|
Heart Of Stone (medicine)
Calciphylaxis, also known as calcific uremic arteriolopathy (CUA) or “Grey Scale”, is a rare syndrome characterized by painful skin lesions. The pathogenesis of calciphylaxis is unclear but believed to involve calcification of the small blood vessels located within the fatty tissue and deeper layers of the skin, blood clots, and eventual death of skin cells due to lack of blood flow. It is seen mostly in people with end-stage kidney disease but can occur in the earlier stages of chronic kidney disease and rarely in people with normally functioning kidneys. Calciphylaxis is a rare but serious disease, believed to affect 1-4% of all dialysis patients. It results in chronic non-healing wounds and indicates poor prognosis, with typical life expectancy of less than one year. Calciphylaxis is one type of extraskeletal calcification. Similar extraskeletal calcifications are observed in some people with high levels of calcium in the blood, including people with milk-alkali syndrome, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, apoptosis is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates in the surrounding tissue an inflammatory response, which attracts leukocytes and nearby phagocytes which eliminate the dead cells by phagocytosis. However, microbial damaging substances released by leukocytes would crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
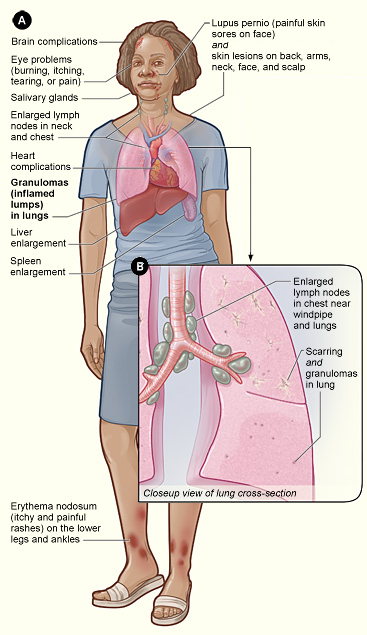
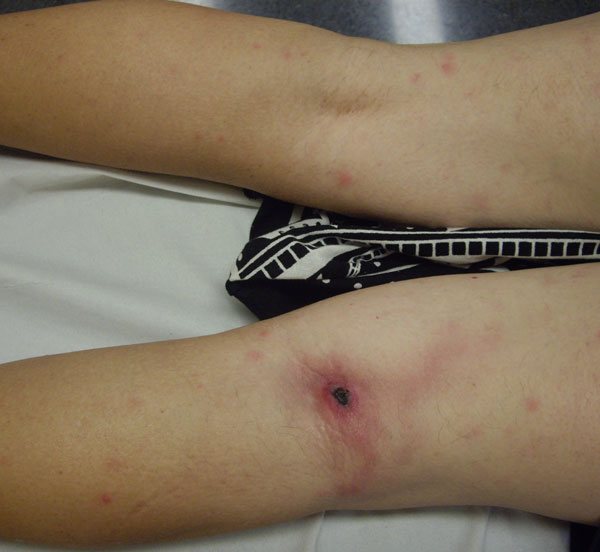
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly affected are the eyes, liver, heart, and brain. Any organ can be affected though. The signs and symptoms depend on the organ involved. Often, no, or only mild, symptoms are seen. When it affects the lungs, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain may occur. Some may have Löfgren syndrome with fever, large lymph nodes, arthritis, and a rash known as erythema nodosum. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Some believe it may be due to an immune reaction to a trigger such as an infection or chemicals in those who are genetically predisposed. Those with affected family members are at greater risk. Diagnosis is partly based on signs and symptoms, which may be supported by biopsy. Findings that make it likely include large lymph n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein S Deficiency
Protein S deficiency is a disorder associated with increased risk of venous thrombosis. Protein S, a vitamin K-dependent physiological anticoagulant, acts as a nonenzymatic cofactor to activate protein C in the degradation of factor Va and factor VIIIa. Decreased (antigen) levels or impaired function of protein S leads to decreased degradation of factor Va and factor VIIIa and an increased propensity to venous thrombosis. Protein S circulates in human plasma in two forms: approximately 60 percent is bound to complement component C4b β-chain while the remaining 40 percent is free, only free protein S has activated protein C cofactor activity Signs and symptoms Among the possible presentation of protein S deficiency are: Cause In terms of the cause of protein S deficiency it can be in ''inherited'' via autosomal dominance. A mutation in the PROS1 gene triggers the condition. The cytogenetic location of the gene in question is chromosome 3, specifically 3q11.1 Protein S deficie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein C Deficiency
Protein C deficiency is a rare genetic trait that predisposes to thrombotic disease. It was first described in 1981. The disease belongs to a group of genetic disorders known as thrombophilias. Protein C deficiency is associated with an increased incidence of venous thromboembolism (relative risk 8–10), whereas no association with arterial thrombotic disease has been found. Presentation Complications Protein C is vitamin K-dependent. Patients with Protein C deficiency are at an increased risk of developing skin necrosis while on warfarin. Protein C has a short half life (8 hour) compared with other vitamin K-dependent factors and therefore is rapidly depleted with warfarin initiation, resulting in a transient hypercoagulable state. Pathophysiology The main function of protein C is its anticoagulant property as an inhibitor of coagulation factors V and VIII. A deficiency results in a loss of the normal cleaving of Factors Va and VIIIa. There are two main types of protein C mut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over ; the range is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis. Obesity has individual, socioeconomic, and environmental causes. Some known causes are diet, physical activity, automation, urbanization, genetic susceptibility, medications, mental disorders, economic policies, endocrine disorders, and exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals. While a majority of obese individuals at any given time are attempting to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipocyte
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through adipogenesis. In cell culture, adipocyte progenitors can also form osteoblasts, myocytes and other cell types. There are two types of adipose tissue, white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT), which are also known as white and brown fat, respectively, and comprise two types of fat cells. Structure White fat cells White fat cells contain a single large lipid droplet surrounded by a layer of cytoplasm, and are known as unilocular. The nucleus is flattened and pushed to the periphery. A typical fat cell is 0.1 mm in diameter with some being twice that size, and others half that size. However, these numerical estimates of fat cell size depend largely on the measurement method and the location of the adipose tissue. The fat stored i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastatic Calcification
Metastatic calcification is deposition of calcium salts in otherwise normal tissue, because of elevated serum levels of calcium, which can occur because of deranged metabolism as well as increased absorption or decreased excretion of calcium and related minerals, as seen in hyperparathyroidism. In contrast, dystrophic calcification is caused by abnormalities or degeneration of tissues resulting in mineral deposition, though blood levels of calcium remain normal. These differences in pathology also mean that metastatic calcification is often found in many tissues throughout a person or animal, whereas dystrophic calcification is localized. Metastatic calcification can occur widely throughout the body but principally affects the interstitial tissues of the vasculature, kidneys, lungs, and gastric mucosa. For the latter three, acid secretions or rapid changes in pH levels contribute to the formation of salts. Causes Hypercalcemia, elevated blood calcium, has numerous causes, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) refers to undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. They are usually referred to as an over-reaction of the immune system and these reactions may be damaging and uncomfortable. This is an immunologic term and is not to be confused with the psychiatric term of being hypersensitive which implies to an individual who may be overly sensitive to physical (i.e. sound, touch, light, etc.) and/or emotional stimuli. Although there is a relation between the two – studies have shown that those individuals that have ADHD (a psychiatric disorder) are more likely to have hypersensitivity reactions such as allergies, asthma, eczema than those who do not have ADHD. Hypersensitivity reactions can be classified into four types. Type I: IgE mediated immediate reaction Type II: Antibody-mediated reaction (IgG or IgM antibodies) Type III: Immune complex-mediated rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunica Media
The tunica media (New Latin "middle coat"), or media for short, is the middle tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It lies between the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside. Artery Tunica media is made up of smooth muscle cells, elastic tissue and collagen. It lies between the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside. The middle coat (tunica media) is distinguished from the inner (tunica intima) by its color and by the transverse arrangement of its fibers. * In the ''smaller arteries'' it consists principally of smooth muscle fibers in fine bundles, arranged in lamellæ and disposed circularly around the vessel. These lamellæ vary in number according to the size of the vessel; the smallest arteries having only a single layer, and those slightly larger three or four layers - up to a maximum of six layers. It is to this coat that the thickness of the wall of the artery is mainly due. * In the ''larger arteries'', as the ilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eschar
An eschar (; Greek: ''ἐσχάρᾱ'', ''eskhara''; Latin: ''eschara'') is a slough or piece of dead tissue that is cast off from the surface of the skin, particularly after a burn injury, but also seen in gangrene, ulcer, fungal infections, necrotizing spider bite wounds, tick bites associated with spotted fevers and exposure to cutaneous anthrax. The term ‘eschar’ is not interchangeable with ‘scab’. An eschar contains necrotic tissue whereas a scab is composed of dried blood and exudate. Black eschars are most frequently attributed in medicine to cutaneous anthrax (infection by '' Bacillus anthracis''), which may be contracted through herd animal exposure and also from ''Pasteurella multocida'' exposure in cats and rabbits. A newly identified human rickettsial infection, ''R. parkeri'' rickettsiosis, can be differentiated from Rocky Mountain spotted fever by the presence of an eschar at the site of inoculation. Eschar is sometimes called a ''black wound'' becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livedo Reticularis
Livedo reticularis is a common skin finding consisting of a mottled reticulated vascular pattern that appears as a lace-like purplish discoloration of the skin. The discoloration is caused by reduction in blood flow through the arterioles that supply the cutaneous capillaries, resulting in deoxygenated blood showing as blue discoloration. This can be a secondary effect of a condition that increases a person's risk of forming blood clots, including a wide array of pathological and nonpathological conditions. Examples include hyperlipidemia, microvascular hematological or anemia states, nutritional deficiencies, hyper- and autoimmune diseases, and drugs/toxins. The condition may be normal or related to more severe underlying pathology. Its differential diagnosis is broadly divided into possible blood diseases, autoimmune (rheumatologic) diseases, cardiovascular diseases, cancers, and endocrine disorders. It can usually (in 80% of cases) be diagnosed by biopsy. It may be aggravated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |