|
Hartree Product
In 1927, a year after the publication of the Schrödinger equation, Hartree formulated what are now known as the Hartree equations for atoms, using the concept of ''self-consistency'' that Lindsay had introduced in his study of many electron systems in the context of Bohr theory. Hartree assumed that the nucleus together with the electrons formed a spherically symmetric field. The charge distribution of each electron was the solution of the Schrödinger equation for an electron in a potential v(r) , derived from the field. Self-consistency required that the final field, computed from the solutions, was self-consistent with the initial field, and he thus called his method the self-consistent field method. History In order to solve the equation of an electron in a spherical potential, Hartree first introduced atomic units to eliminate physical constants. Then he converted the Laplacian from Cartesian to spherical coordinates to show that the solution was a product of a ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schrödinger Equation
The Schrödinger equation is a linear partial differential equation that governs the wave function of a quantum-mechanical system. It is a key result in quantum mechanics, and its discovery was a significant landmark in the development of the subject. The equation is named after Erwin Schrödinger, who postulated the equation in 1925, and published it in 1926, forming the basis for the work that resulted in his Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933. Conceptually, the Schrödinger equation is the quantum counterpart of Newton's second law in classical mechanics. Given a set of known initial conditions, Newton's second law makes a mathematical prediction as to what path a given physical system will take over time. The Schrödinger equation gives the evolution over time of a wave function, the quantum-mechanical characterization of an isolated physical system. The equation can be derived from the fact that the time-evolution operator must be unitary, and must therefore be generated by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slater Determinant
In quantum mechanics, a Slater determinant is an expression that describes the wave function of a multi-fermionic system. It satisfies anti-symmetry requirements, and consequently the Pauli principle, by changing sign upon exchange of two electrons (or other fermions).Molecular Quantum Mechanics Parts I and II: An Introduction to QUANTUM CHEMISTRY (Volume 1), P. W. Atkins, Oxford University Press, 1977, . Only a small subset of all possible fermionic wave functions can be written as a single Slater determinant, but those form an important and useful subset because of their simplicity. The Slater determinant arises from the consideration of a wave function for a collection of electrons, each with a wave function known as the spin-orbital \chi(\mathbf), where \mathbf denotes the position and spin of a single electron. A Slater determinant containing two electrons with the same spin orbital would correspond to a wave function that is zero everywhere. The Slater determinant is named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Chemistry
Quantum chemistry, also called molecular quantum mechanics, is a branch of physical chemistry focused on the application of quantum mechanics to chemical systems, particularly towards the quantum-mechanical calculation of electronic contributions to physical and chemical properties of Molecule, molecules, Material, materials, and solutions at the atomic level. These calculations include systematically applied approximations intended to make calculations computationally feasible while still capturing as much information about important contributions to the computed Wave function, wave functions as well as to observable properties such as structures, spectra, and thermodynamic properties. Quantum chemistry is also concerned with the computation of quantum effects on molecular dynamics and chemical kinetics. Chemists rely heavily on spectroscopy through which information regarding the Quantization (physics), quantization of energy on a molecular scale can be obtained. Common metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Structure Methods
Electronic may refer to: *Electronics, the science of how to control electric energy in semiconductor * ''Electronics'' (magazine), a defunct American trade journal *Electronic storage, the storage of data using an electronic device *Electronic commerce or e-commerce, the trading in products or services using computer networks, such as the Internet *Electronic publishing or e-publishing, the digital publication of books and magazines using computer networks, such as the Internet *Electronic engineering, an electrical engineering discipline Entertainment *Electronic (band), an English alternative dance band ** ''Electronic'' (album), the self-titled debut album by British band Electronic *Electronic music, a music genre *Electronic musical instrument *Electronic game, a game that employs electronics See also *Electronica, an electronic music genre *Consumer electronics Consumer electronics or home electronics are electronic (analog or digital) equipment intended for everyday ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Differential Equations
In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation which imposes relations between the various partial derivatives of a multivariable function. The function is often thought of as an "unknown" to be solved for, similarly to how is thought of as an unknown number to be solved for in an algebraic equation like . However, it is usually impossible to write down explicit formulas for solutions of partial differential equations. There is, correspondingly, a vast amount of modern mathematical and scientific research on methods to numerically approximate solutions of certain partial differential equations using computers. Partial differential equations also occupy a large sector of pure mathematical research, in which the usual questions are, broadly speaking, on the identification of general qualitative features of solutions of various partial differential equations, such as existence, uniqueness, regularity, and stability. Among the many open questions are the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John C
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Fock
Vladimir Aleksandrovich Fock (or Fok; russian: Влади́мир Алекса́ндрович Фок) (December 22, 1898 – December 27, 1974) was a Soviet Union, Soviet physicist, who did foundational work on quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics. Biography He was born in St. Petersburg, Russia. In 1922 he graduated from Saint Petersburg State University, Petrograd University, then continued postgraduate studies there. He became a professor there in 1932. In 1919–1923 and 1928–1941 he collaborated with the Vavilov State Optical Institute, in 1924–1936 with the Leningrad Institute of Physics and Technology, in 1934–1941 and 1944–1953 with the Lebedev Physical Institute. Scientific work His primary scientific contribution lies in the development of quantum physics and the theory of gravitation, although he also contributed significantly to the fields of mechanics, theoretical optics, physics of continuous media. In 1926, he de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrange Multipliers
In mathematical optimization, the method of Lagrange multipliers is a strategy for finding the local maxima and minima of a function subject to equality constraints (i.e., subject to the condition that one or more equations have to be satisfied exactly by the chosen values of the variables). It is named after the mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange. The basic idea is to convert a constrained problem into a form such that the derivative test of an unconstrained problem can still be applied. The relationship between the gradient of the function and gradients of the constraints rather naturally leads to a reformulation of the original problem, known as the Lagrangian function. The method can be summarized as follows: in order to find the maximum or minimum of a function f(x) subjected to the equality constraint g(x) = 0, form the Lagrangian function :\mathcal(x, \lambda) = f(x) + \lambda g(x) and find the stationary points of \mathcal considered as a function of x and the Lagrange mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Field
In physics and probability theory, Mean-field theory (MFT) or Self-consistent field theory studies the behavior of high-dimensional random (stochastic) models by studying a simpler model that approximates the original by averaging over degrees of freedom (the number of values in the final calculation of a statistic that are free to vary). Such models consider many individual components that interact with each other. The main idea of MFT is to replace all interactions to any one body with an average or effective interaction, sometimes called a ''molecular field''. This reduces any many-body problem into an effective one-body problem. The ease of solving MFT problems means that some insight into the behavior of the system can be obtained at a lower computational cost. MFT has since been applied to a wide range of fields outside of physics, including statistical inference, graphical models, neuroscience, artificial intelligence, epidemic models, queueing theory, computer-network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Born–von Karman Boundary Condition
Born–von Karman boundary conditions are periodic boundary conditions which impose the restriction that a wave function must be periodic on a certain Bravais lattice. Named after Max Born and Theodore von Kármán, this condition is often applied in solid state physics to model an ideal crystal. Born and von Karman published a series of articles in 1912 and 1913 that presented one of the first theories of specific heat of solids based on the crystalline hypothesis and included these boundary conditions. The condition can be stated as : \psi(\mathbf+N_i \mathbf_i)=\psi(\mathbf), \, where ''i'' runs over the dimensions of the Bravais lattice, the a''i'' are the primitive vectors of the lattice, and the ''Ni'' are integers (assuming the lattice has ''N'' cells where ''N=N1N2N3''). This definition can be used to show that : \psi(\mathbf+\mathbf)=\psi(\mathbf) for any lattice translation vector T such that: : \mathbf = \sum_i N_i \mathbf_i. Note, however, the Born–v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermions
In particle physics, a fermion is a particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics. Generally, it has a half-odd-integer spin: spin , spin , etc. In addition, these particles obey the Pauli exclusion principle. Fermions include all quarks and leptons and all composite particles made of an odd number of these, such as all baryons and many atoms and nuclei. Fermions differ from bosons, which obey Bose–Einstein statistics. Some fermions are elementary particles (such as electrons), and some are composite particles (such as protons). For example, according to the spin-statistics theorem in relativistic quantum field theory, particles with integer spin are bosons. In contrast, particles with half-integer spin are fermions. In addition to the spin characteristic, fermions have another specific property: they possess conserved baryon or lepton quantum numbers. Therefore, what is usually referred to as the spin-statistics relation is, in fact, a spin statistics-quantum number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
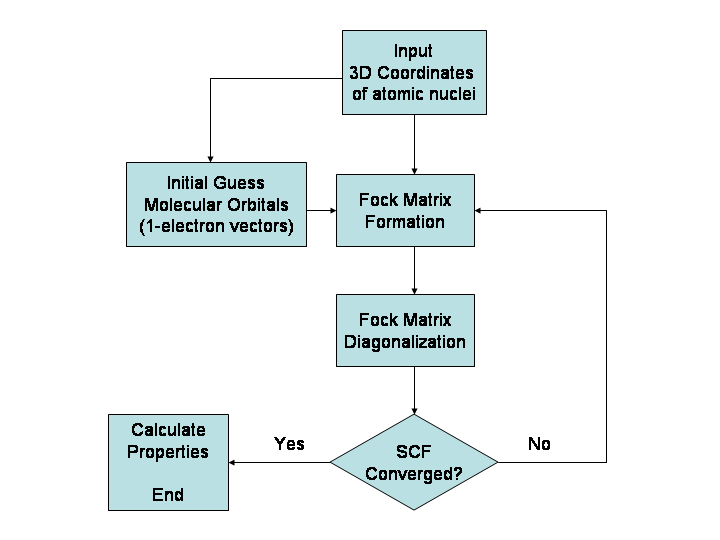
Hartree–Fock Method
In computational physics and chemistry, the Hartree–Fock (HF) method is a method of approximation for the determination of the wave function and the energy of a quantum many-body system in a stationary state. The Hartree–Fock method often assumes that the exact ''N''-body wave function of the system can be approximated by a single Slater determinant (in the case where the particles are fermions) or by a single permanent (in the case of bosons) of ''N'' spin-orbitals. By invoking the variational method, one can derive a set of ''N''-coupled equations for the ''N'' spin orbitals. A solution of these equations yields the Hartree–Fock wave function and energy of the system. Especially in the older literature, the Hartree–Fock method is also called the self-consistent field method (SCF). In deriving what is now called the Hartree equation as an approximate solution of the Schrödinger equation, Hartree required the final field as computed from the charge distribution to be "s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)