|
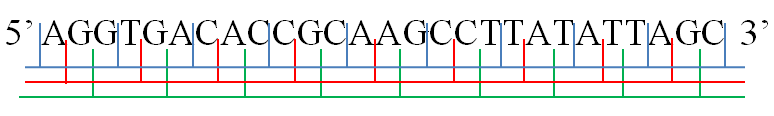
Hepatitis C Alternative Reading Frame Stem-loop
Hepatitis C alternative reading frame stem-loop is a conserved secondary structure motif identified in the RNA genome of the Hepatitis C virus (HCV) which is proposed to have an important role in regulating translation and repression of the viral genome. The core protein-coding region of the Hepatitis C virus (HCV) genome contains a +1 alternative reading frame (ARF) and two proposed phylogenetically conserved RNA helix-forming stem loop structures ( IV and VII). The proteins translated from the ARF appear to be translated during the normal viral life cycle but are not essential to virus replication. The two predicted stem loops shown here (SLV and SLVI) are proposed to be important for HCV translation and repression; these stem loops are located downstream of the Internal ribosome entry site An internal ribosome entry site, abbreviated IRES, is an RNA element that allows for translation initiation in a cap-independent manner, as part of the greater process of protein synthesis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets, though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary structure. Secondary structure is formally defined by the pattern of hydrogen bonds between the amino hydrogen and carboxyl oxygen atoms in the peptide backbone. Secondary structure may alternatively be defined based on the regular pattern of backbone dihedral angles in a particular region of the Ramachandran plot regardless of whether it has the correct hydrogen bonds. The concept of secondary structure was first introduced by Kaj Ulrik Linderstrøm-Lang at Stanford in 1952. Other types of biopolymers such as nucleic acids also possess characteristic secondary structures. Types The most common secondary st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Conservation
In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar Sequence (biology), sequences in nucleic acids (DNA sequence, DNA and RNA) or peptide sequence, proteins across species (homology (biology)#Orthology, orthologous sequences), or within a genome (homology (biology)#Paralogy, paralogous sequences), or between donor and receptor taxa (Sequence homology#Xenology, xenologous sequences). Conservation indicates that a sequence has been maintained by natural selection. A highly conserved sequence is one that has remained relatively unchanged far back up the phylogenetic tree, and hence far back in geological time. Examples of highly conserved sequences include the Ribosomal RNA, RNA components of ribosomes present in all domain (biology), domains of life, the homeobox sequences widespread amongst Eukaryotes, and the tmRNA in Bacteria. The study of sequence conservation overlaps with the fields of genomics, proteomics, evolutionary biology, phylogenetics, bioinformatics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-regulatory Element
''Cis''-regulatory elements (CREs) or ''Cis''-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogenesis, the development of anatomy, and other aspects of embryonic development, studied in evolutionary developmental biology. CREs are found in the vicinity of the genes that they regulate. CREs typically regulate gene transcription by binding to transcription factors. A single transcription factor may bind to many CREs, and hence control the expression of many genes (pleiotropy). The Latin prefix ''cis'' means "on this side", i.e. on the same molecule of DNA as the gene(s) to be transcribed. CRMs are stretches of DNA, usually 100–1000 DNA base pairs in length, where a number of transcription factors can bind and regulate expression of nearby genes and regulate their transcription rates. They are labeled as ''cis'' because they are ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a wikt:submicroscopic, submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
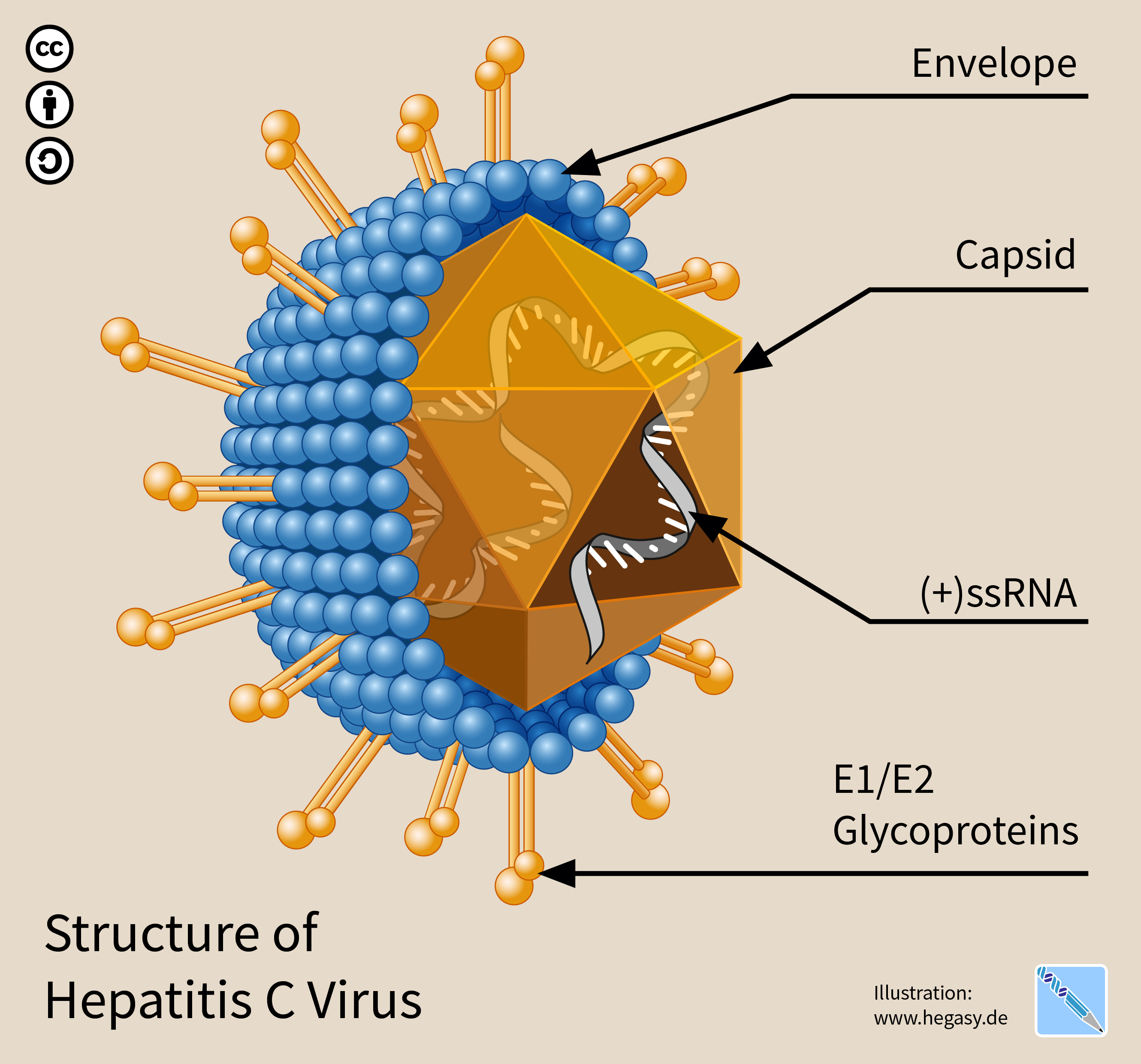
Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family '' Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans. Taxonomy The hepatitis C virus belongs to the genus '' Hepacivirus'', a member of the family '' Flaviviridae''. Before 2011, it was considered to be the only member of this genus. However a member of this genus has been discovered in dogs: canine hepacivirus. There is also at least one virus in this genus that infects horses. Several additional viruses in the genus have been described in bats and rodents. Structure The hepatitis C virus particle consists of a lipid membrane envelope that is 55 to 65 nm in diameter. Two viral envelope glycoproteins, E1 and E2, are embedded in the lipid envelope. They take part in viral attachment and entry into the cell. Within the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (biology)
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's nucleus. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later folds into an active protein and performs its functions in the cell. The ribosome facilitates decoding by inducing the binding of complementary tRNA anticodon sequences to mRNA codons. The tRNAs carry specific amino acids that are chained together into a polypeptide as the mRNA passes through and is "read" by the ribosome. Translation proceeds in three phases: # Initiation: The ribosome assembles around the target mRNA. The first tRNA is attached at the start codon. # Elongation: The last tRNA validated by the small ribosomal subunit (''accom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading Frame
In molecular biology, a reading frame is a way of dividing the sequence of nucleotides in a nucleic acid ( DNA or RNA) molecule into a set of consecutive, non-overlapping triplets. Where these triplets equate to amino acids or stop signals during translation, they are called codons. A single strand of a nucleic acid molecule has a phosphoryl end, called the 5′-end, and a hydroxyl or 3′-end. These define the 5′→3′ direction. There are three reading frames that can be read in this 5′→3′ direction, each beginning from a different nucleotide in a triplet. In a double stranded nucleic acid, an additional three reading frames may be read from the other, complementary strand in the 5′→3′ direction along this strand. As the two strands of a double-stranded nucleic acid molecule are antiparallel, the 5′→3′ direction on the second strand corresponds to the 3′→5′ direction along the first strand. In general, at the most, one reading frame in a given se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Loop
Stem-loop intramolecular base pairing is a pattern that can occur in single-stranded RNA. The structure is also known as a hairpin or hairpin loop. It occurs when two regions of the same strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence when read in opposite directions, base-pair to form a double helix that ends in an unpaired loop. The resulting structure is a key building block of many RNA secondary structures. As an important secondary structure of RNA, it can direct RNA folding, protect structural stability for messenger RNA (mRNA), provide recognition sites for RNA binding proteins, and serve as a substrate for enzymatic reactions. Formation and stability The formation of a stem-loop structure is dependent on the stability of the resulting helix and loop regions. The first prerequisite is the presence of a sequence that can fold back on itself to form a paired double helix. The stability of this helix is determined by its length, the number of mismatches or bulges it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis C Stem-loop IV
The Hepatitis C stem-loop IV is part of a putative RNA element found in the NS5B Nonstructural protein 5B (NS5B) is a viral protein found in the hepatitis C virus (HCV). It is an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, having the key function of replicating HCV's viral RNA by using the viral positive RNA strand as a template to catalyze ... coding region. This element along with stem-loop VII, is important (but not essential) for colony formation, though its exact function and mechanism are unknown. See also * Hepatitis C alternative reading frame stem-loop * Hepatitis C virus (HCV) cis-acting replication element (CRE) * Hepatitis C virus 3'X element * Hepatitis E virus cis-reactive element References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements Hepatitis C virus {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis C Virus Stem-loop VII
Hepatitis C virus stem-loop VII is a regulatory element found in the coding region of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene, NS5B. Similarly to stem-loop IV, the stem-loop structure is important (but not essential) for colony formation, though its exact function and mechanism are unknown. See also * Hepatitis C alternative reading frame stem-loop Hepatitis C alternative reading frame stem-loop is a conserved secondary structure motif identified in the RNA genome of the Hepatitis C virus (HCV) which is proposed to have an important role in regulating Translation (biology), translation and r ... * Hepatitis C virus (HCV) cis-acting replication element (CRE) * Hepatitis C virus 3'X element References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements Hepatitis C virus {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Ribosome Entry Site
An internal ribosome entry site, abbreviated IRES, is an RNA element that allows for translation initiation in a cap-independent manner, as part of the greater process of protein synthesis. In eukaryotic translation, initiation typically occurs at the 5' end of mRNA molecules, since 5' cap recognition is required for the assembly of the initiation complex. The location for IRES elements is often in the 5'UTR, but can also occur elsewhere in mRNAs. History IRES sequences were first discovered in 1988 in the poliovirus (PV) and encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) RNA genomes in the labs of Nahum Sonenberg and Eckard Wimmer, respectively. They are described as distinct regions of RNA molecules that are able to recruit the eukaryotic ribosome to the mRNA. This process is also known as cap-independent translation. It has been shown that IRES elements have a distinct secondary or even tertiary structure, but similar structural features at the levels of either primary or secondary str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis E Virus Cis-reactive Element
The hepatitis E virus cis-reactive element is an RNA element that is believed to be essential for "some step in gene expression". The mutation of this element resulted in hepatitis E strains which were unable to infect rhesus macaque The rhesus macaque (''Macaca mulatta''), colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies that are split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally b ...s (''Macaca mulatta''). References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements Hepeviridae {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |