|
Heligolandic Frisian
Heligolandic (''Halunder'') is the dialect of the North Frisian language spoken on the German island of Heligoland in the North Sea. It is spoken today by some 500 of the island's 1,650 inhabitants and is also taught in schools. Heligolandic is closely related to the insular North Frisian dialects of Fering and Öömrang because medieval fishery around Heligoland attracted Frisians from Föhr and Amrum, and close contacts have been maintained ever since. In fact Fering and Öömrang are closer in linguistic aspects to the dialect of Heligoland than to that of their neighbouring island Sylt, Söl'ring. Heligolandic also contains a variety of loanwords from 19th-century Modern English due to the 83-year British control of the island. James Krüss is probably the most notable author of poems and narrations in Heligolandic while Maria Leitgeber (1906–1979) wrote the most substantial prose. On 24 December 2004, a state law became effective in the German state of Schleswig-Holste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg. The region is called ''Slesvig-Holsten'' in Danish and pronounced . The Low German name is ''Sleswig-Holsteen'', and the North Frisian name is ''Slaswik-Holstiinj''. In more dated English, it is also known as ''Sleswick-Holsatia''. Historically, the name can also refer to a larger region, containing both present-day Schleswig-Holstein and the former South Jutland County (Northern Schleswig; now part of the Region of Southern Denmark) in Denmark. It covers an area of , making it the 5th smallest German federal state by area (including the city-states). Schleswig was under Danish control during the Viking Age, but in the 12th century it escaped full control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Flensburg
The University of Flensburg (''Europa-Universität Flensburg'') is a university in the city of Flensburg, Germany. It was founded in 1994 and is the northernmost university in Germany. Although having full university status and the right to award PhDs, Europa-Universität Flensburg mainly offers courses in education and other fields of the social sciences. The university holds German-Danish study courses in cooperation with the University of Southern Denmark at Sønderborg, which involve an association with the Fachhochschule Flensburg. Academics The university has 200 permanent employees and more than 400 visiting professors and lecturers. In the winter semester 2006/2007, the university received around 4,200 applications for places, but in the winter semester of the previous academic year the number was only 2,566. At the top of the applications in the winter semester 2006/2007 was the B.A. course in Teaching Science, 1977 applicants, followed by the B.A. course in Internatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Krüss
James Krüss (31 May 1926 – 2 August 1997) was a German writer of children's and picture books, illustrator, poet, dramatist, scriptwriter, translator, and collector of children's poems and folk songs. For his contribution as a children's writer he received the Hans Christian Andersen Award in 1968. Biography Krüss was born as the son of the electrician Ludwig Krüss and his wife Margaretha Krüss (born Friedrichs) in Heligoland. In 1941, during World War II, the inhabitants of the island were evacuated to Arnstadt, Thuringia, later to Hertigswalde, near Sebnitz, Saxony. After finishing high school in 1943, he studied to become a teacher, first in Lunden until 1943, Schleswig-Holstein, then in Ratzeburg until 1944, then finally in Brunswick. In 1944, he volunteered into the air force and was stationed in Ústí nad Labem, now Czech Republic at the end of World War II. From 1945 he lived with his parents in Cuxhaven. Career In 1946, he published his first book, ''Der goldene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Söl'ring
Sylt Frisian, or ''Söl'ring'', is the dialect of the North Frisian language spoken on the island of Sylt in the German region of North Frisia. ''Söl'ring'' refers to the ''Söl'ring'' Frisian word for Sylt, ''Söl''. Together with the Fering, Öömrang, and Heligolandic dialects, it forms part of the insular group of North Frisian dialects. It differs from the mainland dialects because of its relatively strong Danish influence. Due to mass tourism on Sylt, the dialect has been largely displaced by forms of German and ''Söl'ring'' is spoken only by a few hundred people, many of whom no longer reside on Sylt. Although it is taught in several primary schools A primary school (in Ireland, the United Kingdom, Australia, Trinidad and Tobago, Jamaica, and South Africa), junior school (in Australia), elementary school or grade school (in North America and the Philippines) is a school for primary ed ..., its prospects for survival are unfavorable compared with other ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
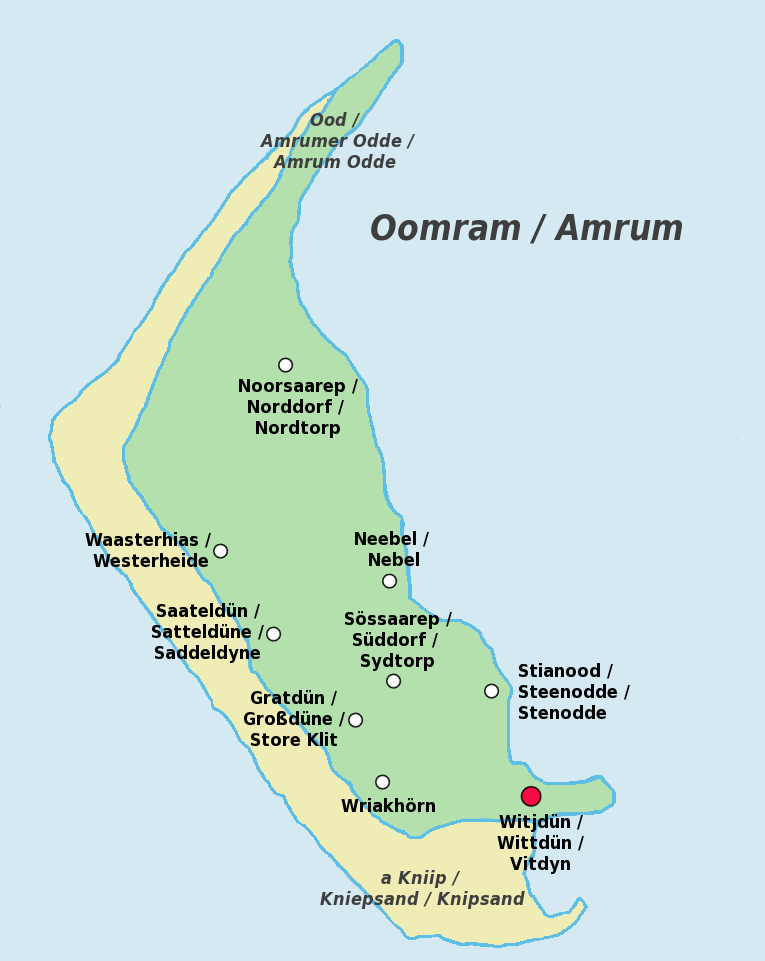
Amrum
Amrum (; Öömrang, ''Öömrang'' North Frisian: ''Oomram'') is one of the North Frisian Islands on the Germany, German North Sea coast, south of Sylt and west of Föhr. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein and has approximately 2,300 inhabitants. The island is made up of a sandy core of geestland and features an extended beach all along its west coast, facing the open North Sea. The east coast borders to mudflats of the Wadden Sea. Sand dunes are a characteristic part of Amrum's landscape, resulting in a vegetation that is largely made up of heath and shrubs. The island's only forest was planted in 1948. Amrum is a refuge for many species of birds and a number of marine mammals including the grey seal and harbour porpoise. Settlements on Amrum have been traced back to the Neolithic period when the area was still a part of the mainland of the Jutland peninsula. During the Middle Ages, Frisians, Frisian settlers arrived at Amrum and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Föhr
Föhr ( ''Fering'' North Frisian: ''Feer''; da, Før) is one of the North Frisian Islands on the German coast of the North Sea. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein. Föhr is the second-largest North Sea island of Germany and a popular destination for tourists. A town and eleven distinct municipalities are located on the island. The climate is oceanic with moderate winters and relatively cool summers. Being a settlement area already in neolithic times, Föhr had been part of mainland North Frisia until 1362. Then the coastline was destroyed by a heavy storm flood known as Saint Marcellus's flood and several islands were formed, Föhr among them. The northern parts of Föhr consist of marshes while the southern parts consist of sandy geest. From the middle-ages until 1864, Föhr belonged to the Danish realm and to the Duchy of Schleswig, but was then transferred to Prussia as a result of the Second Schleswig War. Seafaring has long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Öömrang
Amrum Frisian, or ''Öömrang'', is the dialect of the North Frisian language spoken on the island of Amrum in the German region of North Frisia. ''Öömrang'' refers to the ''Öömrang'' Frisian name of Amrum, ''Oomram''. Together with the Fering, Söl'ring, and Heligolandic dialects, it forms part of the insular group of North Frisian dialects, and it is very similar to Fering. ''Öömrang'' is spoken by about one third of Amrum's 2300 people. Characteristics *Differentiation between long and short vowels by doubling of the vowel letter (e.g., ''lun'' and, countryand ''skuul'' chool *Use of numerous diphthongs and one triphthong, "uai" (e.g. ''spuai'' o tell fortunes *Frequent use of umlauts *Final "w" is pronounced like a short "u" (e.g. ''leew'' ear, sweet *The "r" is rolled (as in Italian) Personal and family names Personal names on Amrum are still today greatly influenced by a Frisian element. Notably, hypocorisms and names with two elements are common. Early bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die Tageszeitung
''Die Tageszeitung'' (, “The Daily Newspaper”), is counted as being one of modern Germany's most important newspapers and amongst the top seven. taz is stylized as ''die tageszeitung'' and commonly referred to as ''taz'', is a cooperative-owned German daily newspaper administrated by its employees and a co-operative of shareholders who invest in a free independent press, rather than to depend on advertising and, these days, pay-walls. Founded in 1978 in Berlin as part of an independent, progressive and politically left-leaning movement, it has focused on current politics, social issues such as inequality, ecological crises both local and international, and other topics not covered by the more traditional and conservative newspapers. It mostly supports the alternative green political sphere and the German Green Party, but ''Die Tageszeitung'' has also been critical of the SPD/Greens coalition government (1998–2005). It is being described as alternative-left and critical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heligoland
Heligoland (; german: Helgoland, ; Heligolandic Frisian: , , Mooring Frisian: , da, Helgoland) is a small archipelago in the North Sea. A part of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein since 1890, the islands were historically possessions of Denmark, then became the possessions of the United Kingdom from 1807 to 1890, and briefly managed as a war prize from 1945 to 1952. The islands are located in the Heligoland Bight (part of the German Bight) in the southeastern corner of the North Sea and had a population of 1,127 at the end of 2016. They are the only German islands not in the vicinity of the mainland. They lie approximately by sea from Cuxhaven at the mouth of the River Elbe. During a visit to the islands, August Heinrich Hoffmann von Fallersleben wrote the lyrics to "", which became the national anthem of Germany. In addition to German, the local population, who are ethnic Frisians, speak the Heligolandic dialect of the North Frisian language called . Name Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |