|
Henry Kelsey
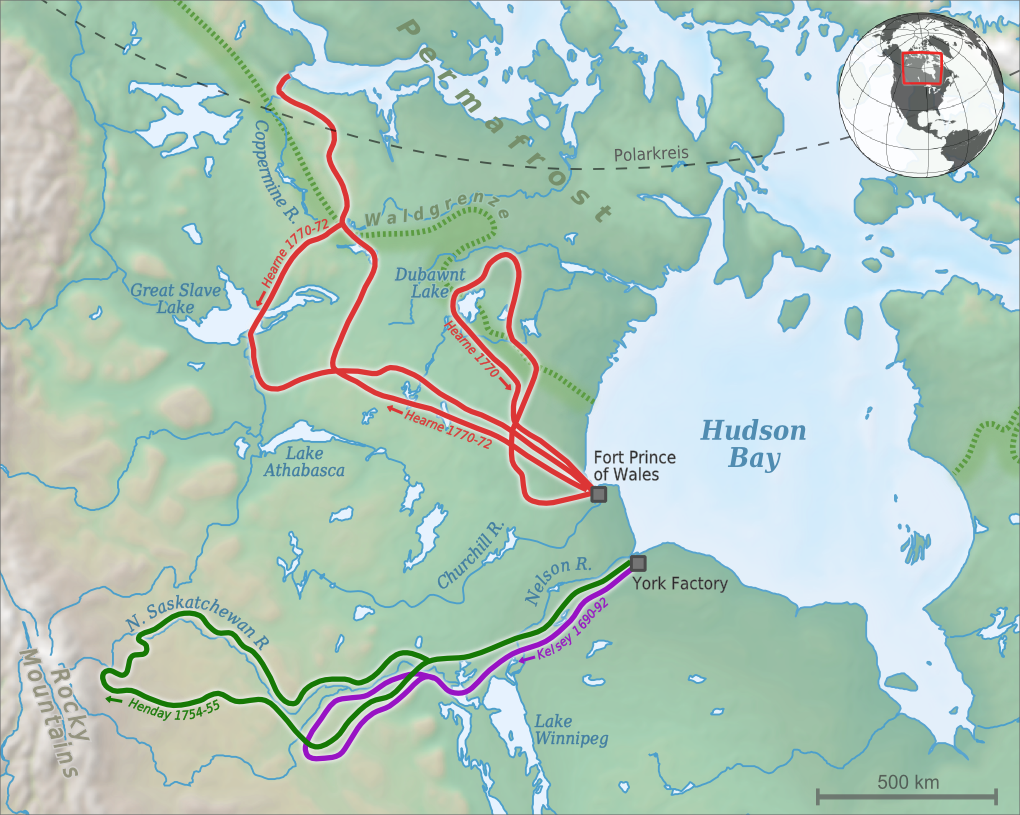
Henry Kelsey ( – 1 November 1724) was an English fur trader, explorer, and sailor who played an important role in establishing the Hudson's Bay Company in Canada. He is the first recorded European to have visited the present-day provinces of Saskatchewan and, possibly, Alberta, as well as the first to have explored the Great Plains from the north. In his travels to the plains he encountered several Plains First Nations, as well as vast herds of the American bison, their primary source of food. Early life and career Kelsey was born and married in East Greenwich, south-east of central London. Kelsey was apprenticed in London at age 17 to the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) in 1684 and departed England for Canada on 6 May 1684. He was posted at a fort on Hudson's Bay near present-day York Factory, Manitoba, near the mouth of the Nelson River on Hudson Bay. Kelsey started exploring in the winter of 1688–1689 when he and a First Nations boy carried mail overland 200 miles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenwich
Greenwich ( , ,) is a town in south-east London, England, within the ceremonial county of Greater London. It is situated east-southeast of Charing Cross. Greenwich is notable for its maritime history and for giving its name to the Greenwich Meridian (0° longitude) and Greenwich Mean Time. The town became the site of a royal palace, the Palace of Placentia from the 15th century, and was the birthplace of many Tudors, including Henry VIII and Elizabeth I. The palace fell into disrepair during the English Civil War and was demolished to be replaced by the Royal Naval Hospital for Sailors, designed by Sir Christopher Wren and his assistant Nicholas Hawksmoor. These buildings became the Royal Naval College in 1873, and they remained a military education establishment until 1998 when they passed into the hands of the Greenwich Foundation. The historic rooms within these buildings remain open to the public; other buildings are used by University of Greenwich and Trinity Laban C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
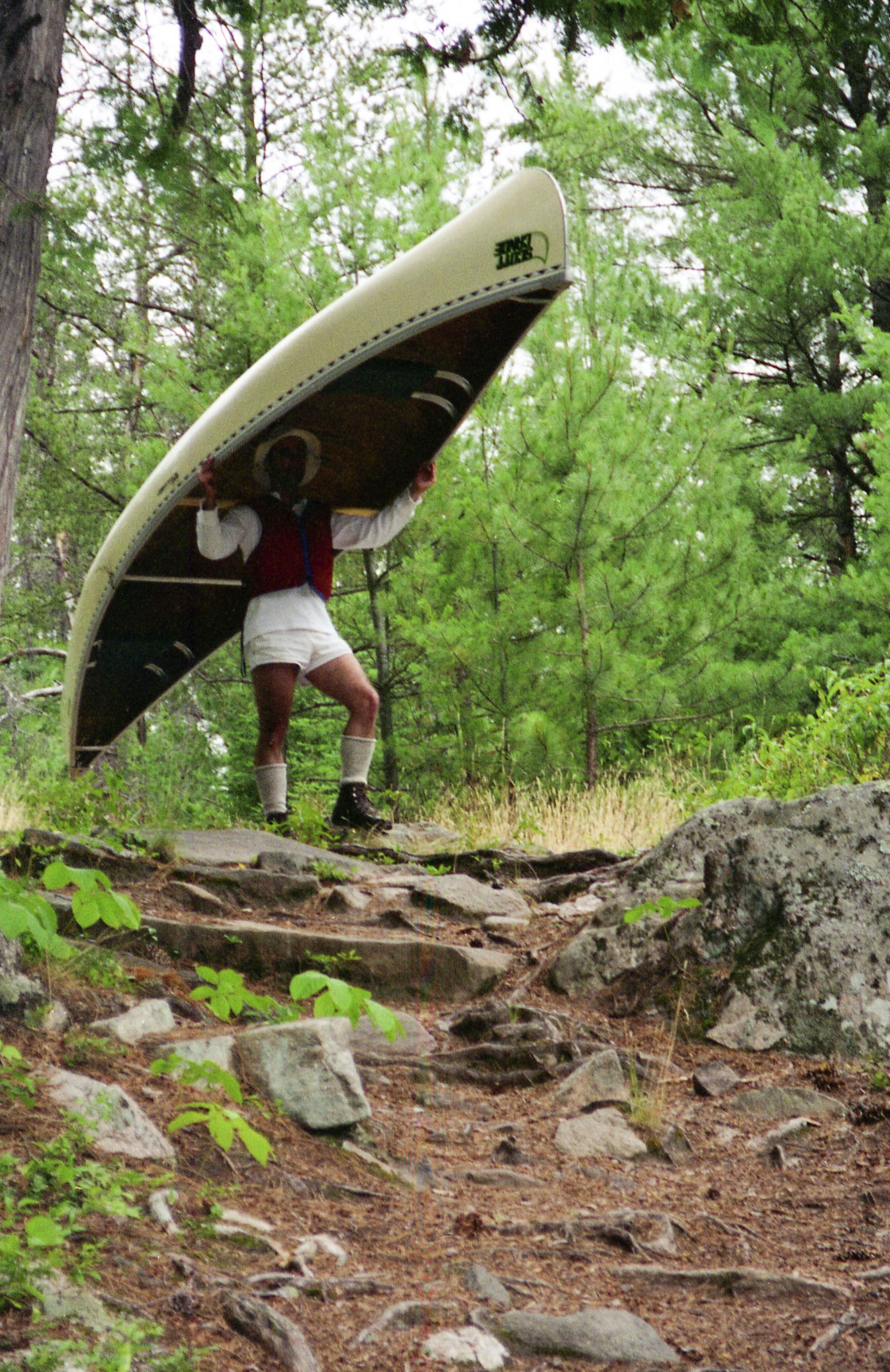
Portage
Portage or portaging (Canada: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a ''portage.'' The term comes from French, where means "to carry," as in "portable". In Canada, the term "carrying-place" was sometimes used. Early French explorers in New France and French Louisiana encountered many rapids and cascades. The Native Americans carried their canoes over land to avoid river obstacles. Over time, important portages were sometimes provided with canals with locks, and even portage railways. Primitive portaging generally involves carrying the vessel and its contents across the portage in multiple trips. Small canoes can be portaged by carrying them inverted over one's shoulders and the center strut may be designed in the style of a yoke to facilitate this. Historically, voyageurs often employed tump lines on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hidatsa People
The Hidatsa are a Siouan people. They are enrolled in the federally recognized Three Affiliated Tribes of the Fort Berthold Reservation in North Dakota. Their language is related to that of the Crow, and they are sometimes considered a parent tribe to the modern Crow in Montana. Name The Hidatsa's autonym is Hiraacá. According to the tribal tradition, the word ''hiraacá'' derives from the word "willow"; however, the etymology is not transparent and the similarity to ''mirahací'' ‘willows’ inconclusive. The present name ''Hidatsa'' was formerly borne by one of the three tribal villages. When the villages consolidated, the name was adopted for the tribe as a whole. They are called the ''Mį́nįtaree'' (″to cross the water″) by their allies, the Mandan; in Assiniboine the Assiniboine (called Hidusidi by the Hidatsa) know them as: ''wakmúhaza yúde, ȟewáktųkta'' Occasionally they have also been confused with the Gros Ventres in present-day Montana and Prairie Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoney People
The Nakoda (also known as Stoney or ) are an Indigenous people in Western Canada and, originally, the United States. They used to inhabit large parts of what is now Alberta, Saskatchewan and Montana, but their reserves are now located in Alberta and in Saskatchewan, where they are scarcely differentiated from the Assiniboine. Through their language they are related to the Dakota and Lakota nations of the Great Plains and the Rocky Mountains, part of the large Sioux Nation. They refer to themselves in their own language as " Nakoda", meaning ''friend'', ''ally''. The name "Stoney" was given them by white explorers, because of their technique of using fire-heated rocks to boil broth in rawhide bowls. They are very closely related to the Assiniboine, who are also known as ''Stone Sioux'' (from the Ojibwe ). Alberta's Nakoda First Nation comprises three bands: Bearspaw, Chiniki and Wesley. The Stoney were "excluded" from Banff National Park between 1890 and 1920. In 2010 the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatoon
Saskatoon () is the largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It straddles a bend in the South Saskatchewan River in the central region of the province. It is located along the Trans-Canada Highway, Trans-Canada Yellowhead Highway, and has served as the cultural and economic hub of central Saskatchewan since its founding in 1882 as a Temperance movement, Temperance colony. With a Canada 2021 Census, 2021 census population of 266,141, Saskatoon is the List of cities in Saskatchewan, largest city in the province, and the List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, 17th largest Census Metropolitan Area in Canada, with a 2021 census population of 317,480. Saskatoon is home to the University of Saskatchewan, the Meewasin Valley Authority (which protects the South Saskatchewan River and provides for the city's popular riverbank park spaces), and Wanuskewin Heritage Park (a National Historic Site of Canada and UNES ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grizzly Bear
The grizzly bear (''Ursus arctos horribilis''), also known as the North American brown bear or simply grizzly, is a population or subspecies of the brown bear inhabiting North America. In addition to the mainland grizzly (''Ursus arctos horribilis''), other morphological forms of brown bear in North America are sometimes identified as grizzly bears. These include three living populations—the Kodiak bear (''U. a. middendorffi''), the Kamchatka bear (''U. a. beringianus''), and the peninsular grizzly (''U. a. gyas'')—as well as the extinct California grizzly (''U. a. californicus''†), Mexican grizzly (formerly ''U. a. nelsoni''†), and Ungava-Labrador grizzly (formerly ''U. a. ungavaesis''†). On average, grizzly bears near the coast tend to be larger while inland grizzlies tend to be smaller. The Ussuri brown bear (''U. a. lasiotus''), inhabiting Russia, Northern China, Japan, and Korea, is sometimes referred to as the "black grizzly", although it is no more closely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assiniboine People
The Assiniboine or Assiniboin people ( when singular, Assiniboines / Assiniboins when plural; Ojibwe: ''Asiniibwaan'', "stone Sioux"; also in plural Assiniboine or Assiniboin), also known as the Hohe and known by the endonym Nakota (or Nakoda or Nakona), are a First Nations/Native American people originally from the Northern Great Plains of North America. Today, they are centred in present-day Saskatchewan. They have also populated parts of Alberta and southwestern Manitoba in Canada, and northern Montana and western North Dakota in the United States. They were well known throughout much of the late 18th and early 19th century, and were members of the Iron Confederacy with the Cree. Images of Assiniboine people were painted by 19th-century artists such as Karl Bodmer and George Catlin. Names The Europeans and Americans adopted names that other tribes used for the Assiniboine; they did not until later learn the tribe's autonym, their name for themselves. In Siouan, they traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Touchwood Hills
Touchwood Hills are a range of hills located in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The hills are composed of the "Big" Touchwood Hills and the Little Touchwood Hills. Together they are referred to as the Touchwood Uplands. The hills are in the Prairie Pothole Region of North America, which extends throughout three Canadian provinces and five U.S. states, and within Palliser's Triangle and the Great Plains ecoregion of Canada. The hills make up a large plateau that is north-east of Saskatchewan's capital city, Regina. To the west of the hills is Last Mountain Lake; to the north are the Quill Lakes, Foam Lake, and Fishing Lake; to the east is Good Spirit Lake; and to the south is the Qu'Appelle Valley. Several rivers flow out of the hills, such as the south flowing Qu'Appelle River tributaries of East Loon Creek (via Loon Creek), Jumping Deer Creek, Pheasant Creek, and Pearl Creek. To the north, rivers such as Dafoe Brook, Birch Creek, Bevcar Brook, Beckett Brook, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yorkton
Yorkton is a city located in south-eastern Saskatchewan, Canada. It is about 450 kilometres north-west of Winnipeg and 300 kilometres south-east of Saskatoon and is the sixth largest city in the province. As of 2017 the census population of the city was 19,643. Yorkton has had a growth rate of 4.3% since 2011. Yorkton was founded in 1882 and incorporated as a city in 1928. The city is bordered by the rural municipalities of Orkney to the north, west, and south, and Wallace on the east. History In 1882 a group of businessmen and investors formed the York Farmers Colonization Company. Authorized to issue up to $300,000 in debentures and lenient government credit terms on land purchases encouraged company representatives to visit the District of Assiniboia of the North-West Territories with the intent to view some crown land available near the Manitoba border. They were impressed with what they saw and the group purchased portions of six townships near the Little Whitesand Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrot River (Saskatchewan)
The Carrot River is a river in north-eastern Saskatchewan, and north-western Manitoba. Its headwaters originate in the Cudworth and Tiger Hill Plains near the Town of Wakaw. The outlet of Wakaw Lake marks the beginning of the Carrot River and, from there, this river flows northeast through the Melfort and Red Earth Plains until it joins into the Saskatchewan River west of The Pas, Manitoba. The Carrot River is about 300 km in length and it parallels the course of the South Saskatchewan and Saskatchewan Rivers. The Carrot River serves as the main watershed for north-eastern Saskatchewan as all smaller streams and rivers empty into the Carrot River. This causes major flood problems during the spring run off and rainy seasons around the Town of Carrot River and Red Earth Indian Reserve. The floods usually strand everyone east of the river with very few ways around the flooded area. Another Carrot River enters Oxford Lake on the Hayes River. History The Carrot River va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cree People
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations. In Canada, over 350,000 people are Cree or have Cree ancestry. The major proportion of Cree in Canada live north and west of Lake Superior, in Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and the Northwest Territories. About 27,000 live in Quebec. In the United States, Cree people historically lived from Lake Superior westward. Today, they live mostly in Montana, where they share the Rocky Boy Indian Reservation with Ojibwe (Chippewa) people. The documented westward migration over time has been strongly associated with their roles as traders and hunters in the North American fur trade. Sub-groups / Geography The Cree are generally divided into eight groups based on dialect and region. These divisions do not necessarily represent ethnic sub-divisions within the larger ethnic gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the dominant vegetation type. Temperate grassland regions include the Pampas of Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay, and the steppe of Ukraine, Russia and Kazakhstan. Lands typically referred to as "prairie" tend to be in North America. The term encompasses the area referred to as the Geography of North America, Interior Lowlands of Canada, the United States, and Mexico, which includes all of the Great Plains as well as the wetter, hillier land to the east. In the U.S., the area is constituted by most or all of the states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, and Oklahoma, and sizable parts of the states of Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, New Mexico, Texas, Missouri, Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, Wisconsin, and western and southern Minnesota. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


.png)