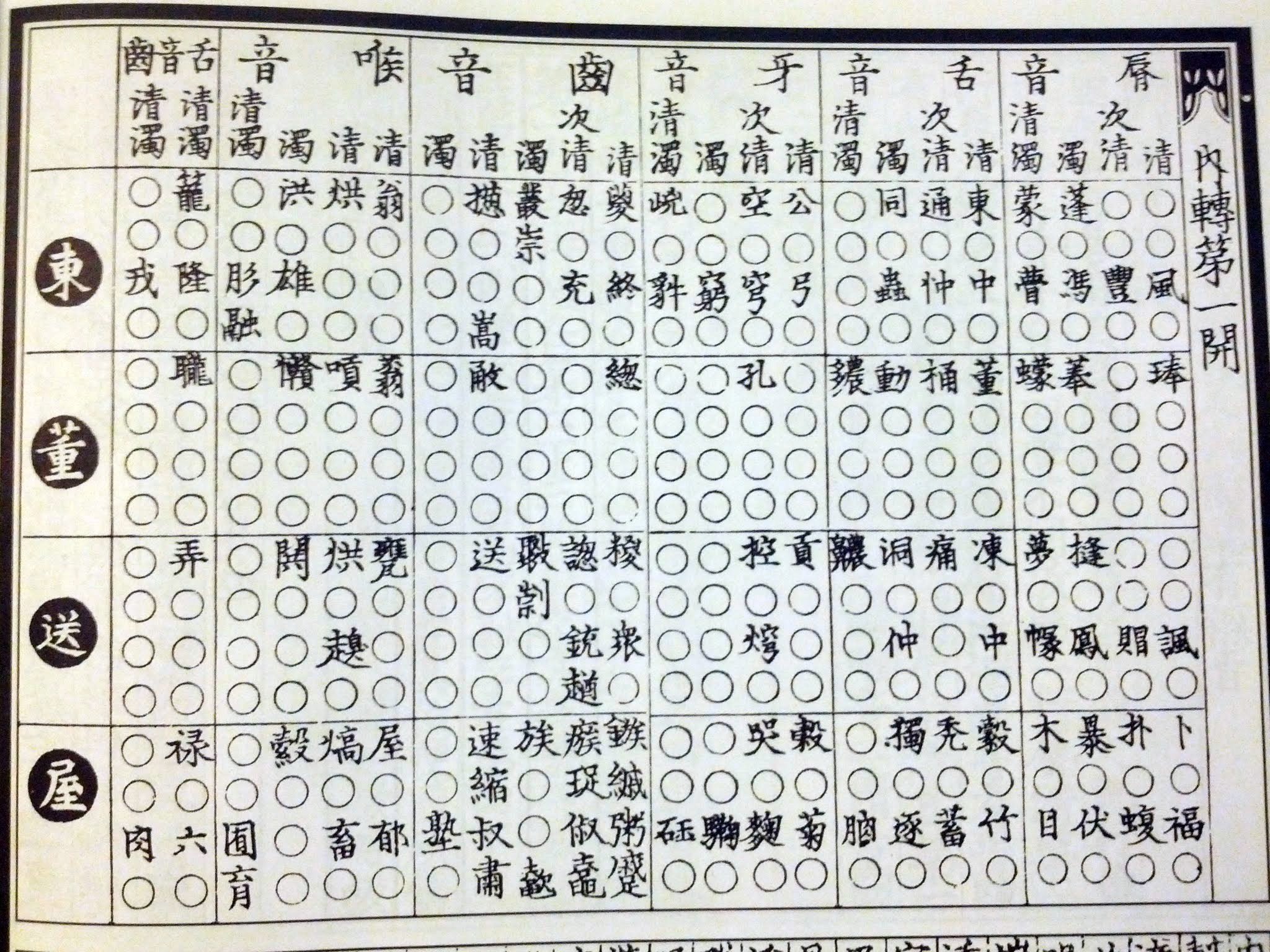
The ''Yunjing'' contains 43 tables (), each of which tabulates combinations of a particular final rhyme (listed in rows) with various initials (listed in columns), in up to four tones, to show in a grid pattern all possible syllables. Empty circles on the grid denote that the author(s) were unaware of any word with that particular pronunciation. By locating a character in ''Yunjing'', a reader could identify its initial consonant (by looking at its column) and its "rhyme", or main vowel and ending consonant (by looking at its row), and combine the two to obtain the word's pronunciation. Zhang Linzhi's prefaces list a total of 36 possible initial consonants () – by comparison, modern Standard Mandarin
Standard Chinese ()—in linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin Chinese—is a modern standar ...
only has 23 and modern Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding are ...
only has 18 or 19.
Historical Chinese phonology
Historical Chinese phonology deals with reconstructing the sounds of Chinese from the past. As Chinese is written with logographic characters, not alphabetic or syllabary, the methods employed in Historical Chinese phonology differ considerably ...
uses the ''Yunjing'' as an accurate representation of Late Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese (formerly known as Ancient Chinese) or the Qieyun system (QYS) is the historical variety of Chinese recorded in the ''Qieyun'', a rime dictionary first published in 601 and followed by several revised and expanded editions. The S ...
(10th – 12th century) phonology. The ''Yunjings use of this system represents a significant advancement in the Chinese' analysis of their own language, and is believed to have been inspired by their studies of Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
phonological treatises and Buddhist mantras written in the Siddham script during the Sui and Tang dynasties.
Layout

Rows (Finals/Rhymes)
Each of the 43 tables in the ''Yunjing'' is first divided into four large rows that correspond to thefour tones of Middle Chinese
The four tones of Chinese poetry and dialectology () are four traditional tone classes of Chinese words. They play an important role in Chinese poetry and in comparative studies of tonal development in the modern varieties of Chinese, both in tr ...
: the level tone (), the rising tone (), the departing tone (), and the entering tone (). They are not explicitly marked as such, but the four characters are taken from each of the tone categories of the '' Guangyun'' rhyme dictionary
A rime dictionary, rhyme dictionary, or rime book () is an ancient type of Chinese dictionary that collates characters by tone and rhyme, instead of by radical. The most important rime dictionary tradition began with the '' Qieyun'' (601), ...
. In the image at right, the first row – the level tone – is occupied by the level tone rhyme ''dōng'' 東, the second row – the rising tone – by the ''dǒng'' 董 rhyme, the third row – the departing tone – by ''sòng'' 送, and the fourth row – the entering tone – by ''wū'' 屋 (Cantonese
Cantonese ( zh, t=廣東話, s=广东话, first=t, cy=Gwóngdūng wá) is a language within the Chinese (Sinitic) branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages originating from the city of Guangzhou (historically known as Canton) and its surrounding are ...
: uk1).
Each large row is further subdivided into four grades or divisions (), forming four rows within each larger row. Characters' placement in the first through fourth grade seems to be related to their medial (glide) and main vowel, though their exact distinction is unclear.
Columns (Initials)
Each table is divided into six large columns representing syllables'place of articulation
In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation (also point of articulation) of a consonant is a location along the vocal tract where its production occurs. It is a point where a constriction is made between an active and a passive articula ...
:
*"Lip sounds" ()
*"Tongue sounds" ()
*" Molar sounds" ()
*"Tooth sounds" ()
*"Throat sounds" ()
*"Tongue-tooth sounds" ()
Large columns are further subdivided into two to five smaller columns, which can represent one of four possible sub-categories:
**"Clear" sounds () – voiceless
In linguistics, voicelessness is the property of sounds being pronounced without the larynx vibrating. Phonologically, it is a type of phonation, which contrasts with other states of the larynx, but some object that the word phonation implies v ...
unaspirated
In linguistics, a tenuis consonant ( or ) is an obstruent that is voiceless, unaspirated and unglottalized.
In other words, it has the "plain" phonation of with a voice onset time close to zero (a zero-VOT consonant), as Spanish ''p, t, ch ...
**"Secondarily-clear" sounds () – voiceless
In linguistics, voicelessness is the property of sounds being pronounced without the larynx vibrating. Phonologically, it is a type of phonation, which contrasts with other states of the larynx, but some object that the word phonation implies v ...
aspirated
**"Muddy" sounds () – voiced
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds (usually consonants). Speech sounds can be described as either voiceless (otherwise known as ''unvoiced'') or voiced.
The term, however, is used to refer ...
**"Clear-muddy" sounds () – nasal stop
In phonetics, a nasal, also called a nasal occlusive or nasal stop in contrast with an oral stop or nasalized consonant, is an occlusive consonant produced with a lowered velum, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. The vast majorit ...
s
The ''Yunjing'' tables have only 23 columns – some columns represent more than one of the 36 possible initial consonants. Other rhyme tables, such as the ''Qieyun zhizhangtu'' (), do not combine the initials and have 36 full columns.
See also
*Rhyme dictionary
A rime dictionary, rhyme dictionary, or rime book () is an ancient type of Chinese dictionary that collates characters by tone and rhyme, instead of by radical. The most important rime dictionary tradition began with the '' Qieyun'' (601), ...
* ''Qiyin lüe
The ''Qiyin lüe'' () is a Chinese rime table, which dates to before 1161. This reference work survived to the present largely because the Song dynasty historian Zheng Qiao (/; ''Cheng Ch'iao''; 1104–1162) included it in his 1161 encyclopedia ...
''
Citations
*Further reading
* Coblin, W. South. "Northwest reflections on the ''Yunjing''." ''T’oung Pao'' 82 (1996): 349-363. *Pulleyblank, Edwin G.
Edwin George "Ted" Pulleyblank (August 7, 1922 – April 13, 2013) was a Canadian sinologist and professor at the University of British Columbia. He was known for his studies of the historical phonology of Chinese.
Life and career
Edwin G. ...
"''Qieyun'' and ''Yunjing'': The Essential Foundation for Chinese Historical Linguistics." ''Journal of the American Oriental Society'' 118.2 (1998): 200-216.
External links
''Yunjing''
(page scans) at the
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, ...
''Yunjing''
(page scans) at the
Chinese Text Project
The Chinese Text Project (CTP; ) is a digital library project that assembles collections of early Chinese texts. The name of the project in Chinese literally means "The Chinese Philosophical Book Digitization Project", showing its focus on books ...
{{Authority control
Chinese dictionaries
Middle Chinese
Song dynasty
Traditional Chinese phonology
12th-century Chinese books