|
Helicity (fluid Mechanics)
:''This page is about helicity in fluid dynamics. For helicity of magnetic fields, see magnetic helicity. For helicity in particle physics, see helicity (particle physics).'' In fluid dynamics, helicity is, under appropriate conditions, an invariant of the Euler equations of fluid flow, having a topological interpretation as a measure of linkage and/or knottedness of vortex lines in the flow. This was first proved by Jean-Jacques Moreau in 1961 and Moffatt derived it in 1969 without the knowledge of Moreau's paper. This helicity invariant is an extension of Woltjer's theorem for magnetic helicity. Let \mathbf(x,t) be the velocity field and \nabla\times\mathbf the corresponding vorticity field. Under the following three conditions, the vortex lines are transported with (or 'frozen in') the flow: (i) the fluid is inviscid; (ii) either the flow is incompressible (\nabla\cdot\mathbf = 0), or it is compressible with a barotropic relation p = p(\rho) between pressure p and density ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
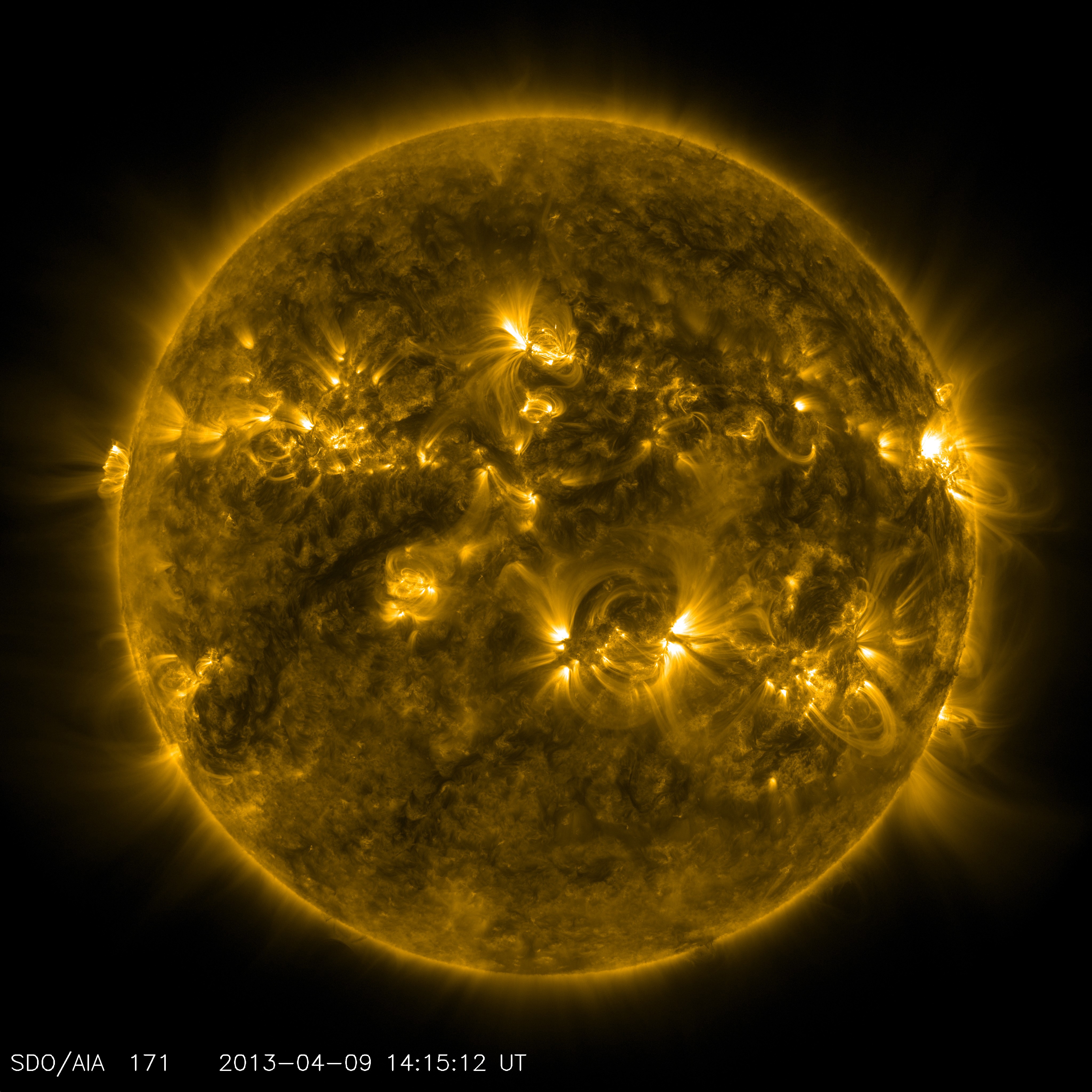
Magnetic Helicity
In plasma physics, magnetic helicity is a measure of the linkage, twist, and writhe of a magnetic field. In ideal magnetohydrodynamics, magnetic helicity is conserved. When a magnetic field contains magnetic helicity, it tends to form large-scale structures from small-scale ones. This process can be referred as an inverse transfer in Fourier space. This second property makes magnetic helicity special: three-dimensional turbulent flows tend to "destroy" structure, in the sense that large-scale vortices break-up in smaller and smaller ones (a process called "direct energy cascade", described by Lewis Fry Richardson and Andrey Nikolaevich Kolmogorov). At the smallest scales, the vortices are dissipated in heat through viscous effects. Through a sort of "inverse cascade of magnetic helicity", the opposite happens: small helical structures (with a non-zero magnetic helicity) lead to the formation of large-scale magnetic fields. This is for example visible in the heliospheric curren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renzo L
Renzo, the diminutive of Lorenzo, is an Italian masculine given name and a surname. Given name Notable people named Renzo include the following: *Renzo Alverà (1933–2005), Italian bobsledder *Renzo Arbore (born 1937), Italian TV host, showman, singer, musician, film actor, and film director *Renzo Barbieri (1940–2007), Italian author and editor of Italian comics *Renzo Caldara (born 1943), Italian bobsledder *Renzo Cesana (1907–1970), Italian-American actor, writer, composer, and songwriter *Renzo Cramerotti (born 1947), Italian male javelin thrower *Renzo Dalmazzo (1886–?), Italian lieutenant general *Renzo De Felice (1929–1996), Italian historian *Renzo De Vecchi (1894–1967), Italian football player and coach * Renzo Fenci (1914–1999), Italian-American sculptor based in Southern California. *Renzo Furlan (born 1970), Italian tennis player * Renzo Fujiwara (born 1973), A minor character in the movie The End of Cygnus *Renzo Gobbo (born 1961), Italian associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalar Product
In mathematics, the dot product or scalar productThe term ''scalar product'' means literally "product with a scalar as a result". It is also used sometimes for other symmetric bilinear forms, for example in a pseudo-Euclidean space. is an algebraic operation that takes two equal-length sequences of numbers (usually coordinate vectors), and returns a single number. In Euclidean geometry, the dot product of the Cartesian coordinates of two vectors is widely used. It is often called the inner product (or rarely projection product) of Euclidean space, even though it is not the only inner product that can be defined on Euclidean space (see Inner product space for more). Algebraically, the dot product is the sum of the products of the corresponding entries of the two sequences of numbers. Geometrically, it is the product of the Euclidean magnitudes of the two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them. These definitions are equivalent when using Cartesian coordinates. In mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpendicular
In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle (90 degrees or π/2 radians). The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the ''perpendicular symbol'', ⟂. It can be defined between two lines (or two line segments), between a line and a plane, and between two planes. Perpendicularity is one particular instance of the more general mathematical concept of '' orthogonality''; perpendicularity is the orthogonality of classical geometric objects. Thus, in advanced mathematics, the word "perpendicular" is sometimes used to describe much more complicated geometric orthogonality conditions, such as that between a surface and its '' normal vector''. Definitions A line is said to be perpendicular to another line if the two lines intersect at a right angle. Explicitly, a first line is perpendicular to a second line if (1) the two lines meet; and (2) at the point of intersection the straight angle on one side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometry, geographical survey, sport, or atmospheric pressure). Although the term ''altitude'' is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage. Vertical distance measurements in the "down" direction are commonly referred to as depth. In aviation In aviation, the term altitude can have several meanings, and is always qualified by explicitly adding a modifier (e.g. "true altitude"), or implicitly through the context of the communication. Parties exchanging altitude information must be clear which definition is being used. Aviation altitude is measured using either mean sea level (MSL) or local ground level (above ground level, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their spatial scale, their speed and direction, the forces that cause them, the regions in which they occur, and their effect. Winds have various asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place in soft solids or mixtures where particles can flow. Convective flow may be transient (such as when a multiphase mixture of oil and water separates) or steady state (see Convection cell). The convection may be due to gravitational, electromagnetic or fictitious body forces. Heat transfer by natural convection plays a role in the structure of Earth's atmosphere, its oceans, and its mantle. Discrete convective cells in the atmosphere can be identified by clouds, with stronger convection resulting in thunderstorms. Natural convection also plays a role in stellar physics. Convection is often categorised or d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vorticity
In continuum mechanics, vorticity is a pseudovector field that describes the local spinning motion of a continuum near some point (the tendency of something to rotate), as would be seen by an observer located at that point and traveling along with the flow. It is an important quantity in the dynamical theory of fluids and provides a convenient framework for understanding a variety of complex flow phenomena, such as the formation and motion of vortex rings. Mathematically, the vorticity \vec is the curl of the flow velocity \vec: :\vec \equiv \nabla \times \vec\,, where \nabla is the nabla operator. Conceptually, \vec could be determined by marking parts of a continuum in a small neighborhood of the point in question, and watching their ''relative'' displacements as they move along the flow. The vorticity \vec would be twice the mean angular velocity vector of those particles relative to their center of mass, oriented according to the right-hand rule. In a two-dimensional fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UKMET
The Meteorological Office, abbreviated as the Met Office, is the United Kingdom's national weather service. It is an executive agency and trading fund of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy and is led by CEO Penelope Endersby, who took on the role as Chief Executive in December 2018 and is the first woman to do so. The Met Office makes meteorological predictions across all timescales from weather forecasts to climate change. History The Met Office was established on 1 August 1854 as a small department within the Board of Trade under Vice Admiral Robert FitzRoy as a service to mariners. The loss of the passenger vessel, the ''Royal Charter'', and 459 lives off the coast of Anglesey in a violent storm in October 1859 led to the first gale warning service. FitzRoy established a network of 15 coastal stations from which visual gale warnings could be provided for ships at sea. The new electric telegraph enabled rapid dissemination of warnings and als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorologist
A meteorologist is a scientist who studies and works in the field of meteorology aiming to understand or predict Earth's atmospheric phenomena including the weather. Those who study meteorological phenomena are meteorologists in research, while those using mathematical models and knowledge to prepare daily weather forecasts are called ''weather forecasters'' or ''operational meteorologists''. Meteorologists work in government agencies, private consulting and research services, industrial enterprises, utilities, radio and television stations, and in education. They are not to be confused with weather presenters, who present the weather forecast in the media and range in training from journalists having just minimal training in meteorology to full fledged meteorologists. Description Meteorologists study the Earth's atmosphere and its interactions with the Earth's surface, the oceans and the biosphere. Their knowledge of applied mathematics and physics allows them to understand the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not begin until the 18th century. The 19th century saw modest progress in the field after weather observation networks were formed across broad regions. Prior attempts at prediction of weather depended on historical data. It was not until after the elucidation of the laws of physics, and more particularly in the latter half of the 20th century the development of the computer (allowing for the automated solution of a great many modelling equations) that significant breakthroughs in weather forecasting were achieved. An important branch of weather forecasting is marine weather forecasting as it relates to maritime and coastal safety, in which weather effects also include atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water. Meteorological pheno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetohydrodynamics
Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD; also called magneto-fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties and behaviour of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magnetofluids include plasmas, liquid metals, salt water, and electrolytes. The word ''magnetohydrodynamics'' is derived from ' meaning magnetic field, ' meaning water, and ' meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970. The fundamental concept behind MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which in turn polarizes the fluid and reciprocally changes the magnetic field itself. The set of equations that describe MHD are a combination of the Navier–Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell’s equations of electromagnetism. These differential equations must be solved simultaneously, either analytically or numerically. History The first record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |