|
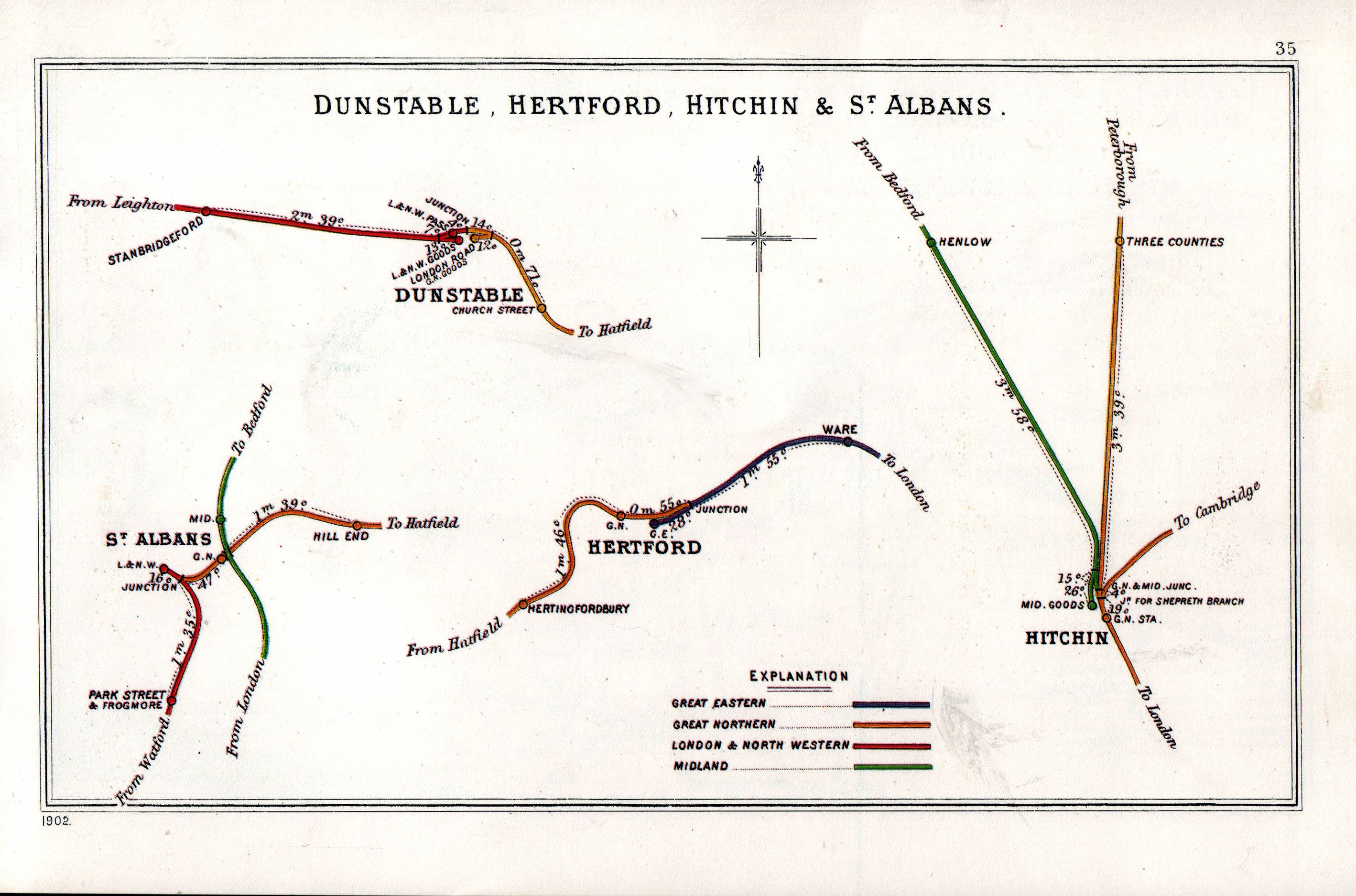
Hatfield And St Albans Railway
The Hatfield & St Albans Railway was a branch of the Great Northern Railway which connected St Albans to Hatfield in Hertfordshire, England. It opened in 1865 with the principal aim of allowing St Albans traffic to access the Great Northern's main line to London at , but soon came into difficulties when the Midland Railway inaugurated a direct route to London through St Albans. Passenger receipts declined in the 1930s, resulting in the temporary withdrawal of services in 1939. Passenger services were permanently withdrawn in 1951, leaving goods traffic to linger on until December 1968. Much of the route of the line is now incorporated into the Alban Way, a footpath and cycleway. History Authorisation and opening The Hatfield and St Albans Railway Company was incorporated by Act of Parliament on 30 June 1862. It had been promoted by various landowners in Hatfield and St Albans in Hertfordshire and supported by the Great Northern Railway, which saw the line as a mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertfordshire
Hertfordshire ( or ; often abbreviated Herts) is one of the home counties in southern England. It borders Bedfordshire and Cambridgeshire to the north, Essex to the east, Greater London to the south, and Buckinghamshire to the west. For government statistical purposes, it forms part of the East of England region. Hertfordshire covers . It derives its name – via the name of the county town of Hertford – from a hart (stag) and a ford, as represented on the county's coat of arms and on the flag. Hertfordshire County Council is based in Hertford, once the main market town and the current county town. The largest settlement is Watford. Since 1903 Letchworth has served as the prototype garden city; Stevenage became the first town to expand under post-war Britain's New Towns Act of 1946. In 2013 Hertfordshire had a population of about 1,140,700, with Hemel Hempstead, Stevenage, Watford and St Albans (the county's only ''city'') each having between 50,000 and 100,000 r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Albans Abbey Railway Station
St Albans Abbey railway station in St Albans, Hertfordshire, England is about south of the city centre in the St Stephen's area. It is the terminus of the Abbey Line from Watford Junction, operated by London Northwestern Railway. It is one of two stations in St Albans, the other being the much larger and busier St Albans City. The unstaffed station consists of a single open-air platform and a car park. Improvement works were carried out in 2008. It was the second UK railway station to receive a Harrington Hump to improve accessibility. History St Albans Abbey was the first railway station in St Albans, built by the London and North Western Railway in 1858. It was, as it is now, a terminus; the company's plans to extend northwards to Luton and Dunstable never materialised. Although the Midland Railway opened their station (St Albans City) in 1868, it was not until 1924 that "Abbey" was added to the station's title to avoid confusion – by this stage, both stations were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Havilland
The de Havilland Aircraft Company Limited () was a British aviation manufacturer established in late 1920 by Geoffrey de Havilland at Stag Lane Aerodrome Edgware on the outskirts of north London. Operations were later moved to Hatfield in Hertfordshire. Known for its innovation, de Havilland was responsible for a number of important aircraft, including the Moth biplane which revolutionised aviation in the 1920s; the 1930s Fox Moth, a commercial light passenger aircraft; the wooden World War II Mosquito multirole aircraft; and the pioneering passenger jet airliner Comet. The de Havilland company became a member of the Hawker Siddeley group in 1960, but lost its separate identity in 1963. Later, Hawker Siddeley merged into what is eventually known today as BAE Systems, the British aerospace and defence business. The de Havilland name lives on in De Havilland Canada, which owns the rights to the name and the aircraft produced by de Havilland's former Canadian subsidiary, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-4-2T
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, represents a configuration of a four-wheeled leading bogie, four powered and coupled driving wheels, and two trailing wheels supporting part of the weight of the boiler and firebox. This allows a larger firebox and boiler than the configuration. This wheel arrangement is commonly known as the Atlantic type, although it is also sometimes called a Milwaukee or 4-4-2 Milwaukee, after the Milwaukee Road, which employed it in high speed passenger service. Overview While the wheel arrangement and type name Atlantic would come to fame in the fast passenger service competition between railroads in the United States by mid-1895, the tank locomotive version of the Atlantic type first made its appearance in the United Kingdom in 1880, when William Adams designed the 1 Class T of the London, Tilbury and Southend Railway (LT&SR). The is the tank locomotive equivalent of a 4-4-0 American ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNR Class C2
The Great Northern Railway class C2 locomotives were a class of 4-4-2 tank locomotives built by the Great Northern Railway (GNR) between 1898 and 1907. They were used on local and commuter passenger trains in Yorkshire and North London. They were withdrawn between 1957 and 1958. Numbering The GNR numbered them 1009A, 1010, 1013–1020 and 1501–1550. All passed to the London and North Eastern Railway in 1923, who renumbered them by adding 3000 to their GNR number. In the post World War II renumbering scheme, the remaining 50 locomotives were renumbered 7350–7399. In 1948, the remaining 49 locomotives passed to British Railways, who renumbered them by prefixing a 6 to their LNER number (i.e. 67350–67399). References * External links LNER Encyclopedia entry for LNER class C12 (GNR class C2) C2 Railway locomotives introduced in 1898 Standard gauge steam locomotives of Great Britain Scrapped locomotives 4-4-2T locomotives {{England-steam-loco-stub Passenger loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertford Cowbridge Railway Station
Hertford Cowbridge railway station was a station on the Hertford and Welwyn Junction Railway, and was situated in Hertford, England England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b .... History The station was opened on 1 March 1858, originally being named ''Hertford Cowbridge''. It was situated on the branch from , between and a junction with the Great Eastern Railway just to the east of their Hertford station. On 1 July 1923, the station was renamed ''Hertford North'', but did not last long under that name. When the Hertford Loop Line opened on 2 June 1924, a new ' station was opened on that line, the old one being closed the same day. Route Notes References * * External linksSite of Hertford Cowbridge on a navigable 1946 O.S. map Disused railway stations in H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luton Bute Street Railway Station
Luton Bute Street railway station was the first to be built in Luton, England. It was opened by the Luton, Dunstable and Welwyn Junction Railway Company in 1858, which was an extension of the Welwyn and Hertford Railway. The track to Welwyn was completed in 1860 and taken over by the Great Northern the following year. History The station was valuable to Luton people not only for passengers but also for facilitating the London market for the town's trade in plaited straw goods. The station, and the line to Welwyn, closed in 1965.Radford, B., (1983) ''Midland Line Memories: a Pictorial History of the Midland Railway Main Line Between London (St Pancras) & Derby'' London: Bloomsbury Books Following closure to passengers in 1965, the station buildings were quickly demolished despite the line remaining open for freight until 1989–1990. The site of the station was used later as a car park for Luton railway station. Throughout the years, various local pressure groups have been su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receivership
In law, receivership is a situation in which an institution or enterprise is held by a receiver—a person "placed in the custodial responsibility for the property of others, including tangible and intangible assets and rights"—especially in cases where a company cannot meet its financial obligations and is said to be insolvent.Philip, Ken, and Kerin Kaminski''Secured Lender'', January/February 2007, Vol. 63 Issue 1, pages 30-34,36. The receivership remedy is an equitable remedy that emerged in the English chancery courts, where receivers were appointed to protect real property. Receiverships are also a remedy of last resort in litigation involving the conduct of executive agencies that fail to comply with constitutional or statutory obligations to populations that rely on those agencies for their basic human rights. Receiverships can be broadly divided into two types: *Those related to insolvency or enforcement of a security interest. *Those where either **One is Incapable of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archibald Sturrock
Archibald Sturrock (30 September 1816 – 1 January 1909) was a Scottish mechanical engineer who was born at Petruchie, Angus, Scotland. He was locomotive superintendent of the Great Northern Railway from 1850 until c. 1866, having from 1840 been Daniel Gooch's assistant on the Great Western Railway. Archibald Sturrock is often remembered for his unsuccessful experiment with steam tenders. However, his principal achievement was the opening of the Great Northern main line and the establishment of GNR's reputation for a reliable and comfortable passenger service from London to York and beyond. Career Dundee Foundry Sturrock was born in 1816. His father, who was agent to the Bank of Scotland, was shocked when Sturrock, aged 15, took an apprenticeship at the Dundee Foundry. Here he was involved with the construction of a locomotive for the Dundee and Newtyle Railway and met Daniel Gooch, who was to become Locomotive Superintendent of the Great Western Railway. Great Western Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0-4-2T
T, or t, is the twentieth letter in the modern English alphabet and the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its name in English is ''tee'' (pronounced ), plural ''tees''. It is derived from the Semitic letters taw (ת, ܬ, ت) via the Greek letter τ (tau). In English, it is most commonly used to represent the voiceless alveolar plosive, a sound it also denotes in the International Phonetic Alphabet. It is the most commonly used consonant and the second most common letter in English-language texts. History '' Taw'' was the last letter of the Western Semitic and Hebrew alphabets. The sound value of Semitic ''Taw'', Greek alphabet Tαυ (''Tau''), Old Italic and Latin T has remained fairly constant, representing in each of these; and it has also kept its original basic shape in most of these alphabets. Use in writing systems English In English, usually denotes the voiceless alveolar plosive (International Phonetic Alphabet and X-SAMPA: ), as in ''tart'', ''tee'', or ''ties'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-2-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-2-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, two powered driving wheels on one axle, and two trailing wheels on one axle. The wheel arrangement both provided more stability and enabled a larger firebox than the earlier 0-2-2 and 2-2-0 types. This configuration was introduced in 1834 on Robert Stephenson's ' Patentee locomotive' but it was later popularly named Jenny Lind, after the Jenny Lind locomotive which in turn was named after the popular singer. They were also sometimes described as Singles, although this name could be used to describe any kind of locomotive with a single pair of driving wheels. Equivalent classifications Other equivalent classifications are: *UIC classification: 1A1 (also known as German classification and Italian classification) *French classification: 111 *Turkish classification: 13 *Swiss classification: 1/3 History The 2-2-2 configuration appears to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |