|
Histidine Triad Nucleotide-binding Protein 1
Histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 also known as adenosine 5'-monophosphoramidase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''HINT1'' gene. HINT1 hydrolyzes purine nucleotide phosphoramidates with a single phosphate group. In addition, functions as scaffolding protein that modulates transcriptional activation. It is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor gene that inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in colon cancer cells and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) activity in human mast cells. In the LysRS-Ap4A-MITF signaling pathway, HINT1 inhibits the MITF transcriptional activity by direct association. Upon pathway activation, HINT1 is released from MITF by diadenosine tetraphosphate Diadenosine tetraphosphate or Ap4A is a putative alarmone, ubiquitous in nature being common to everything from bacteria to humans. It is made up of two adenosines joined together by a 5′-5′ linked chain of four phosphates. Adenosine polyphosp ... (Ap4A), produced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoramidate
Phosphoramidates (sometimes also called amidophosphates) are a class of phosphorus compounds structurally related to phosphates (or organophosphates) via the substitution of an OR for a NR2. They are derivatives of phosphoramidic acids O=P(OH)(NR2)2, O=P(OH)2(NR2). A phosphorodiamidate (or diamidophosphate) is a phosphate that has two of its OH groups substituted by NR2 groups to give a species with the general formula O=P(OH)(NH2)2. The substitution of all three OH groups gives the phosphoric triamides (O=P(NR2)3), which are commonly referred to as phosphoramides. Examples Two examples of natural phosphoramidates are phosphocreatine and the phosphoramidate formed when histidine residues in histidine kinases are phosphorylated. An example of a phosphorodiamidate is morpholino which is used in molecular biology. See also *Phosphoramidite A phosphoramidite (RO)2PNR2 is a monoamide of a phosphite diester. The key feature of phosphoramidites is their markedly high reactivity toward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
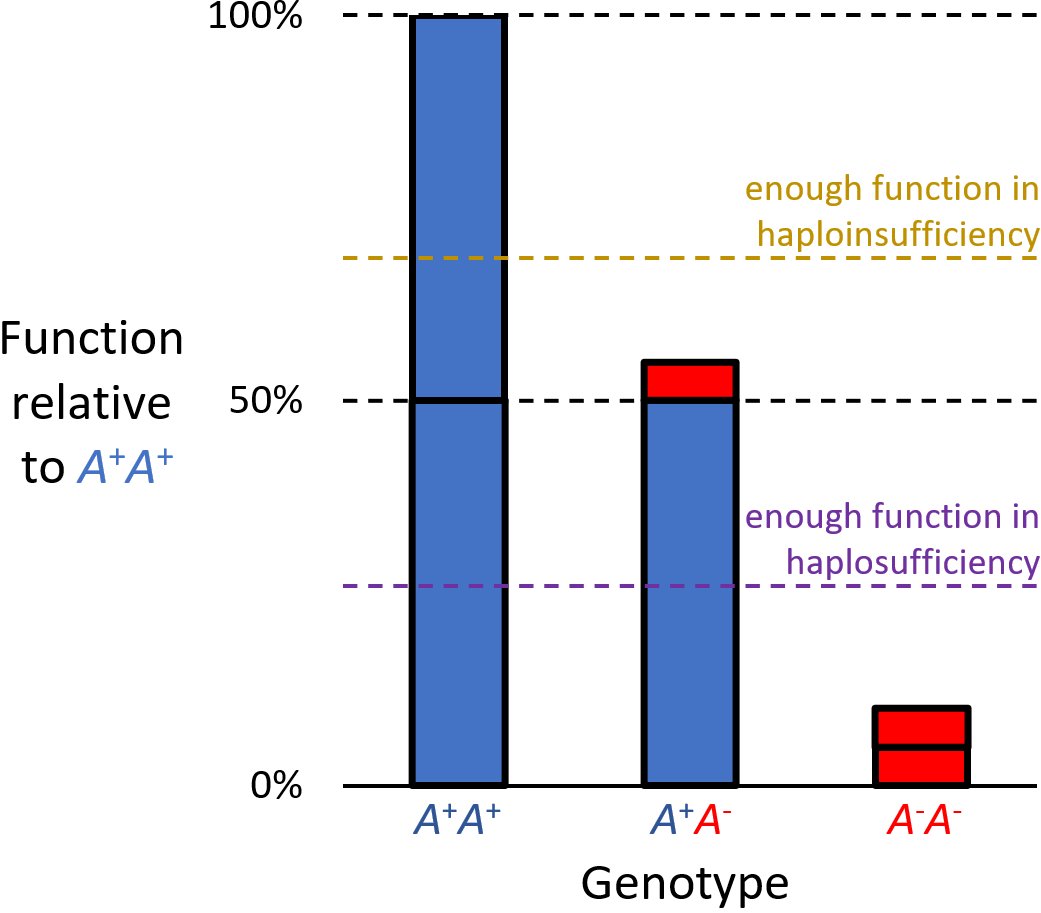
Haploinsufficient
Haploinsufficiency in genetics describes a model of dominant gene action in diploid organisms, in which a single copy of the wild-type allele at a locus in heterozygous combination with a variant allele is insufficient to produce the wild-type phenotype. Haploinsufficiency may arise from a ''de novo'' or inherited loss-of-function mutation in the variant allele, such that it yields little or no gene product (often a protein). Although the other, standard allele still produces the standard amount of product, the total product is insufficient to produce the standard phenotype. This heterozygous genotype may result in a non- or sub-standard, deleterious, and (or) disease phenotype. Haploinsufficiency is the standard explanation for dominant deleterious alleles. In the alternative case of haplosufficiency, the loss-of-function allele behaves as above, but the single standard allele in the heterozygous genotype produces sufficient gene product to produce the same, standard phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wnt Signaling Pathway
The Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans. Three Wnt signaling pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. All three pathways are activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand to a Frizzled family receptor, which passes the biological signal to the Dishevelled protein inside the cell. The canonical Wnt pathway leads to regulation of gene transcription, and is thought to be negatively regulated in part by the SPATS1 gene. The noncanonical plana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microphthalmia-associated Transcription Factor
Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor also known as class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 32 or bHLHe32 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MITF'' gene. MITF is a basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper transcription factor involved in lineage-specific pathway regulation of many types of cells including melanocytes, osteoclasts, and mast cells. The term "lineage-specific", since it relates to MITF, means genes or traits that are only found in a certain cell type. Therefore, MITF may be involved in the rewiring of signaling cascades that are specifically required for the survival and physiological function of their normal cell precursors. MITF, together with transcription factor EB (TFEB), TFE3 and TFEC, belong to a subfamily of related bHLHZip proteins, termed the MiT-TFE family of transcription factors. The factors are able to form stable DNA-binding homo- and heterodimers. The gene that encodes for MITF resides at the ''mi'' locus in mice, and its protumor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadenosine Tetraphosphate
Diadenosine tetraphosphate or Ap4A is a putative alarmone, ubiquitous in nature being common to everything from bacteria to humans. It is made up of two adenosines joined together by a 5′-5′ linked chain of four phosphates. Adenosine polyphosphates are capable of inducing multiple physiological effects. Function In Eukaryotes Ap4A can be created by a non-canonical activity of the Lysyl-tRNA synthetase (LysRS). This function of LysRS is activated by the phosphorylation of LysRS on serine 207, its subsequent dissociation from the multi-synthetase complex (MSC). The molecule's role as a second messenger has recently been discovered in The LysRS-Ap4A-MITF signaling pathway. Ap4A binds to the MITF-HINT1 inhibitory complex, specifically to the molecule histidine triad nucleotide–binding protein 1(HINT1), releasing the Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) and causing an increase in the transcription of its target genes. Ap4A also positively regulates the ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KARS (gene)
Lysyl-tRNA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''KARS'' gene. Function Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are a class of enzymes that charge tRNAs with their cognate amino acids. Lysyl-tRNA synthetase is a homodimer localized to the cytoplasm which belongs to the class II family of tRNA synthetases. It has been shown to be a target of autoantibodies in the human autoimmune diseases, polymyositis or dermatomyositis Besides its role in translation, Lysyl-tRNA synthetase is involved in a signaling pathway leading to gene activation. Following physiological stimulation of a variety of cells, Lysyl-tRNA synthetase binds to the transcription factors Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor, MITF and USF2 and can then influence their transcriptional activities. Such physiological stimulation includes immunological activation of mast cells, so this pathway maybe relevant to the allergic response. Interactions KARS (gene) has been shown to Protein-protein intera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |