|
Hawart
Hawart ( 13th century) was a German poet in the tradition of ''Minnesang'' (love lyric). His surviving works focus on both love and politics. His reference in one poem to the Holy Places being in the hands of the heathen places it after the fall of Jerusalem in 1244.. In another song he laments the failure of the princes of the Holy Roman Empire to unite behind one emperor, a clear reference to the Great Interregnum (1254–1273).. The identity of the poet named Hawart is uncertain. In the 19th century he was identified with the Tyrolean knight Hawart von Antholz., pp. 291–293. More recently he has been identified with Johannes Hawart the Elder of Strasbourg, who is mentioned in texts of 1289 and 1292 and died in 1302 in old age. Where in Germany the ''Minnesinger'' was active is also unknown. Reinhard Bleck suggests, on the basis of his crusade songs and his possible identification with Hawart of Strasbourg, that he was most likely from Alsace, the only part of Germany to see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crusade Of 1267
The Crusade of 1267 was a military expedition from the Upper Rhenish regions of the Holy Roman Empire for the defence of the Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was one of several minor crusades of the 1260s that resulted from a period of Papally-sponsored crusade preaching of unprecedented intensity. The only major crusade to come of it was the Eighth Crusade in 1270. Something is known of the preaching and organization of the crusade, but nothing for certain of its results. Several hundred crusaders and pilgrims did reach the Kingdom of Jerusalem under the leadership of two ministerials, but they probably waited in vain for the arrival of the Eighth Crusade without undertaking major military actions. Most of the crusaders of 1267 returned home before the Eighth Crusade even set out. The main source for the Crusade of 1267 is the ''Bassler Chronick'' of Christian Wurstisen, which appeared in 1580. Although a late source with a confused chronology, Wurstisen is generally reliable and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minnesang
(; "love song") was a tradition of lyric- and song-writing in Germany and Austria that flourished in the Middle High German period. This period of medieval German literature began in the 12th century and continued into the 14th. People who wrote and performed ''Minnesang'' were known as ''Minnesänger'' (), and a single song was called a ''Minnelied'' (). The name derives from ''minne'', the Middle High German Middle High German (MHG; german: Mittelhochdeutsch (Mhd.)) is the term for the form of German spoken in the High Middle Ages. It is conventionally dated between 1050 and 1350, developing from Old High German and into Early New High German. High ... word for love, as that was ''Minnesang'''s main subject. The ''Minnesänger'' were similar to the Occitan language, Provençal troubadours and northern French language, French ''trouvères'' in that they wrote love poetry in the tradition of courtly love in the High Middle Ages. Social status In the absence of reliable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minnesingers
(; "love song") was a tradition of lyric- and song-writing in Germany and Austria that flourished in the Middle High German period. This period of medieval German literature began in the 12th century and continued into the 14th. People who wrote and performed ''Minnesang'' were known as ''Minnesänger'' (), and a single song was called a ''Minnelied'' (). The name derives from ''minne'', the Middle High German word for love, as that was ''Minnesang'''s main subject. The ''Minnesänger'' were similar to the Provençal troubadours and northern French ''trouvères'' in that they wrote love poetry in the tradition of courtly love in the High Middle Ages. Social status In the absence of reliable biographical information, there has been debate about the social status of the ''Minnesänger''. Some clearly belonged to the higher nobility – the 14th century Codex Manesse includes songs by dukes, counts, kings, and the Emperor Henry VI. Some ''Minnesänger'', as indicated by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
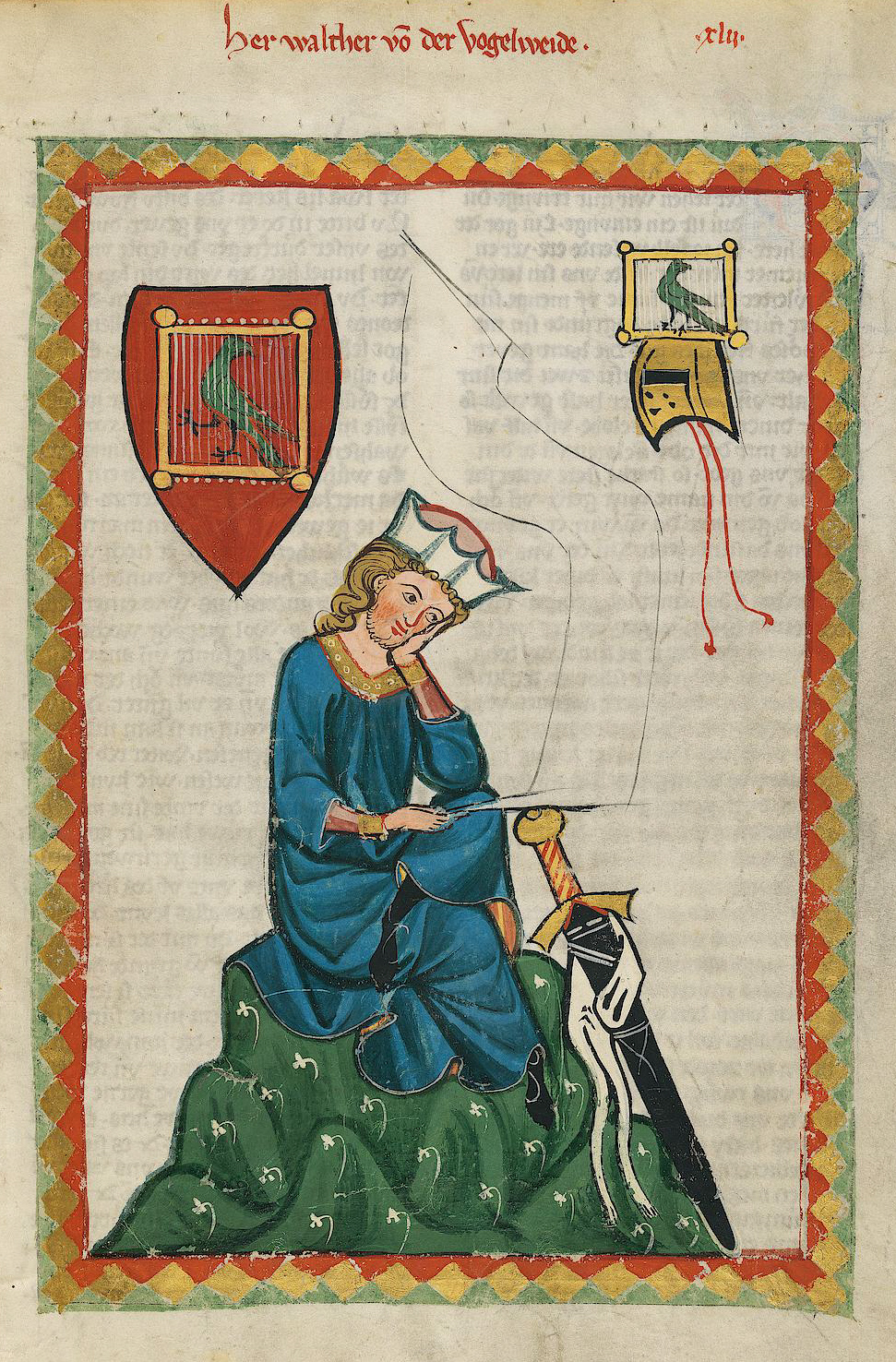
Codex Manesse 313r Hawart
The codex (plural codices ) was the historical ancestor of the modern book. Instead of being composed of sheets of paper, it used sheets of vellum, papyrus, or other materials. The term ''codex'' is often used for ancient manuscript books, with handwritten contents. A codex, much like the modern book, is bound by stacking the pages and securing one set of edges by a variety of methods over the centuries, yet in a form analogous to modern bookbinding. Modern books are divided into paperback or softback and those bound with stiff boards, called hardbacks. Elaborate historical bindings are called treasure bindings. At least in the Western world, the main alternative to the paged codex format for a long document was the continuous scroll, which was the dominant form of document in the ancient world. Some codices are continuously folded like a concertina, in particular the Maya codices and Aztec codices, which are actually long sheets of paper or animal skin folded into pages. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle High German
Middle High German (MHG; german: Mittelhochdeutsch (Mhd.)) is the term for the form of German spoken in the High Middle Ages. It is conventionally dated between 1050 and 1350, developing from Old High German and into Early New High German. High German is defined as those varieties of German which were affected by the Second Sound Shift; the Middle Low German and Middle Dutch languages spoken to the North and North West, which did not participate in this sound change, are not part of MHG. While there is no ''standard'' MHG, the prestige of the Hohenstaufen court gave rise in the late 12th century to a supra-regional literary language (') based on Swabian, an Alemannic dialect. This historical interpretation is complicated by the tendency of modern editions of MHG texts to use ''normalised'' spellings based on this variety (usually called "Classical MHG"), which make the written language appear more consistent than it actually is in the manuscripts. Scholars are uncertain as to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Christian Holy Places In The Holy Land
The list of Christian holy places in the Holy Land outlines sites within cities located in the Holy Land that are regarded as having a special religious significance to Christians, usually by association with Jesus or other persons mentioned in the Bible. The identification of the Christian holy sites became of increased importance especially from around the time of Constantine the Great of the Roman Empire. Interest was also strong during Emperor Charlemagne, as was also the case during the Crusades, when Christian pilgrims often sought out ''holy places'' in the Outremer, especially in early 12th century immediately after the capture of Jerusalem.Sean Martin, ''The Knights Templar: The History & Myths of the Legendary Military Order'', 2005. The search for the Christian holy places was the foundation of 19th-century European Biblical archaeology in Ottoman Syria and later in the British Mandate Palestine. Definition The primary holy places are connected to the main events i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Jerusalem (1244)
The 1244 siege of Jerusalem took place after the Sixth Crusade, when a Khwarazmian army conquered the city on July 15, 1244. Prelude Emperor Frederick II of the Holy Roman Empire led the Sixth Crusade from 1228 to 1229 and claimed the title of King of Jerusalem as the husband of Isabella II of Jerusalem, queen since 1212. The army brought by the emperor and his reputation in the Muslim world were enough to recover Jerusalem, Bethlehem, Nazareth and several strongholds without fighting, as signed by a treaty with the Ayyubid Sultan al-Kamil. However, Jerusalem did not remain in the hands of Christians for long, as, despite further territorial gains a few years earlier in the Barons' Crusade, the latter did not control the surroundings of the city sufficiently to be able to ensure an effective defense. The Khwarazmian army consisted of 10,000 cavalry, comprising both some of the remnants of the predominantly Kipchak army of the last Khwarazmshah, Jalal al-Din Mangburni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princes Of The Holy Roman Empire
Prince of the Holy Roman Empire ( la, princeps imperii, german: Reichsfürst, cf. ''Fürst'') was a title attributed to a hereditary ruler, nobleman or prelate recognised as such by the Holy Roman Emperor. Definition Originally, possessors of the princely title bore it as immediate vassals of the Emperor who held a fief (secular or ecclesiastical) that had no suzerain except the Emperor. However, by the time the Holy Roman Empire was abolished in 1806, there were a number of holders of Imperial princely titles who did not meet these criteria. Thus, there were two main types of princes: those who exercised '' Landeshoheit'' (sovereignty within one's territory while respecting the laws and traditions of the empire) as well as an individual or shared vote in the College of Princes, and those whose title was honorary (the possessor lacking an immediate Imperial fief and/or a vote in the Imperial Diet). The first came to be reckoned as "royalty" in the sense of being treated as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Interregnum
In the Holy Roman Empire, the Great Interregnum (so-called to distinguish it from the shorter period between 924 and 962) was a period of time following the death of Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II where the succession of the Holy Roman Empire was contested and fought over between pro- and anti-Hohenstaufen factions. Starting around 1250 with the death of Frederick II, conflict over who was the rightful emperor and King of the Romans would continue into the 1300s until Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV of Luxembourg was elected Holy Roman Emperor, emperor and secured succession for his son Wenceslaus IV of Bohemia, Wenceslaus. This period saw a multitude of emperors and kings be elected or propped up by rival factions and princes, with many kings and emperors having short reigns or reigns that became heavily contested by rival claimants. The long-lasting effects of the Interregnum were primarily the end of centralization of the imperial monarchy and the fragme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary, from its formation in the 12th century until 1919. In 1919, following World War I and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, it was divided into two modern administrative parts through the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye: * State of Tyrol: Formed through the merger of North and East Tyrol, as part of Austria * Region of Trentino-Alto Adige: At that time still with Souramont (Cortina d'Ampezzo, Livinallongo del Col di Lana and Colle Santa Lucia) and the municipalities Valvestino, Magasa, and Pedemonte, seized in 1918 by the Kingdom of Italy, and thus since 1946 part of the Italian Republic. With the founding of the European region Tyrol-South Tyrol-Trentino the area has its own legal entity since 2011 in the form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label=Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label=Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the European Parliament. Located at the border with Germany in the historic region of Alsace, it is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin department. In 2019, the city proper had 287,228 inhabitants and both the Eurométropole de Strasbourg (Greater Strasbourg) and the Arrondissement of Strasbourg had 505,272 inhabitants. Strasbourg's metropolitan area had a population of 846,450 in 2018, making it the eighth-largest metro area in France and home to 14% of the Grand Est region's inhabitants. The transnational Eurodistrict Strasbourg-Ortenau had a population of 958,421 inhabitants. Strasbourg is one of the ''de facto'' four main capitals of the European Union (alongside Brussels, Luxembourg and Frankfurt), as it is the seat of several European insti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
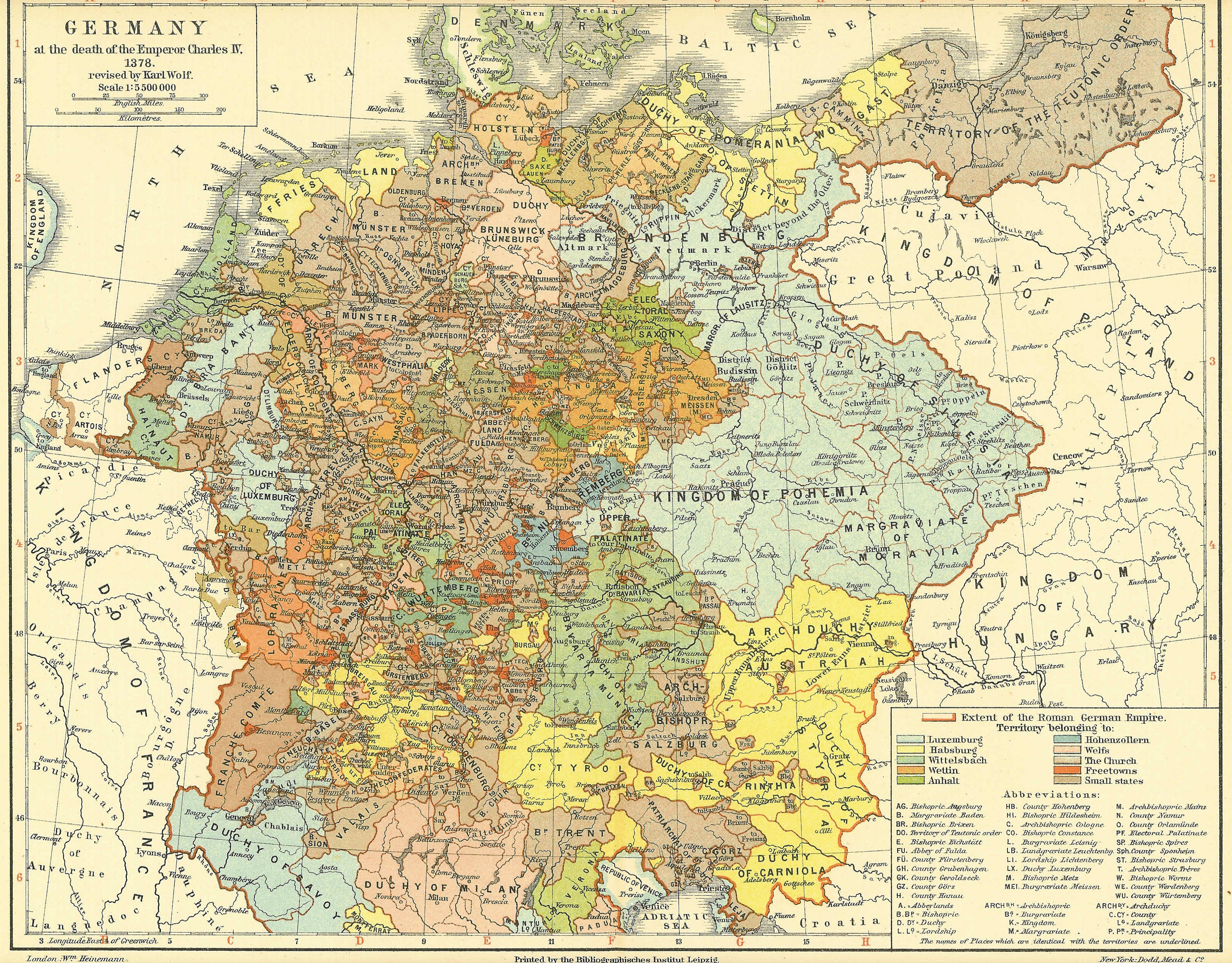
Kingdom Of Germany
The Kingdom of Germany or German Kingdom ( la, regnum Teutonicorum "kingdom of the Germans", "German kingdom", "kingdom of Germany") was the mostly Germanic-speaking East Frankish kingdom, which was formed by the Treaty of Verdun in 843, especially after the kingship passed from Frankish kings to the Saxon Ottonian dynasty in 919. The king was elected, initially by the rulers of the stem duchies, who generally chose one of their own. After 962, when Otto I was crowned emperor, East Francia formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire, which also included the Kingdom of Italy and, after 1032, the Kingdom of Burgundy. Like medieval England and medieval France, medieval Germany consolidated from a conglomerate of smaller tribes, nations or polities by the High Middle Ages. The term ''rex teutonicorum'' (" king of the Germans") first came into use in Italy around the year 1000. It was popularized by the chancery of Pope Gregory VII during the Investiture Controversy (late 11th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |