|
History Of Latitude
The Greeks studied the results of the measurements of latitude by the explorer Pytheas who voyaged to Britain and beyond, as far as the Arctic Circle (observing the midnight sun), in 325 BC. They used several methods to measure latitude, including the height of the Sun above the horizon at midday, measured using a gnōmōn (a word that originally meant an interpreter or judge); the length of the day at the summer solstice, and the elevation of the Sun at winter solstice. The Greek Marinus of Tyre (AD 70–130) was the first to assign a latitude and longitude to every place on his maps. From the late 9th century CE, the Arabian Kamal was used in equatorial regions, to measure the height of Polaris above the horizon. This instrument could only be used in latitudes where Polaris is close to the horizon. The mariner's astrolabe which gives the angle of the Sun from the horizon at noon, or the angle of a known star at night, was used from around the 15th to the 17th centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Lines of constant latitude, or ''parallels'', run east–west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and ''longitude'' are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term "latitude" normally refers to the ''geodetic latitude'' as defined below. Briefly, the geodetic latitude of a point is the angle formed between the vector perpendicular (or '' normal'') to the ellipsoidal surface from the point, and the plane of the equator. Background Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definitions of latitude and longitude. In the first step the physical surface is modeled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over the oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal: :* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira. It features the westernmost point in continental Europe, its mainland west and south border with the North Atlantic Ocean and in the north and east, the Portugal-Spain border, constitutes the longest uninterrupted border-line in the European Union. Its archipelagos form two autonomous regions with their own regional governments. On the mainland, Alentejo region occupies the biggest area but is one of the least densely populated regions of Europe. Lisbon is the capital and largest city by population, being also the main spot for tourists alongside Porto, the Algarve and Madeira. One of the oldest countries in Europe, its territory has been continuously settled and fought over since prehistoric tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Latitude Service
__NOTOC__ The International Latitude Service was created by the International Geodetic Association in 1899 to study variations in latitude caused by polar motion, precession, or "wobble" of the Earth's axis. The original ''International Latitude Observatories'' were a system of six observatories located near the parallel of 39° 08' north latitude. The alignment of all six stations along the parallel helped the observatories to perform uniform data analysis. The original six observatories were located in: * Gaithersburg, Maryland, United States * Cincinnati, Ohio, United States * Ukiah, California, United StatesHogle, Gene ''NAC Green Book of Pacific Coast Touring'' (1931) National Automobile Club p.43 * Mizusawa, Iwate, Japan * Charjui, Turkmenistan * Carloforte, Italy Twelve groups of stars were studied in the program, each group containing six pairs of stars. Each night, each station observed two of the star groups along a preset schedule and later compared the data against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Navigation
The history of navigation, or the history of seafaring, is the art of directing vessels upon the open sea through the establishment of its position and course by means of traditional practice, geometry, astronomy, or special instruments. Many peoples have excelled as seafarers, prominent among them the Austronesians ( Islander Southeast Asians, Malagasy, Islander Melanesians, Micronesians, and Polynesians), the Harappans, the Phoenicians, the Iranians, the ancient Greeks, the Romans, the Arabs, the ancient Indians, the Norse, the Chinese, the Venetians, the Genoese, the Hanseatic Germans, the Portuguese, the Spanish, the English, the French, the Dutch, and the Danes. Antiquity Indo-Pacific Navigation in the Indo-Pacific began with the maritime migrations of the Austronesians from Taiwan who spread southwards into Island Southeast Asia and Island Melanesia during a period between 3000 and 1000 BC. Their first long-distance voyaging was the colonization of Microne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Longitude
The history of longitude describes the centuries-long effort by astronomers, cartographers and navigators to discover a means of determining the longitude of any given place on Earth. The measurement of longitude is important to both cartography and navigation. In particular, for safe ocean navigation, knowledge of both latitude and longitude is required. Finding an accurate and practical method of determining longitude took centuries of study and invention by some of the greatest scientists and engineers. After increasingly accurate methods based on astronomical observations and chronometers, today the problem of longitude has been solved to centimeter accuracy through satellite navigation. Longitude before the telescope Eratosthenes in the 3rd century BCE first proposed a system of latitude and longitude for a map of the world. His prime meridian (line of longitude) passed through Alexandria and Rhodes, while his parallels (lines of latitude) were not regularly spaced, but p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Geodesy
The history of geodesy deals with the historical development of measurements and representations of the Earth. The corresponding scientific discipline, ''geodesy'' ( /dʒiːˈɒdɪsi/), began in pre-scientific antiquity and blossomed during the Age of Enlightenment. Early ideas about the figure of the Earth held the Earth to be flat (see flat Earth), and the heavens a physical dome spanning over it. Two early arguments for a spherical Earth were that lunar eclipses were seen as circular shadows which could only be caused by a spherical Earth, and that Polaris is seen lower in the sky as one travels South. Hellenic world Initial development from a diversity of views Though the earliest written mention of a spherical Earth comes from ancient Greek sources, there is no account of how the sphericity of Earth was discovered, or if it was initially simply a guess.James Evans, (1998), ''The History and Practice of Ancient Astronomy'', page 47, Oxford University Press A plausible e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Godfrey (inventor)
Thomas Godfrey (January 10, 1704 – December 1749) was a glazier and self-taught mathematician and astronomer in the Pennsylvania Colony, who invented the octant in 1730. A similar octant was also independently invented about the same time by John Hadley in London with Hadley receiving the greater share of the credit for development. He published almanacs and contributed essays on mathematics, astronomy and general topics to the ''Pennsylvania Gazette'' and ''Pennsylvania Journal''. He assisted the Welsh surveyor Lewis Evans in conducting astronomical observations to correct the longitude of Philadelphia on maps published by Evans. He was friends with Benjamin Franklin and a founding member of the Junto club, which was the precursor of the American Philosophical Society. He served as a director of the Library Company of Philadelphia and was a member of American Philosophical Society with the title "mathematician". Early life Godfrey was born January 10, 1704, to Joseph and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hadley
John Hadley (16 April 1682 – 14 February 1744) was an English mathematician, and laid claim to the invention of the octant, two years after Thomas Godfrey claimed the same. Biography He was born in Bloomsbury, London the eldest son of George Hadley of Osidge, East Barnet, Hertfordshire and his wife Katherine FitzJames. His younger brother George Hadley became a noted meteorologist. In 1717 John became a member (and later vice-president) of the Royal Society of London. In 1729 he inherited his father's East Barnet estate. He died in East Barnet in 1744 and is buried in the local churchyard with other members of his family. He had married Elizabeth, daughter of Thomas Hodges, FRS (former Attorney General of Barbados) and had one child, a son and heir John, born in 1738. Work In 1730 Hadley invented the reflecting octant, which could be used to measure the altitude of the sun or other celestial objects above the horizon at sea. A mobile arm carrying a mirror and piv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a " natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus. In the , Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint for centuries until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, accoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
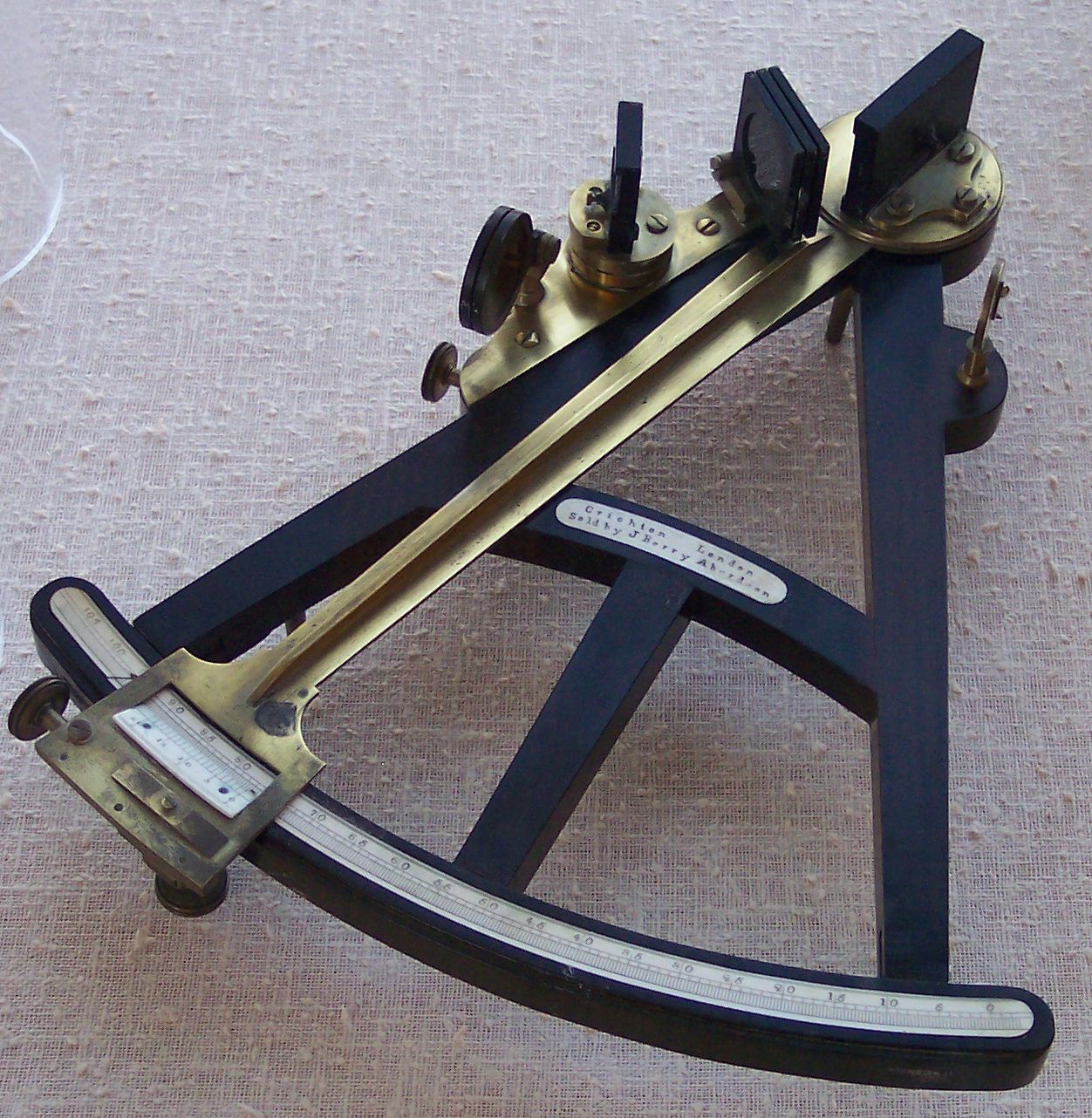
Sextant
A sextant is a doubly reflecting navigation instrument that measures the angular distance between two visible objects. The primary use of a sextant is to measure the angle between an astronomical object and the horizon for the purposes of celestial navigation. The estimation of this angle, the altitude, is known as ''sighting'' or ''shooting'' the object, or ''taking a sight''. The angle, and the time when it was measured, can be used to calculate a position line on a nautical or aeronautical chart—for example, sighting the Sun at noon or Polaris at night (in the Northern Hemisphere) to estimate latitude (with sight reduction). Sighting the height of a landmark can give a measure of ''distance off'' and, held horizontally, a sextant can measure angles between objects for a position on a chart. A sextant can also be used to measure the lunar distance between the moon and another celestial object (such as a star or planet) in order to determine Greenwich Mean Time and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octant (instrument)
The octant, also called a reflecting quadrant, is a reflecting instrument used in navigation. Etymology The name ''octant'' derives from the Latin ''octans'' meaning ''eighth part of a circle'', because the instrument's arc is one eighth of a circle. ''Reflecting quadrant'' derives from the instrument using mirrors to reflect the path of light to the observer and, in doing so, doubles the angle measured. This allows the instrument to use a one-eighth of a turn to measure a quarter-turn or quadrant. Origin of the octant Newton's reflecting quadrant Isaac Newton's reflecting quadrant was invented around 1699. A detailed description of the instrument was given to Edmond Halley, but the description was not published until after Halley's death in 1742. It is not known why Halley did not publish the information during his life, as this prevented Newton from getting the credit for the invention that is generally given to John Hadley and Thomas Godfrey. One copy of this ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Davis Quadrant
The backstaff is a navigational instrument that was used to measure the altitude of a celestial body, in particular the Sun or Moon. When observing the Sun, users kept the Sun to their back (hence the name) and observed the shadow cast by the upper vane on a horizon vane. It was invented by the English navigator John Davis, who described it in his book ''Seaman's Secrets'' in 1594. Types of backstaffs Backstaff is the name given to any instrument that measures the altitude of the sun by the projection of a shadow. It appears that the idea for measuring the sun's altitude using back observations originated with Thomas Harriot. Many types of instruments evolved from the cross-staff that can be classified as backstaves. Only the Davis quadrant remains dominant in the history of navigation instruments. Indeed, the Davis quadrant is essentially synonymous with backstaff. However, Davis was neither the first nor the last to design such an instrument and others are considered here ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_tombstone_in_Laurel_Hill_Cemetery.jpg)