|
Hidradenoma
Hidradenoma refers to a benign adnexal tumor of the apical sweat gland. These are 1–3 cm translucent blue cystic nodules. It usually presents as a single, small skin-colored lesion, and may be considered closely related to or a variant of poromas. Hidradenomas are often sub-classified based on subtle histologic differences, for example: * Eccrine acrospiroma * Clear-cell hidradenoma or acrospiroma * Nodular hidradenoma or acrospiroma * Solid-cystic hidradenoma Discussion of sweat gland tumors can be difficult and confusing due to the complex classification and redundant terminology used to describe the same tumors. For example, acrospiroma and hidradenoma are synonymous, and sometimes the term ''acrospiroma'' is used to generally describe benign sweat gland tumors. In addition, a single lesion may contain a mixture of cell-types. There has also been a change in understanding about how tumors that were previously believed to strictly derive from specific sweat gland types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poroma
Poromas are rare, benign, cutaneous adnexal tumors. Cutaneous adnexal tumors are a group of skin tumors consisting of tissues that have differentiated (i.e. matured from stem cells) towards one or more of the four primary adnexal structures found in normal skin: hair follicles, sebaceous sweat glands, apocrine sweat glands, and eccrine sweat glands. Poromas are eccrine or apocrine sweat gland tumors derived from the cells in the terminal portion of these glands' ducts. This part of the sweat gland duct is termed the acrosyringium and had led to grouping poromas in the acrospiroma class of skin tumors ( syringofibroadenomas and syringoacanthomas are classified as acrospiromas). Here, poromas are regarded as distinct sweat gland tumors that differ from other sweat gland tumors by their characteristic clinical presentations, microscopic histopathology, and the genetic mutations that their neoplastic cells have recently been found to carry. As currently viewed, there are 4 por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cutaneous Conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The two main types of human skin are: glabrous skin, the hairless skin on the palms and soles (also referred to as the "palmoplantar" surfaces), and hair-bearing skin.Burns, Tony; ''et al''. (2006) ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology CD-ROM''. Wiley-Blackwell. . Within the latter type, the hairs occur in structures called pilosebaceous units, each with hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and associated arrector pili muscle. In the embryo, the epidermis, hair, and glands form from the ectoderm, which is chemically influenced by the underlying mesoderm th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
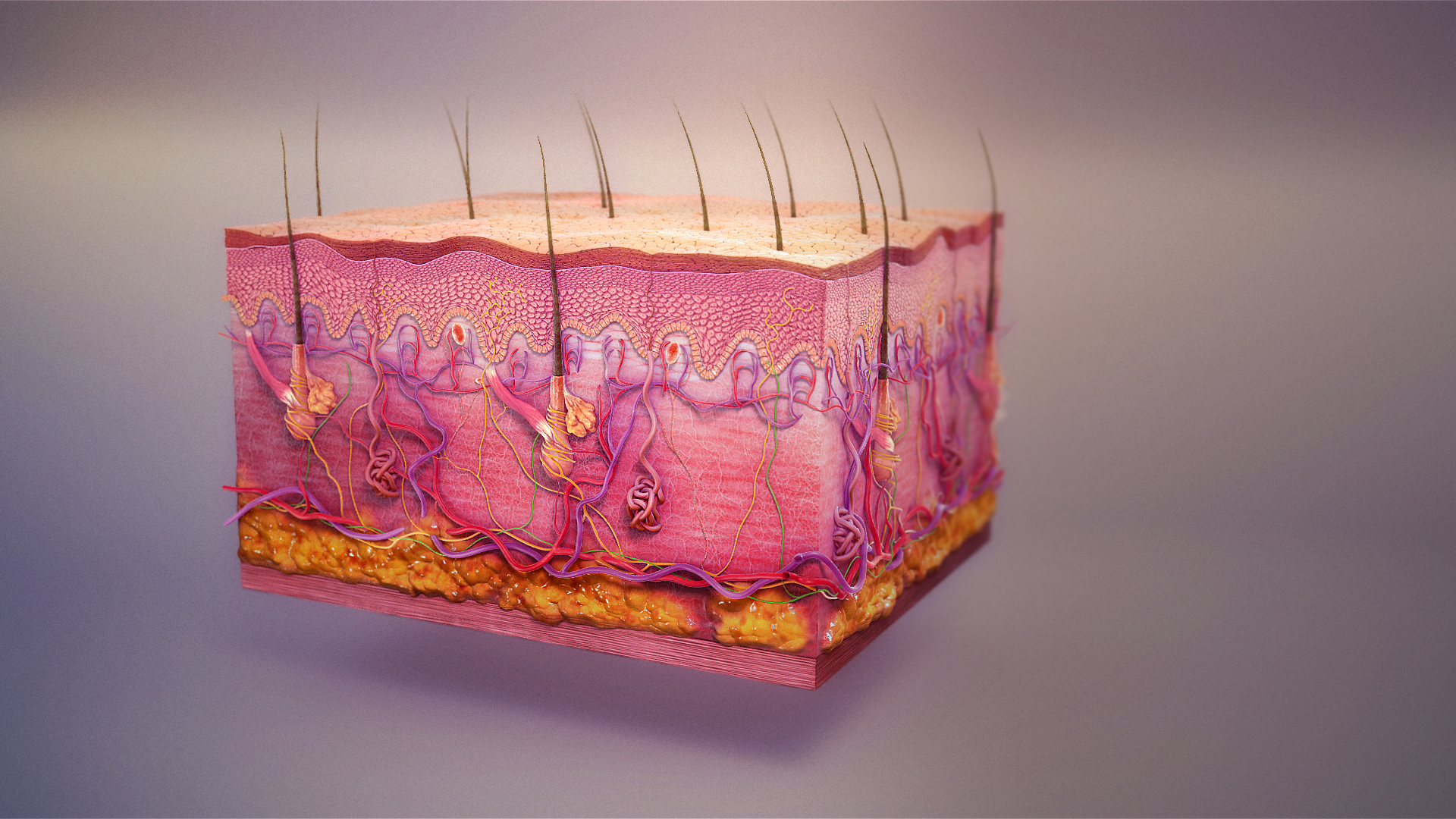
Sweat Gland
Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous or sudoriparous glands, , are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. There are two main types of sweat glands that differ in their structure, function, secretory product, mechanism of excretion, anatomic distribution, and distribution across species: * Eccrine sweat glands are distributed almost all over the human body, in varying densities, with the highest density in palms and soles, then on the head, but much less on the trunk and the extremities. Its water-based secretion represents a primary form of cooling in humans. * Apocrine sweat glands are mostly limited to the axillae (armpits) and perineal area in humans. They are not significant for cooling in humans, but are the sole effective sweat glands in hoofed animals, such as the camels, donkeys, horses, and cattle. Ceruminou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
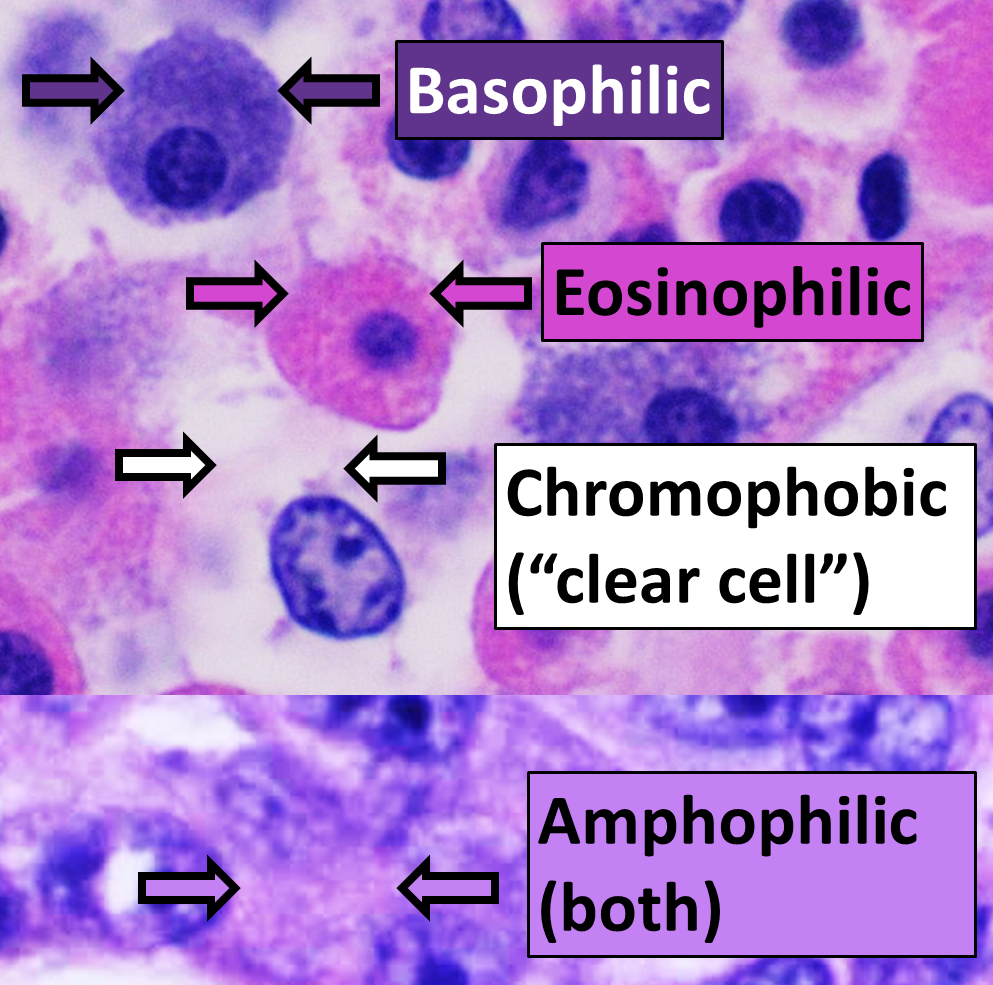
H&E Stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E. H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin. The hematoxylin stains cell nuclei a purplish blue, and eosin stains the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm pink, with other structures taking on different shades, hues, and combinations of these colors. Hence a pathologist can easily differentiate between the nuclear and cytoplasmic parts of a cell, and additionally, the overall patterns of coloration from the stain show the general layout and distribution of cells and provides a general overview of a tissue sample's structure. Thus, pattern recogniti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatology
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical doctor who manages diseases related to skin, hair, nails, and some cosmetic problems. Etymology Attested in English in 1819, the word "dermatology" derives from the Greek δέρματος (''dermatos''), genitive of δέρμα (''derma''), "skin" (itself from δέρω ''dero'', "to flay") and -λογία '' -logia''. Neo-Latin ''dermatologia'' was coined in 1630, an anatomical term with various French and German uses attested from the 1730s. History In 1708, the first great school of dermatology became a reality at the famous Hôpital Saint-Louis in Paris, and the first textbooks (Willan's, 1798–1808) and atlases ( Alibert's, 1806–1816) appeared in print around the same time.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Appendage
Skin appendages (or adnexa of skin) are anatomical skin-associated structures that serve a particular function including sensation, contractility, lubrication and heat loss in animals. In humans, some of the more common skin appendages are hairs (sensation, heat loss, filter for breathing, protection), arrector pilli (smooth muscles that pull hairs straight), sebaceous glands (secrete sebum onto hair follicle, which oils the hair), sweat glands (can secrete sweat with strong odour (apocrine) or with a faint odour (merocrine or eccrine)), and nails (protection). Skin appendages are derived from the skin, and are usually adjacent to it. Types of appendages include hair, glands, and nails. Glands * Sweat glands are distributed all over the body except nipples and outer genitals. Although the nipples do have the mammary glands, these are known as ''modified sweat glands''. * Sebaceous gland A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiroma
Spiradenomas (SA) are rare, benign cutaneous adnexal tumors that may progress to become their malignant counterparts, i.e. spiradenocarcinomas (SAC). Cutaneous adnexal tumors are a group of skin tumors consisting of tissues that have differentiated (i.e. matured from stem cells) towards one of the four primary adnexal structures found in normal skin: hair follicles, sebaceous sweat glands, apocrine sweat glands, and eccrine sweat glands. SA and SAC tumors were regarded as eccrine gland tumors and termed eccrine spiradenomas and eccrine spiradenocarcinomas, respectively. However, more recent studies have found them to be hair follicle tumors and commonly term them spiradenomas and spiradenocarcinomas, respectively. Further confusing the situation, SA-like and SAC-like tumors are also 1) manifestations of the inherited disorder, CYLD cutaneous syndrome (CCS), and 2) have repeatedly been confused with an entirely different tumor, adenoid cystic carcinomas of the salivary gland. Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cutaneous Neoplasms Associated With Systemic Syndromes
Many cutaneous neoplasms occur in the setting of systemic syndromes. See also *List of cutaneous conditions *List of contact allergens *List of cutaneous conditions associated with increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer *List of cutaneous conditions associated with internal malignancy *List of cutaneous conditions caused by mutations in keratins *List of cutaneous conditions caused by problems with junctional proteins *List of dental abnormalities associated with cutaneous conditions *List of genes mutated in cutaneous conditions *List of genes mutated in pigmented cutaneous lesions *List of histologic stains that aid in diagnosis of cutaneous conditions *List of immunofluorescence findings for autoimmune bullous conditions *List of inclusion bodies that aid in diagnosis of cutaneous conditions *List of keratins expressed in the human integumentary system *List of radiographic findings associated with cutaneous conditions *List of specialized glands within the human integum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integumentary Neoplasia
The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animal's body. It comprises the skin and its appendages, which act as a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves to protect and maintain the body of the animal. Mainly it is the body's outer skin. The integumentary system includes hair, scales, feathers, hooves, and nails. It has a variety of additional functions: it may serve to maintain water balance, protect the deeper tissues, excrete wastes, and regulate body temperature, and is the attachment site for sensory receptors which detect pain, sensation, pressure, and temperature. Structure Skin The skin is one of the largest organs of the body. In humans, it accounts for about 12 to 15 percent of total body weight and covers 1.5 to 2 m2 of surface area. The skin (integument) is a composite organ, made up of at least two major layers of tissue: the epidermis and the dermis. The epidermis is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |