|
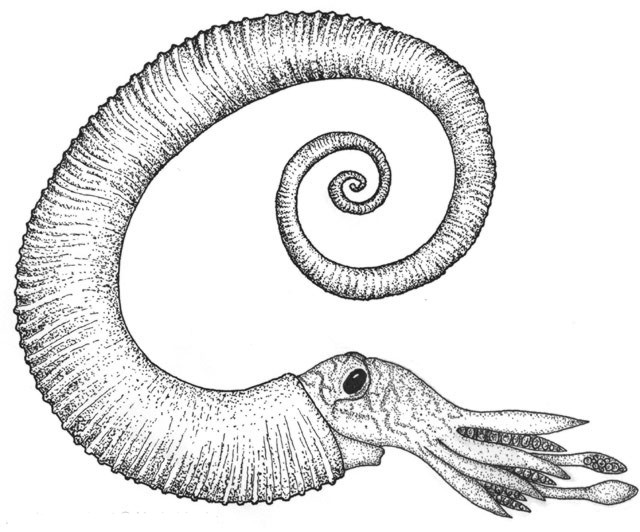
Heteromorph
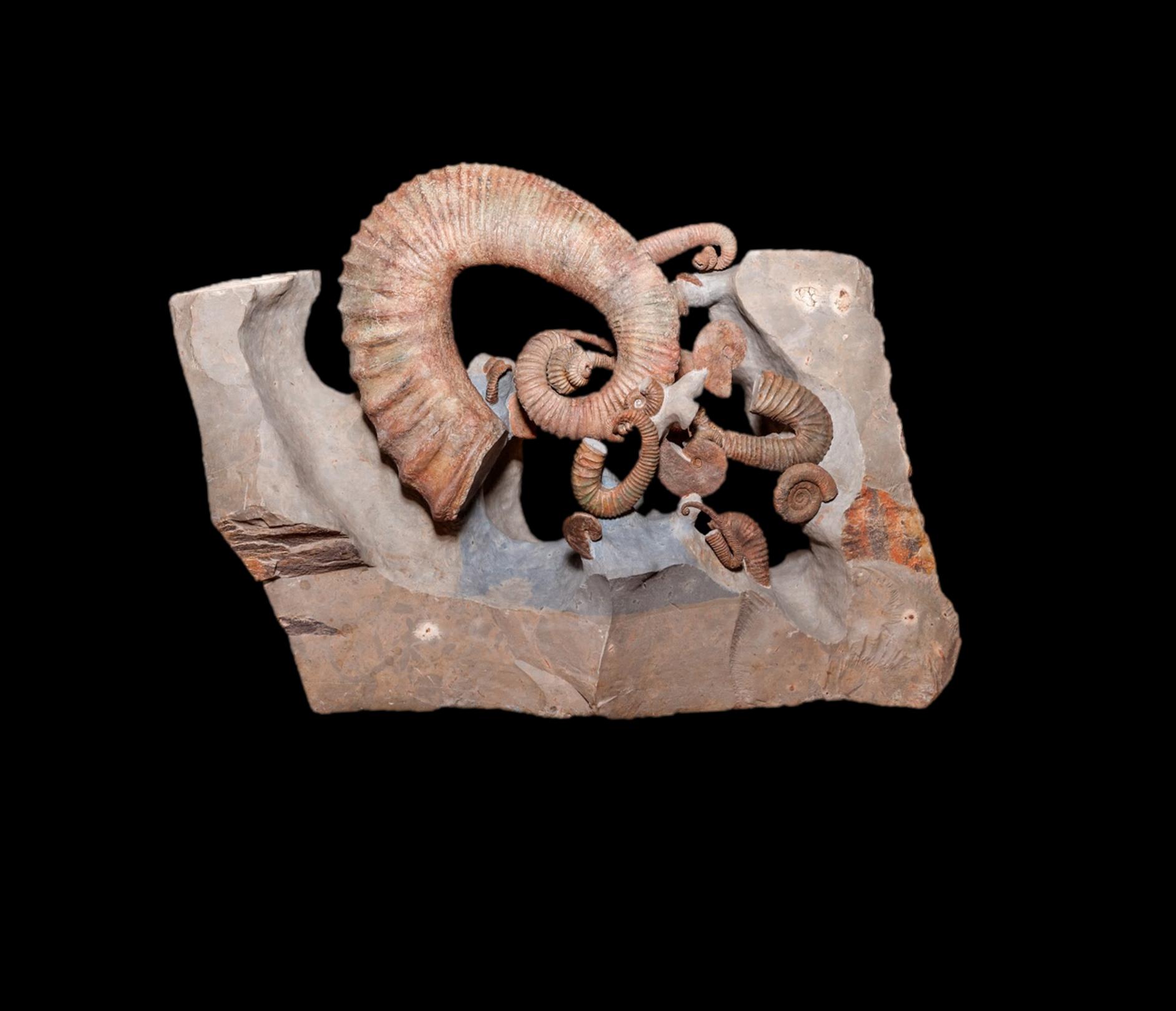
The Ancyloceratina were a diverse suborder of ammonite most closely related to the ammonites of order Lytoceratina. They evolved during the Late Jurassic but were not very common until the Cretaceous period, when they rapidly diversified and became one of the most distinctive components of Cretaceous marine faunas. They have been recorded from every continent and many are used as zonal or index fossils. The most distinctive feature of the majority of the Ancyloceratina is the tendency for most of them to have shells that are not regular spirals like most other ammonites. These irregularly-coiled ammonites are called heteromorph ammonites, in contrast to regularly coiled ammonites, which are called homomorph ammonites. Biology The biology of the heteromorph ammonites is not clear, but one certainty is that their uncoiled shells would have made these forms very poor swimmers. Open shells, particularly ones with spines and ribs, create a lot of drag; but more importantly, the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonite Cemetery
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish) than they are to shelled nautiloids such as the living ''Nautilus'' species. The earliest ammonites appeared during the Devonian, with the last species vanishing during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Ammonites are excellent index fossils, and linking the rock layer in which a particular species or genus is found to specific geologic time periods is often possible. Their fossil shells usually take the form of planispirals, although some helically spiraled and nonspiraled forms (known as heteromorphs) have been found. The name "ammonite", from which the scientific term is derived, was inspired by the spiral shape of their fossilized shells, which somewhat resemble tightly coiled rams' horns. Pliny the Elder ( 79 AD nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamites (genus)
''Hamites'' (" hook-like") is a genus of heteromorph ammonite that evolved late in the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous and lasted into the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous. The genus is almost certainly paraphyletic but remains in wide use as a "catch all" for heteromorph ammonites of the superfamily Turrilitoidea that do not neatly fit into the more derived groupings. In an attempt to identify clades within the genus, it has been divided up into a series of new genera or subgenera by different palaeontologists, including ''Eohamites'', ''Hamitella'', ''Helicohamites'', ''Lytohamites'', ''Planohamites'', ''Psilohamites'', and ''Sziveshamites''. The type species is ''Hamites attenuatus'' from the early Albian, named by James Sowerby in his ''Mineral Conchology of Great Britain'' of 1814, although the genus itself was created by James Parkinson in his 1811 book ''Organic Remains of the Former World''. This James Parkinson is best known as the first scientific descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
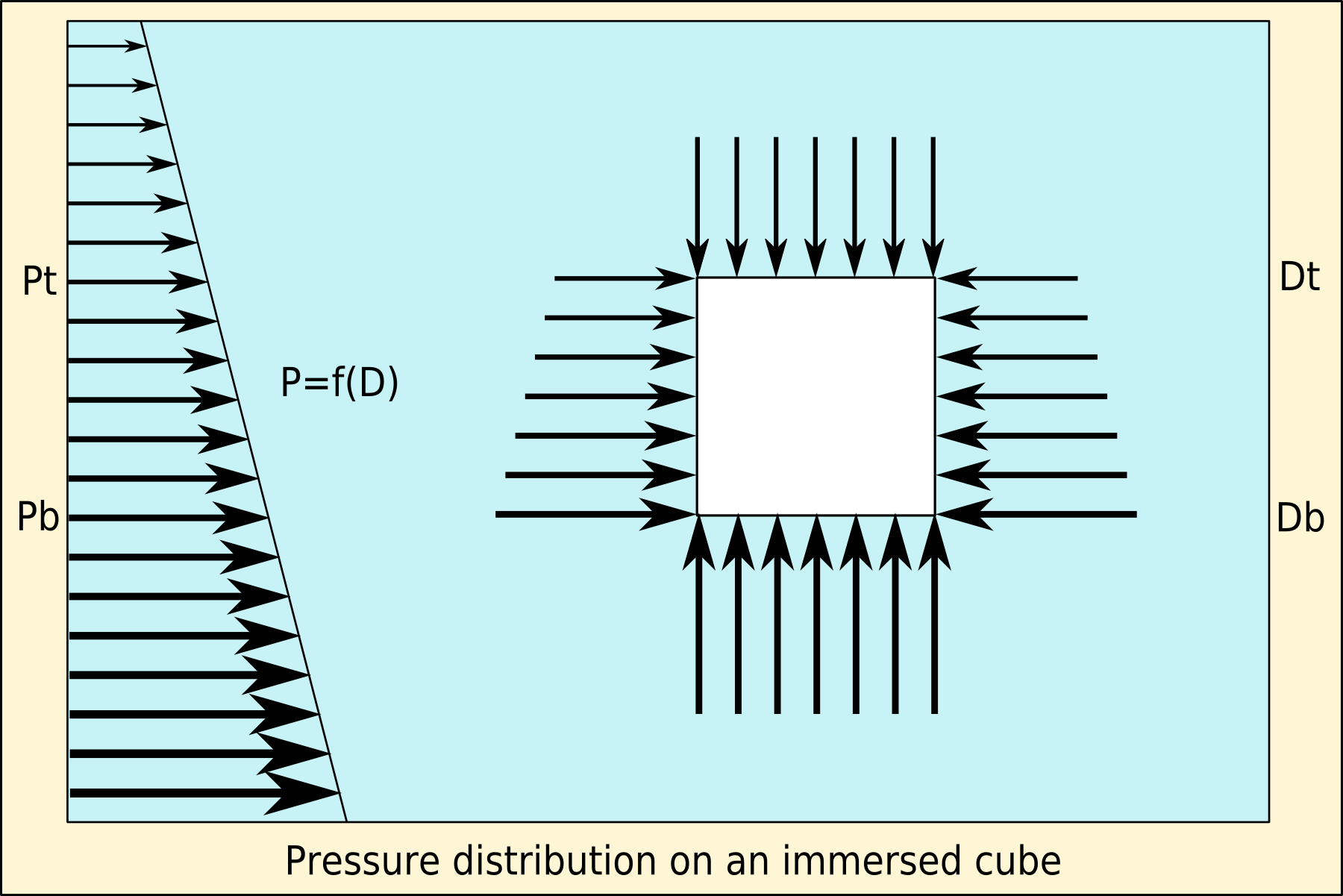
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago and the Russian Far East to the east. The continental landmass is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Africa to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as many of their borders are over land; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data. Eurasia covers around , or around 36.2% of the Earth's total land area. It is also home to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion of a single continent called Americas, America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territory, dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one administrative division, internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands (Leeward Antilles), ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Asce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign ''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'. The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ... country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway (also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, the North American Inland Sea, and the Western Interior Sea) was a large inland sea that split the continent of North America into two landmasses. The ancient sea, which existed from the early Late Cretaceous (100 million years ago) to the earliest Paleocene (66 Ma), connected the Gulf of Mexico, through the United States and Canada, to the Arctic Ocean. The two land masses it created were Laramidia to the west and Appalachia to the east. At its largest extent, it was deep, wide and over long. Origin and geology By Late-Cretaceous times, Eurasia and the Americas had separated along the south Atlantic, and subduction on the west coast of the Americas had commenced, resulting in the Laramide orogeny, the early phase of growth of the modern Rocky Mountains. The Western Interior Seaway may be seen as a downwarping of the continental crust ahead of the growing Laramide/Rockies mountain chain. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar, Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancyloceras
''Ancyloceras'' is an extinct genus of heteromorph ammonites found throughout the world during the Lower Cretaceous, from the Lower Barremian epoch until the genus extinction during the Lower Aptian.Sepkoski, JacSepkoski's Online Genus Database – Cephalopoda/ref> Selected species *''Ancyloceras audouli'' Astier, 1851 *''Ancyloceras fallauxi'' Uhlig, 1883 *''Ancyloceras mantelli'' Casey, 1960 *''Ancyloceras matheronianum'' d'Orbigny, 1842 *''Ancyloceras vandenheckii'' Astier, 1851 Description ''Ancyloceras'' ammonites have a shell reaching a length of about and a width of about . They are known as heteromorph shaped, with a partly uncoiled shell and the aperture directed toward the coiled part. Most ammonites are homomorph, as they maintain the same shape throughout the growth, while the ammonites in this genus have uncoiled shells (heteromorph The Ancyloceratina were a diverse suborder of ammonite most closely related to the ammonites of order Lytoceratina. They evolved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |