|
Hiloula Of Rabbi Haim Pinto
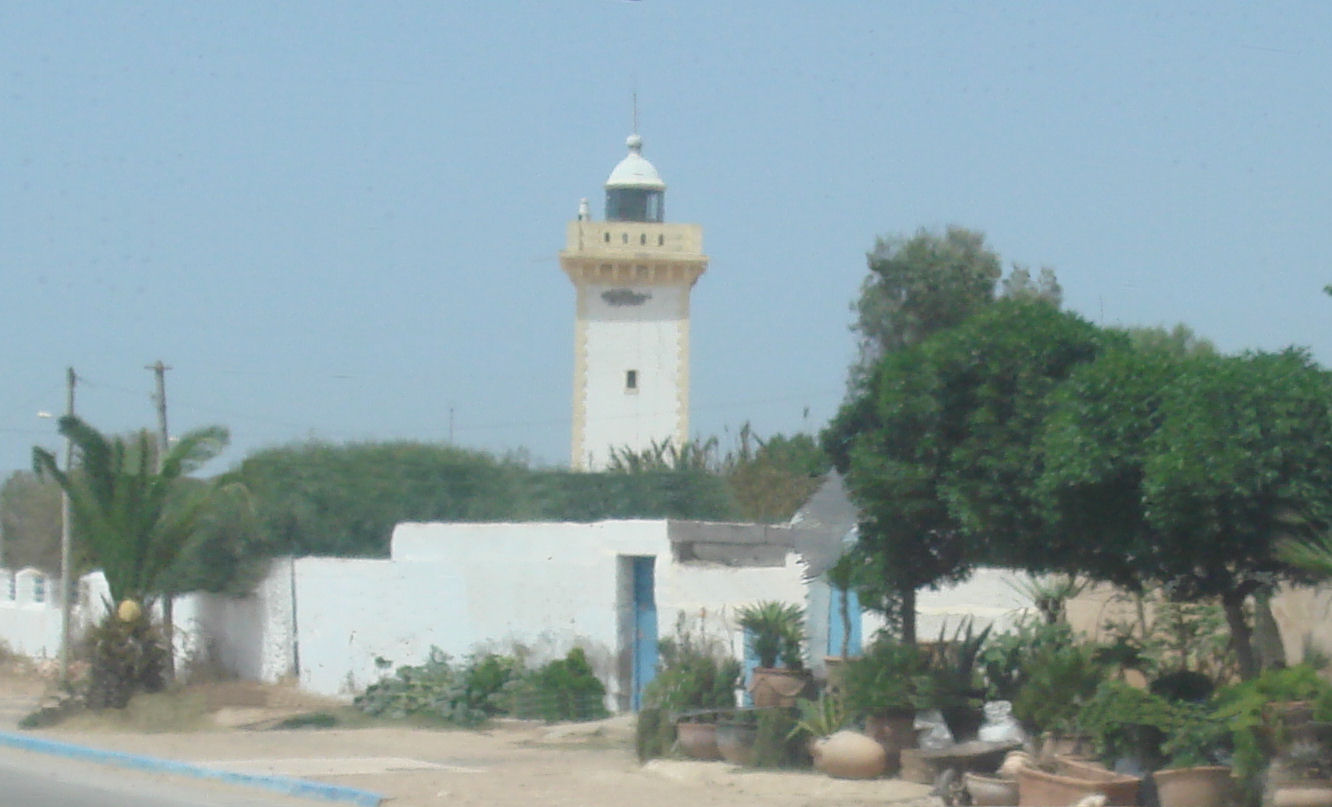
Hiloula of Rabbi Haïm Pinto is the Yom Hillula, or anniversary of the death of Rabbi Haïm Pinto. It is one of the most popular Hiloulas in North Africa. It is celebrated in Essaouira, Morocco. Every year, more than 2000 Jewish pilgrims visit the city for a four-days celebration to commemorate the memory of the Rabbi. History Rabbi Haïm Pinto (1743–1845) was the chief rabbi of the city of Essaouira, and part of a distinguished rabbinic family. After his death on 26 Elul of the year 5605 of the Hebrew calendar The Hebrew calendar ( he, הַלּוּחַ הָעִבְרִי, translit=HaLuah HaIvri), also called the Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today for Jewish religious observance, and as an official calendar of the state of Israel. I ..., his mausoleum, as well as his house became places of pilgrimage and Jews from all over the world come to pray in the family synagogue, and at his grave in the old Jewish cemetery of the city. File:Cimetières Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yom Hillula
A ''Yom Hillula'' ( he, יום הילולא, day of festivity) is another word for ''yahrzeit'' (the anniversary of a death). However, it differs from a regular ''yahrzeit'' in two respects. It refers specifically to the ''yahrzeit'' of a great Tzaddik who taught Kabbalah and/or Chassidus, and unlike a regular ''yahrzeit'', which is marked with sadness and even fasting, a ''Yom Hillula'' is commemorated specifically through simcha (joy), and festive celebration. This term is most often used in Hasidic circles to refer to the day of the death of Hasidic Rebbes. According to Kabbalah, on the Yartzheit of a Tzaddik, all the spiritual redemption of their life shines into this World, contributing to the Messianic redemption and bringing spiritual blessing to all who are connected to them. The supreme Tzadik of the generation is described as the all-inclusive, general soul of the Jewish people, further emphasised in Hasidic doctrine. The observation of a hillula in North African Jewish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaim Pinto
Rabbi Ḥaim Pinto (1748–1845) was the leading rabbi in the seaport city of Essaouira, Morocco, known in his lifetime as Mogador, Morocco. Rabbi Pinto, himself born into a distinguished rabbinic family, had four sons, Rabbi Yehouda also known as Rabbi Haddan, Rabbi Yossef, Rabbi Yehoshiya and Rabbi Yaacov. Annually, on the anniversary of Rabbi Pinto's death, (26 Elloul 5605, in the Hebrew calendar) Jews from around the world come on pilgrimage to pray at the rabbi's grave in the Jewish cemeteries of Essaouira, old jewish cemetery of Essaouira. Rabbi Pinto is remembered as a man whose prayers were received in heaven in such a way that miracles resulted. The Chaim Pinto Synagogue, the building that was Rabbi Pinto's home, office and synagogue is preserved as an historic site. Rabbi Pinto's followers and descendants have a number of synagogues worldwide, including the Pinto Center synagogue on Pico Boulevard in Los Angeles, California, which was founded by Rabbi Yaacov Pinto. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in the west, to Egypt's Suez Canal. Varying sources limit it to the countries of Algeria, Libya, Morocco, and Tunisia, a region that was known by the French during colonial times as "''Afrique du Nord''" and is known by Arabs as the Maghreb ("West", ''The western part of Arab World''). The United Nations definition includes Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Sudan, and the Western Sahara, the territory disputed between Morocco and the Sahrawi Republic. The African Union definition includes the Western Sahara and Mauritania but not Sudan. When used in the term Middle East and North Africa (MENA), it often refers only to the countries of the Maghreb. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and plazas de s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essaouira
Essaouira ( ; ar, الصويرة, aṣ-Ṣawīra; shi, ⵜⴰⵚⵚⵓⵔⵜ, Taṣṣort, formerly ''Amegdul''), known until the 1960s as Mogador, is a port city in the western Moroccan region of Marakesh-Safi, on the Atlantic coast. It has 77,966 inhabitants as of 2014. The foundation of the city of Essaouira was the work of the Moroccan 'Alawid sultan Mohammed bin Abdallah, who made an original experiment by entrusting it to several renowned architects in 1760, in particular Théodore Cornut and Ahmed al-Inglizi, who designed the city using French captives from the failed French expedition to Larache in 1765, and with the mission of building a city adapted to the needs of foreign merchants. Once built, it continued to grow and experienced a golden age and exceptional development, becoming the country's most important commercial port but also its diplomatic capital between the end of the 18th century and the first half of the 19th century. Name and etymology The nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Mauritania lies to the south of Western Sahara. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It spans an area of or , with a population of roughly 37 million. Its official and predominant religion is Islam, and the official languages are Arabic and Berber; the Moroccan dialect of Arabic and French are also widely spoken. Moroccan identity and culture is a mix of Arab, Berber, and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. In a region inhabited since the Paleolithic Era over 300,000 years ago, the first Moroccan s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The people of the Kingdom of Israel and the ethnic and religious group known as the Jewish people that descended from them have been subjected to a number of forced migrations in their history" and Hebrews of historical History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israel and Judah. Jewish ethnicity, nationhood, and religion are strongly interrelated, "Historically, the religious and ethnic dimensions of Jewish identity have been closely interwoven. In fact, so closely bound are they, that the traditional Jewish lexicon hardly distinguishes between the two concepts. Jewish religious practice, by definition, was observed exclusively by the Jewish people, and notions of Jewish peoplehood, nation, and community were suffused with faith in the Jewish God, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elul
Elul ( he, אֱלוּל, Standard ''ʾElūl'', Tiberian ''ʾĔlūl'') is the twelfth month of the Jewish civil year and the sixth month of the ecclesiastical year on the Hebrew calendar. It is a month of 29 days. Elul usually occurs in August–September on the Gregorian calendar. Etymology The name of the month Elul, like the names of the rest of the Hebrew calendar months, was brought from the Babylonian captivity, and originated from the Akkadian word for "harvest". A similar month name was also used in Akkadian, in the form ''Elūlu''. The month is known as Araḫ Ulūlu, "harvest month", in the Babylonian calendar. Eylül is also the name for September in Turkish; this is derived from ar, أيلول ''ʾAylūl'', used in Iraq and the Levant (see Arabic names of calendar months), from Classical Syriac ܐܝܼܠܘܼܠ ''ʾĪlūl'', also tracing its origin from the Akkadian word Elūlu. In Hebrew, a popular bacronym for Elul is from a verse in the Song of Songs "Ani LeDodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilgrim
A pilgrim (from the Latin ''peregrinus'') is a traveler (literally one who has come from afar) who is on Pilgrimage, a journey to a holy place. Typically, this is a physical journey (often on foot) to some place of special significance to the adherent of a particular religious belief system. In the spiritual literature of Christianity, the concept of pilgrim and pilgrimage may refer to the experience of life in World (theology), the world (considered as a period of exile) or to the inner path of the spiritual aspirant from a state of wretchedness to a state of beatitude. History Pilgrims and the making of pilgrimages are common in many religions, including the faiths of ancient Egypt, Persia in the Mithraism, Mithraic period, India, China, and Japan. The ancient Greece, Greek and Ancient Rome, Roman customs of consulting the Deity, gods at local oracles, such as those at Dodona or Delphi, both in Greece, are widely known. In Greece, pilgrimages could either be personal or state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbi
A rabbi () is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi – known as '' semikha'' – following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of the rabbi developed in the Pharisaic (167 BCE–73 CE) and Talmudic (70–640 CE) eras, when learned teachers assembled to codify Judaism's written and oral laws. The title "rabbi" was first used in the first century CE. In more recent centuries, the duties of a rabbi became increasingly influenced by the duties of the Protestant Christian minister, hence the title " pulpit rabbis", and in 19th-century Germany and the United States rabbinic activities including sermons, pastoral counseling, and representing the community to the outside, all increased in importance. Within the various Jewish denominations, there are different requirements for rabbinic ordination, and differences in opinion regarding who is recognized as a rabbi. For ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
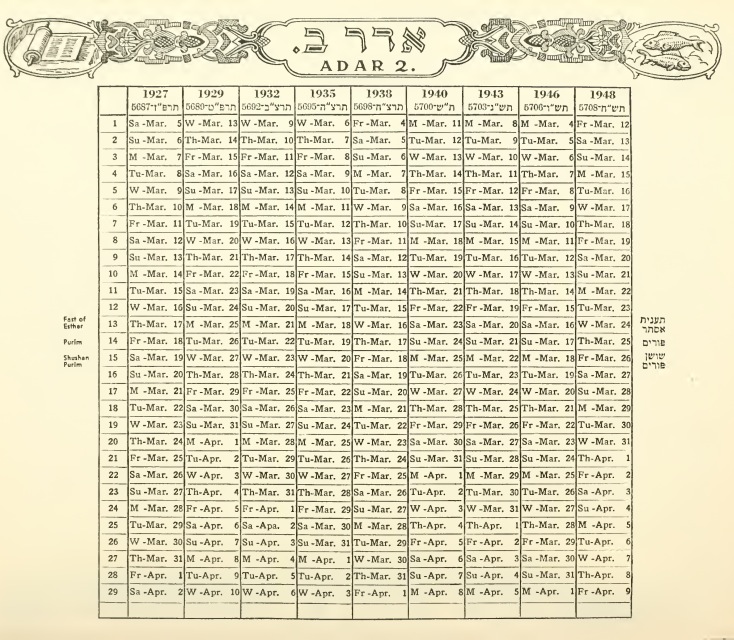
Hebrew Calendar
The Hebrew calendar ( he, הַלּוּחַ הָעִבְרִי, translit=HaLuah HaIvri), also called the Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today for Jewish religious observance, and as an official calendar of the state of Israel. It determines the dates for Jewish holidays and the appropriate Torah reading, public reading of Weekly Torah portion, Torah portions, ''yahrzeits'' (dates to commemorate the death of a relative), and daily Psalm readings, among many ceremonial uses. In Israel, it is used for religious purposes, provides a time frame for agriculture, and is an official calendar for civil holidays, alongside the Gregorian calendar. The present Hebrew calendar is the result of a process of development, including a Babylonian calendar, Babylonian influence. Until the Tannaitic period (approximately 10–220 Common Era, CE), the calendar employed a new lunar phase, crescent moon, with an Intercalation (timekeeping), additional month normally added every two or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaim Pinto Synagogue
The Chaim Pinto Synagogue (in Arabic : كنيس حاييم بينتو), an historic site in Essaouira, Morocco, formerly known as Mogador, Morocco, was the home and synagogue of Rabbi Chaim Pinto. Although there is no longer a Jewish community in Essaouira, the building is an active synagogue, used when pilgrims or Jewish tour groups visit the city. The synagogue is on the second floor of a three-story, courtyard building inside the walls of the old city that also contained Rabbi Pinto's home and office. The building is of whitewashed plaster over masonry. The synagogue consists of a single large room. There are two women's sections, one across the courtyard and one on the third floor, both with windows looking into the synagogue.Zack, Joel, ''The Synagogues of Morocco; An Architectural and Preservation Survey, Jewish Heritage Council and World Monuments Fund, New York, 1992, pp. 23 ff. The synagogue room underwent a modern renovation, concealing the ceiling and column capitals, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jews And Judaism In Essaouira
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The people of the Kingdom of Israel and the ethnic and religious group known as the Jewish people that descended from them have been subjected to a number of forced migrations in their history" and Hebrews of historical Israel and Judah. Jewish ethnicity, nationhood, and religion are strongly interrelated, "Historically, the religious and ethnic dimensions of Jewish identity have been closely interwoven. In fact, so closely bound are they, that the traditional Jewish lexicon hardly distinguishes between the two concepts. Jewish religious practice, by definition, was observed exclusively by the Jewish people, and notions of Jewish peoplehood, nation, and community were suffused with faith in the Jewish God, the practice of Jewish (religious) la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |