|
Г–Г¶mrang
Amrum Frisian, also known as ''Öömrang'', is the dialect of the North Frisian language spoken on the island of Amrum in the North Frisia region of Germany. ''Öömrang'' refers to the ''Öömrang'' Frisian name of Amrum, which is ''Oomram''. Alongside the Fering, Söl'ring, and Heligolandic dialects, it is part of the insular group of North Frisian dialects, and it bears a close resemblance to Fering. ''Öömrang'' is spoken by approximately one-third of Amrum's 2,300 inhabitants. Characteristics *Differentiation between long and short vowels by doubling of the vowel letter (e.g., ''lun'' and, countryand ''skuul'' chool *Use of numerous diphthongs and one triphthong, "uai" (e.g. ''spuai'' o tell fortunes *Frequent use of umlauts *Final "w" is pronounced like a short "u" (e.g. ''leew'' ear, sweet *The "r" is rolled (as in Italian) Personal and family names Personal names on Amrum are still greatly influenced by Frisian elements to this day. Notably, hypocorisms and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Frisian Language
North Frisian is a minority language of Germany, spoken by about 10,000 people in North Frisia. The language is part of the larger group of the West Germanic Frisian languages. The language comprises 10 dialects which are themselves divided into an insular and a mainland group. North Frisian is closely related to the Saterland Frisian language of Northwest Germany and West Frisian which is spoken in the Netherlands. All of these are also closely related to the English language forming the Anglo-Frisian group. The phonological system of the North Frisian dialects is strongly being influenced by Standard German and is slowly adapting to that of the German language. With a number of native speakers probably even less than 10,000 and decreasing use in mainland North Frisia, the North Frisian language is endangered. It is protected as a minority language and has become an official language in the Nordfriesland district and on Heligoland island. Classification The closest relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
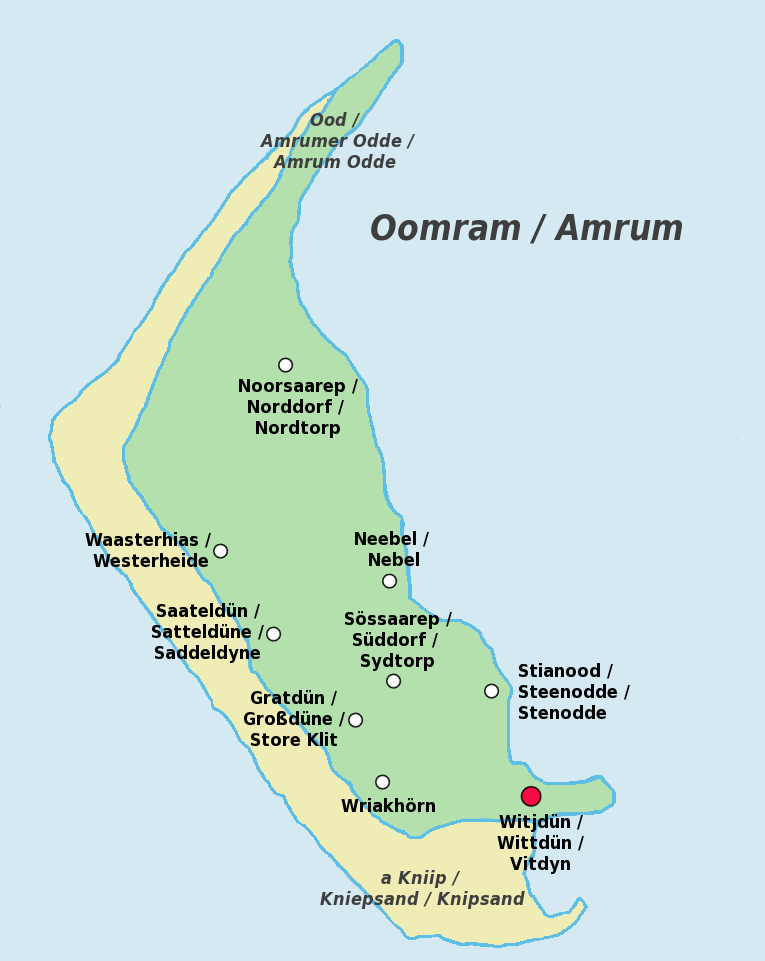
Amrum
Amrum (; Öömrang, ''Öömrang'' North Frisian: ''Oomram'') is one of the North Frisian Islands on the Germany, German North Sea coast, south of Sylt and west of Föhr. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein and has approximately 2,300 inhabitants. The island is made up of a sandy core of geestland and features an extended beach all along its west coast, facing the open North Sea. The east coast borders to mudflats of the Wadden Sea. Sand dunes are a characteristic part of Amrum's landscape, resulting in a vegetation that is largely made up of heath and shrubs. The island's only forest was planted in 1948. Amrum is a refuge for many species of birds and a number of marine mammals including the grey seal and harbour porpoise. Settlements on Amrum have been traced back to the Neolithic period when the area was still a part of the mainland of the Jutland peninsula. During the Middle Ages, Frisians, Frisian settlers arrived at Amrum and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Föhr North Frisian
Föhr Frisian, or ''Fering'', is the dialect of North Frisian spoken on the island of Föhr in the German region of North Frisia. ''Fering'' refers to the ''Fering'' Frisian name of Föhr, ''Feer''. Together with the Öömrang, Söl'ring, and Heligolandic dialects, it forms part of the insular group of North Frisian dialects and it is very similar to Öömrang. Status Around 3,000 of Föhr's 8,700 people speak ''Fering'' (1,500 of them being native speakers), constituting a third of all North Frisian speakers. Fering differs from other North Frisian dialects in that it is also used publicly on Föhr, not only at home. The municipalities of Oldsum and Süderende (Fering: Olersem, Söleraanj) in the western part of Föhr are strongholds of the dialect. Personal and family names Personal names on Föhr are still today greatly influenced by a Frisian element. Notably hypocorisms and names with two elements are common. Early borrowings were made from the Danish language and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heligolandic
Heligolandic (''Halunder'') is the dialect of the North Frisian language spoken on the German island of Heligoland in the North Sea. It is spoken today by some 500 of the island's 1,650 inhabitants and is also taught in schools. Heligolandic is closely related to the insular North Frisian dialects of Fering and Öömrang because medieval fishery around Heligoland attracted Frisians from Föhr and Amrum, and close contacts have been maintained ever since. In fact Fering and Öömrang are closer in linguistic aspects to the dialect of Heligoland than to that of their neighbouring island Sylt, Söl'ring. Heligolandic also contains a variety of loanwords from 19th-century Modern English due to the 83-year British control of the island. James Krüss is probably the most notable author of poems and narrations in Heligolandic while Maria Leitgeber (1906–1979) wrote the most substantial prose. On 24 December 2004, a state law became effective in the German state of Schleswig-Holste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Frisian Languages
The Anglo-Frisian languages are a proposed sub-branch of the West Germanic languages encompassing the Anglic languages ( English, Scots, extinct Fingallian, and extinct Yola) as well as the Frisian languages ( North Frisian, East Frisian, and West Frisian). While this relationship had considerable support historically, many modern scholars have criticized it as a valid phylogenetic grouping. Instead, they believe that the Ingvaeonic languages comprised a dialect continuum which stretched along the North Sea, finally diverging into distinct languages – Old English, Pre–Old Frisian, and Old Saxon – during the Migration Period in the 5th century. There are still proponents of an Anglo-Frisian node in the West Germanic tree, citing strong archeological and genetic evidence for the comingling of these groups. In the 1950s, Hans Kuhn argued that the two languages diverged at the Ingvaeonic level, but later "converged". He argued that this convergence explained the striking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frisian Languages
The Frisian languages ( or ) are a closely related group of West Germanic languages, spoken by about 400,000 Frisian people, who live on the southern fringes of the North Sea in the Netherlands and Germany. The Frisian languages are the closest living language group to the Anglic languages; the two groups make up the Anglo-Frisian languages group and together with the Low German dialects these form the North Sea Germanic languages. However the close genetic relationship between English and Frisian is not reflected in the linguistic distances between the modern languages, which are not Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible. Geographical and historical circumstances have caused the two languages to drift apart linguistically.Charlotte Gooskens & Wilbert Heeringa: The Position of Frisian in the Germanic Language Area, 2012, pp 21-22. There are three different branches of Frisian, which are usually called ''Frisian languages'', despite the fact that dialects within those b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Söl'ring
Sylt Frisian, or ''Söl'ring'', is the dialect of the North Frisian language spoken on the island of Sylt in the German region of North Frisia. ''Söl'ring'' refers to the ''Söl'ring'' Frisian word for Sylt, ''Söl''. Together with the Fering, Öömrang, and Heligolandic dialects, it forms part of the insular group of North Frisian dialects. It differs from the mainland dialects because of its relatively strong Danish influence. Due to mass tourism Tourism is travel for pleasure, and the Commerce, commercial activity of providing and supporting such travel. World Tourism Organization, UN Tourism defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as ... on Sylt, the dialect has been largely displaced by forms of German and ''Söl'ring'' is spoken only by a few hundred people, many of whom no longer reside on Sylt. Although it is taught in several primary schools, its prospects for survival are unfavorable compared with othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Frisian Language
West Frisian (; ), or simply Frisian ( ; ), is a West Germanic language spoken mostly in the province of Friesland () in the north of the Netherlands, mostly by those of Frisians, Frisian ancestry. It is the most widely spoken of the Frisian languages. In the study of the evolution of English language, English, West Frisian is notable as being the most closely related foreign tongue to the various dialects of Old English spoken across the Heptarchy, these being part of the Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian branch of the West Germanic family. Name The name "West Frisian" is only used outside the Netherlands, to distinguish this language from the closely related Frisian languages of East Frisian language, East Frisian, including Saterland Frisian language, Saterland Frisian, and North Frisian language, North Frisian spoken in Germany. Within the Netherlands, however, "West Frisian" refers to the West Frisian Dutch, West Frisian dialect of the Dutch language while the We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of Sail
The Age of Sail is a period in European history that lasted at the latest from the mid-16th (or mid-15th) to the mid-19th centuries, in which the dominance of sailing ships in global trade and warfare culminated, particularly marked by the introduction of naval artillery, and ultimately reached its highest extent at the advent of steam power. Enabled by the advances of the related age of navigation, it is identified as a distinctive element of the early modern period and the Age of Discovery. Periodization Like most periodic eras, defining the age is inexact and serves only as a general description. The term is used differently for warships and merchant vessels. By the 14th century naval artillery was employed in Europe, documented at the Battle of Arnemuiden (1338). The 15th century saw the Iberian naval ventures all the way along the African Atlantic coast and across the Atlantic Ocean, starting the Age of Discovery. For warships, the age of sail runs roughly from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphthong
In phonetics, a triphthong ( , ) (from Greek , ) is a monosyllabic vowel combination involving a quick but smooth movement of the articulator from one vowel quality to another that passes over a third. While "pure" vowels, or monophthongs, are said to have one target articulator position, diphthongs have two and triphthongs three. Triphthongs are not to be confused with disyllabic sequences of a diphthong followed by a monophthong, as in German 'fire', where the final vowel is longer than those found in triphthongs. Examples Triphthongs that feature close elements typically analyzed as and in phonology are not listed. For instance, the Polish word 'tallow' is typically analyzed as - a sequence of a consonant followed by a vowel and another consonant. This is because the palatal approximant is resyllabified in some inflected forms, such as (instr. pl.), and also because occurs word-finally after a consonant just like does (compare 'industry' with 'PrzemyЕ›l'), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patronymic
A patronymic, or patronym, is a component of a personal name based on the given name of one's father, grandfather (more specifically an avonymic), or an earlier male ancestor. It is the male equivalent of a matronymic. Patronymics are used, by custom or official policy, in many countries worldwide, although elsewhere their use has been replaced by or transformed into patronymic surnames. Examples of such transformations include common English surnames such as Johnson (surname), Johnson (son of John). Origins of terms The usual noun and adjective in English is ''patronymic'', but as a noun this exists in free variation alongside ''patronym''. The first part of the word ''patronym'' comes from Greek language, Greek ПЂО±П„О®ПЃ ''patД“r'' 'father' (Genitive case, GEN ПЂО±П„ПЃПЊП‚ ''patros'' whence the combining form ПЂО±П„ПЃОї- ''patro''-); the second part comes from Greek бЅ„ОЅП…ОјО± ''onyma'', a variant form of бЅ„ОЅОїОјО± ''onoma'' 'name'. In the form ''patronymic'', this stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Language
Danish (, ; , ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken by about six million people, principally in and around Denmark. Communities of Danish speakers are also found in Greenland, the Faroe Islands, and the northern Germany, German region of Southern Schleswig, where it has minority language status. Minor Danish-speaking communities are also found in Norway, Sweden, the United States, Canada, Brazil, and Argentina. Along with the other North Germanic languages, Danish is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples who lived in Scandinavia during the Viking Age, Viking Era. Danish, together with Swedish, derives from the ''East Norse'' dialect group, while the Middle Norwegian language (before the influence of Danish) and BokmГҐl, Norwegian BokmГҐl are classified as ''West Norse'' along with Faroese language, Faroese and Icelandic language, Icelandic. A more recent c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |