|
Diadenosine Tetraphosphate
Diadenosine tetraphosphate or Ap4A is a putative alarmone, ubiquitous in nature being common to everything from bacteria to humans. It is made up of two adenosines joined together by a 5′-5′ linked chain of four phosphates. Adenosine polyphosphates are capable of inducing multiple physiological effects. Function In Eukaryotes Ap4A can be created by a non-canonical activity of the Lysyl-tRNA synthetase (LysRS). This function of LysRS is activated by the phosphorylation of LysRS on serine 207, its subsequent dissociation from the multi-synthetase complex (MSC). The molecule's role as a second messenger has recently been discovered in The LysRS-Ap4A-MITF signaling pathway. Ap4A binds to the MITF-HINT1 inhibitory complex, specifically to the molecule histidine triad nucleotide–binding protein 1(HINT1), releasing the Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) and causing an increase in the transcription of its target genes. Ap4A also positively regulates the ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alarmone
An alarmone is an intracellular signal molecule that is produced in bacteria, chloroplasts, and a slim minority of archaea reacting to harsh environmental factors. They regulate the gene expression at transcription level. Alarmones are produced in high concentrations when harsh environmental factors occur in bacteria and plants, such as lack of amino acids, to produce proteins. Stringent factors take uncharged tRNA and convert it to an alarmone. Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is then converted to 5´-diphosphate 3´-diphosphate guanosine (ppGpp (p)ppGpp, guanosine pentaphosphate and tetraphosphate, also known as the "magic spot" nucleotides, are alarmones involved in the stringent response in bacteria that cause the inhibition of RNA synthesis when there is a shortage of amino acids. ...), the archetypical alarmone. ppGpp will bind to RNA polymerase β and β´ subunits, changing promoter preference. It will decrease transcription of rRNA and other genes but will increase tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a protein domain common to many GTPases. Functions GTPases function as molecular switches or timers in many fundamental cellular processes. Examples of these roles include: * Signal transduction in response to activation of cell surface receptors, including transmembrane receptors such as those mediating taste, smell and vision. * Protein biosynthesis (a.k.a. translation) at the ribosome. * Regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation, division and movement. * Translocation of proteins through membranes. * Transport of vesicles within the cell, and vesicle-mediated secretion and uptake, through GTPase control of vesicle coat assembly. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP. In the generalized recepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a complex lipopol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxococcus Xanthus
''Myxococcus xanthus'' is a gram-negative, rod-shaped species of myxobacteria that exhibits various forms of self-organizing behavior in response to environmental cues. Under normal conditions with abundant food, it exists as a predatory, saprophytic single-species biofilm called a swarm. Under starvation conditions, it undergoes a multicellular development cycle. Colony growth A swarm of ''M. xanthus'' is a distributed system, containing millions of bacteria that communicate among themselves in a non-centralized fashion. Simple patterns of cooperative behavior among the members of the colony combine to generate complex group behaviors in a process known as "stigmergy". For example, the tendency for one cell to glide only when in direct contact with another results in the colony forming swarms called "wolf-packs" that may measure up to several inches wide. This behavior is advantageous to the members of the swarm, as it increases the concentration of extracellular digestive enz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription. A transcription factor and its associated transcription mediator complex must be attached to a DNA binding site called a promoter region before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides. RNAP produces RNA that, functionally, is either for protein coding, i.e. messenger RNA (mRNA); or n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
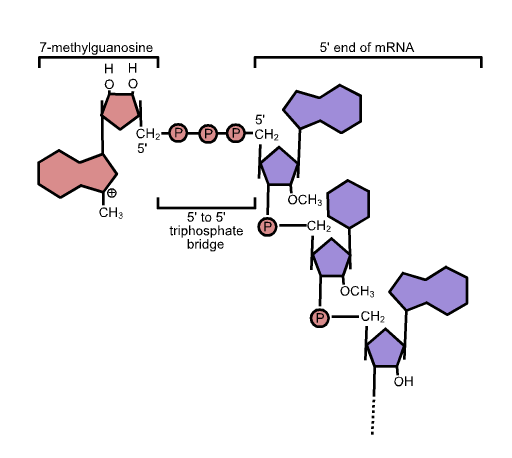
Five-prime Cap
In molecular biology, the five-prime cap (5′ cap) is a specially altered nucleotide on the 5′ end of some primary transcripts such as precursor messenger RNA. This process, known as mRNA capping, is highly regulated and vital in the creation of stable and mature messenger RNA able to undergo translation during protein synthesis. Mitochondrial mRNA and chloroplastic mRNA are not capped. Structure In eukaryotes, the 5′ cap (cap-0), found on the 5′ end of an mRNA molecule, consists of a guanine nucleotide connected to mRNA via an unusual 5′ to 5′ triphosphate linkage. This guanosine is methylated on the 7 position directly after capping ''in vivo'' by a methyltransferase. It is referred to as a 7-methylguanylate cap, abbreviated m7G. In multicellular eukaryotes and some viruses, further modifications exist, including the methylation of the 2′ hydroxy-groups of the first 2 ribose sugars of the 5′ end of the mRNA. cap-1 has a methylated 2′-hydroxy gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolase
Hydrolase is a class of enzyme that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases. Esterases cleave ester bonds in lipids and phosphatases cleave phosphate groups off molecules. An example of crucial esterase is acetylcholine esterase, which assists in transforming the neuron impulse into the acetate group after the hydrolase breaks the acetylcholine into choline and acetic acid. Acetic acid is an important metabolite in the body and a critical intermediate for other reactions such as glycolysis. Lipases hydrolyze glycerides. Glycosidases cleave sugar molecules off carbohydrates and peptidases hydrolyze peptide bonds. Nucleosidases hydrolyze the bonds of nucleotides. Hydrolase enzymes are important for the body because they have degra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
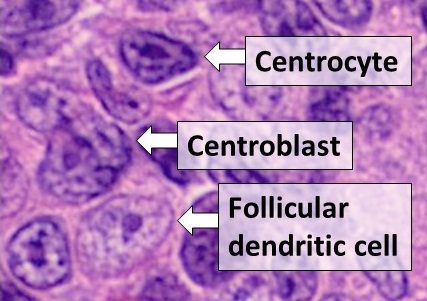
Dendritic Cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the ''dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USF2
Upstream stimulatory factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''USF2'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper family, and can function as a cellular transcription factor. The encoded protein can activate transcription through Pyridine-rich initiator (Inr) elements and E-box motifs. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. Interactions USF2 has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with USF1 (human gene), PPRC1 and BRCA1. Regulation The ''USF2'' gene is Gene regulation, repressed by the microRNA MicroRNA mir-10, miR-10a. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{gene-19-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HINT1
Histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 also known as adenosine 5'-monophosphoramidase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''HINT1'' gene. HINT1 hydrolyzes purine nucleotide phosphoramidates with a single phosphate group. In addition, functions as scaffolding protein that modulates transcriptional activation. It is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor gene that inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in colon cancer cells and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) activity in human mast cells. In the LysRS-Ap4A-MITF signaling pathway, HINT1 inhibits the MITF transcriptional activity by direct association. Upon pathway activation, HINT1 is released from MITF by diadenosine tetraphosphate Diadenosine tetraphosphate or Ap4A is a putative alarmone, ubiquitous in nature being common to everything from bacteria to humans. It is made up of two adenosines joined together by a 5′-5′ linked chain of four phosphates. Adenosine polyphosp ... (Ap4A), produced b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |