|
Haploinsufficient
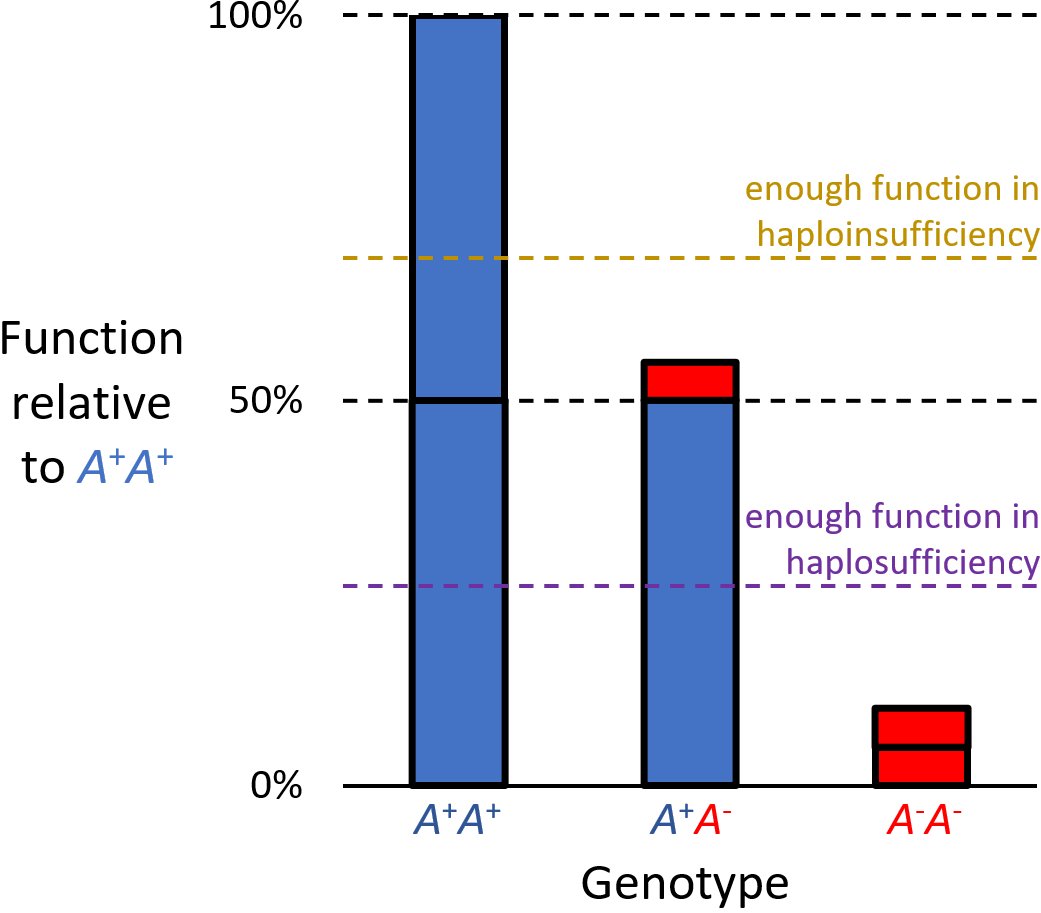
Haploinsufficiency in genetics describes a model of dominant gene action in diploid organisms, in which a single copy of the wild-type allele at a locus in heterozygous combination with a variant allele is insufficient to produce the wild-type phenotype. Haploinsufficiency may arise from a ''de novo'' or inherited loss-of-function mutation in the variant allele, such that it yields little or no gene product (often a protein). Although the other, standard allele still produces the standard amount of product, the total product is insufficient to produce the standard phenotype. This heterozygous genotype may result in a non- or sub-standard, deleterious, and (or) disease phenotype. Haploinsufficiency is the standard explanation for dominant deleterious alleles. In the alternative case of haplosufficiency, the loss-of-function allele behaves as above, but the single standard allele in the heterozygous genotype produces sufficient gene product to produce the same, standard phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haploinsufficiency Graph Only
Haploinsufficiency in genetics describes a model of dominant gene action in diploid organisms, in which a single copy of the wild-type allele at a locus in heterozygous combination with a variant allele is insufficient to produce the wild-type phenotype. Haploinsufficiency may arise from a ''de novo'' or inherited loss-of-function mutation in the variant allele, such that it yields little or no gene product (often a protein). Although the other, standard allele still produces the standard amount of product, the total product is insufficient to produce the standard phenotype. This heterozygous genotype may result in a non- or sub-standard, deleterious, and (or) disease phenotype. Haploinsufficiency is the standard explanation for dominant deleterious alleles. In the alternative case of haplosufficiency, the loss-of-function allele behaves as above, but the single standard allele in the heterozygous genotype produces sufficient gene product to produce the same, standard phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyskeratosis Congenita
Dyskeratosis congenita (DKC), also known as Zinsser-Engman-Cole syndrome, is a rare progressive congenital disorder with a highly variable phenotype. The entity was classically defined by the triad of abnormal skin pigmentation, nail dystrophy, and leukoplakia of the oral mucosa, but these components do not always occur. DKC is characterized by short telomeres. Some of the manifestations resemble premature ageing (similar to progeria). The disease initially mainly affects the skin, but a major consequence is progressive bone marrow failure which occurs in over 80%, causing early mortality. Presentation DKC can be characterized by cutaneous pigmentation, premature graying, dystrophy of the nails, leukoplakia of the oral mucosa, continuous lacrimation due to atresia of the lacrimal ducts, often thrombocytopenia, anemia, testicular atrophy in the male carriers, and predisposition to cancer. Many of these symptoms are characteristic of geriatrics, and those carrying the more seriou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron (journal)
''Neuron'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Cell Press, and imprint of Elsevier. It was established in 1988, and covers neuroscience and related biological processes. The current editor in chief is Mariela Zirlinger. The founding editors were Lily Jan, A. James Hudspeth, Louis Reichardt Louis French Reichardt (born June 4, 1942) is a noted American neuroscientist and mountaineering, mountaineer, the first American to summit both Everest and K2. He was also director of the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative, the largest ..., Roger Nicoll, and Zach Hall. A past Editor in Chief was Katja Brose. Transcript and video available. Click on "Transcript" for text. * See alsoA Career in Science Editing: Katja BroseEditor in Chief, Neuron References External links * Neuroscience journals Cell Press academic journals Publications established in 1988 English-language journals Biweekly journals {{neuroscience-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Stenosis
Aortic stenosis (AS or AoS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart (where the aorta begins), such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occur due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercising. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially when lying down, at night, or with exercise, and swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without narrowing is known as aortic sclerosis. Causes include being born with a bicuspid aortic valve, and rheumatic fever; a normal valve may also harden over the decades. A bicuspid aortic valve affects about one to two percent of the population. As of 2014 rheumatic heart disease mostly occurs in the dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELN (gene)
Elastin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ELN'' gene. Elastin is a key component of the extracellular matrix in gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates). It is highly elastic and present in connective tissue allowing many tissues in the body to resume their shape after stretching or contracting. Elastin helps skin to return to its original position when it is poked or pinched. Elastin is also an important load-bearing tissue in the bodies of vertebrates and used in places where mechanical energy is required to be stored. Function The ''ELN'' gene encodes a protein that is one of the two components of elastic fibers. The encoded protein is rich in hydrophobic amino acids such as glycine and proline, which form mobile hydrophobic regions bounded by crosslinks between lysine residues. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Elastin's soluble precursor is tropoelastin. The characterization of disorder is consistent with an en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-allelic Homologous Recombination
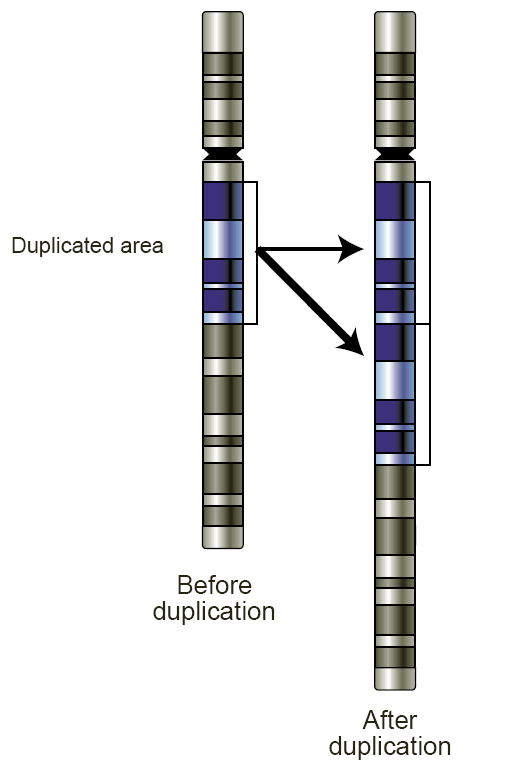
Non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR) is a form of homologous recombination that occurs between two lengths of DNA that have high sequence similarity, but are not alleles. It usually occurs between sequences of DNA that have been previously duplicated through evolution, and therefore have low copy repeats (LCRs). These repeat elements typically range from 10–300 kb in length and share 95-97% sequence identity. During meiosis, LCRs can misalign and subsequent crossing-over can result in genetic rearrangement. When non-allelic homologous recombination occurs between different LCRs, deletions or further duplications of the DNA can occur. This can give rise to rare genetic disorders, caused by the loss or increased copy number of genes within the deleted or duplicated region. It can also contribute to the copy number variation seen in some gene clusters. As LCRs are often found in "hotspots" in the human genome, some chromosomal regions are particularly prone to NAHR. Recu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copy Number Variation
Copy number variation (CNV) is a phenomenon in which sections of the genome are repeated and the number of repeats in the genome varies between individuals. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: specifically, it is a type of duplication or deletion event that affects a considerable number of base pairs. Approximately two-thirds of the entire human genome may be composed of repeats and 4.8–9.5% of the human genome can be classified as copy number variations. In mammals, copy number variations play an important role in generating necessary variation in the population as well as disease phenotype. Copy number variations can be generally categorized into two main groups: short repeats and long repeats. However, there are no clear boundaries between the two groups and the classification depends on the nature of the loci of interest. Short repeats include mainly dinucleotide repeats (two repeating nucleotides e.g. A-C-A-C-A-C...) and trinucleotide repeats. Long r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |