|
Han Xin
Han Xin (; 231/230–196 BC) was a Chinese military general and politician who served Liu Bang during the Chu–Han Contention and contributed greatly to the founding of the Han dynasty. Han Xin was named as one of the "Three Heroes of the early Han dynasty" ( zh, script=Hant, 漢初三傑), along with Zhang Liang and Xiao He. Han Xin is best remembered as a brilliant military leader for the strategies and tactics he employed in warfare, some of which became the origins of certain Chinese idioms, he was undefeated in battle and for his accomplishments he was considered the "God of War". In recognition of Han Xin's contributions, Liu Bang conferred the titles of " King of Qi" on him in 203 BC and "King of Chu" in the following year. However, Liu Bang feared Han Xin's growing influence and gradually reduced his authority, demoting him to "Marquis of Huaiyin" in late 202 BC. In 196 BC, Han Xin was accused of participating in a rebellion and lured into a trap and executed on Empre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han (state)
Han (, Old Chinese: ''*'') was an ancient Chinese state during the Warring States period of ancient China. It is conventionally romanized by scholars as Hann to distinguish it from the later Han dynasty (). It was located in central China (modern-day Shanxi and Henan) in a region south and east of Luoyang, the capital of the Eastern Zhou. It was ruled by a royal family who were former ministers in the state of Jin that had slowly gained power from the Jin royal family until they were able to divide Jin into the three new states of Han, Wei and Zhao with the assistance of two other ministerial families. The state of Han was small and located in a mountainous and unprofitable region. Its territory directly blocked the passage of the state of Qin into the North China Plain.. Although Han had attempted to reform its governance (notably under Chancellor and " Legalist" Shen Buhai who improved state administration and strengthened its military ability) these reforms were not e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chu Kingdom (Han Dynasty)
Chu Kingdom ( zh, 楚國) was a kingdom of China's Han dynasty, located in what is now northern Jiangsu and Anhui provinces. History During the Chu–Han Contention period, the Chu region centered in Pengcheng was the base of the Western Chu regime led by Xiang Yu. After Xiang's death, the Emperor Gaozu of Han first granted Chu to his general Han Xin. After Han was accused of plotting rebellion and executed, his territories was split into two parts. Liu Jiao, brother of the emperor, gained the title "King of Chu" and ruled over the land west of the Huai River, while the rest of Han Xin's territories eventually became the Wu Kingdom. Jiao's kingdom consisted of the commanderies of Xue, Pengcheng and Donghai. In 187 BC, Xue was split off to form the Lu Kingdom (魯國) for Zhang Yan (張偃), a grandson of the Empress Dowager Lü. The commandery was returned to Chu when the Lü clan was removed from power. In 154 BC, Chu under the King Liu Wu joined the Rebellion of the Seven Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
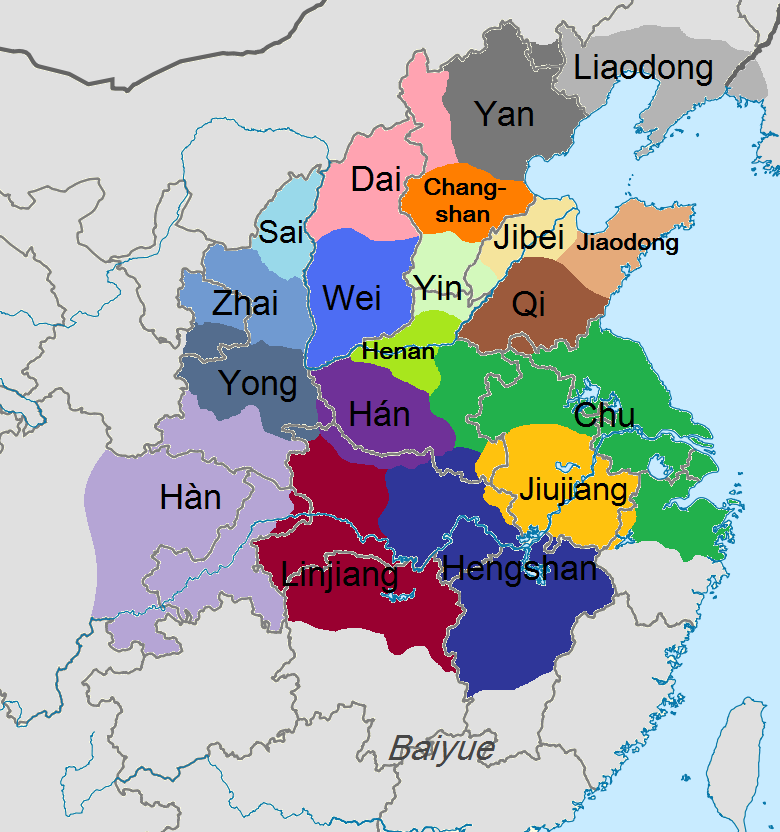
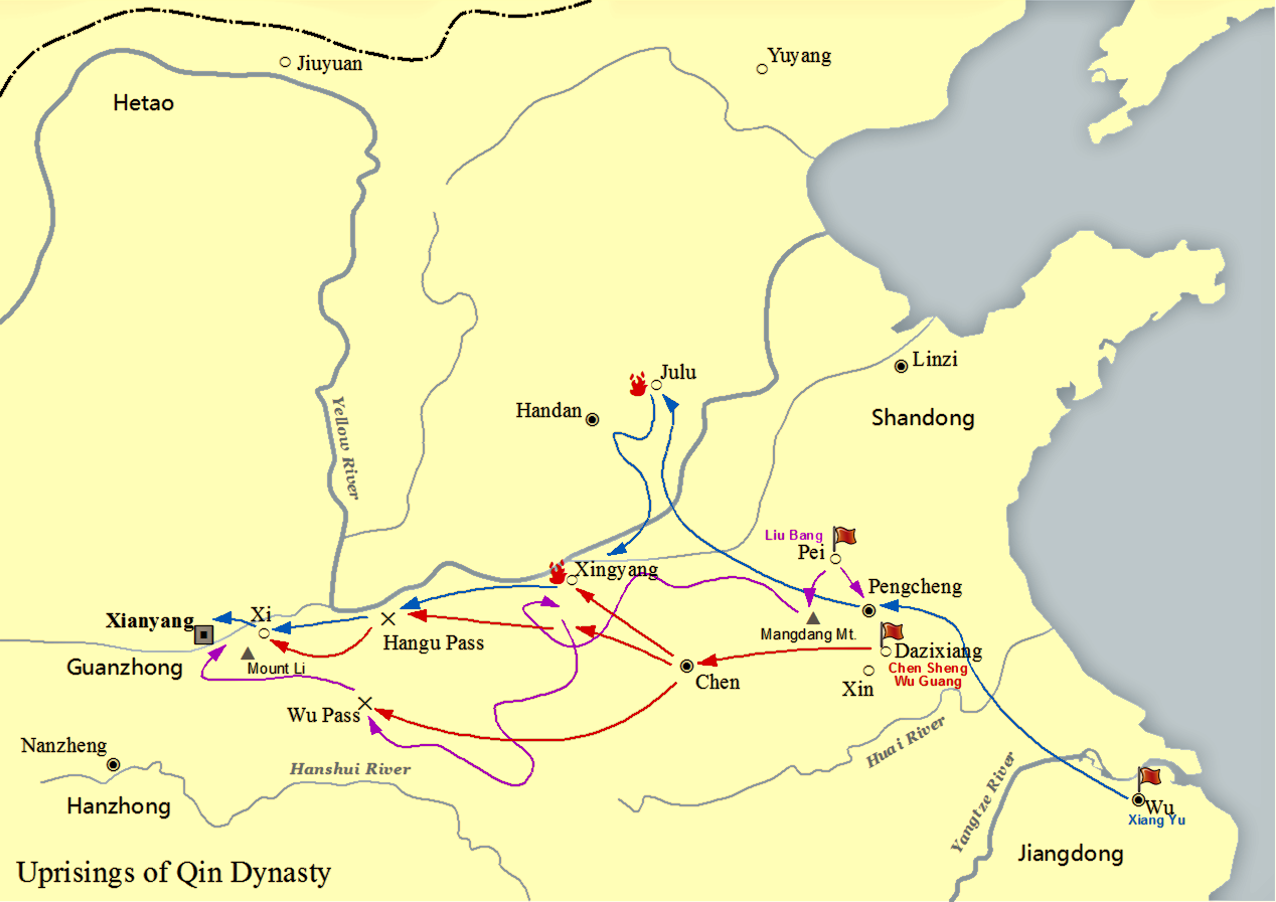
Three Qins
The Three Qins () refer to three of the Eighteen Kingdoms, the short-lived power-sharing arrangement formed in 206 BC after the collapse of the Qin Dynasty. The three kingdoms were located in Guanzhong Plain (in present-day central Shaanxi), the heartland of the Qin Empire. Background In late 208 BC the rebel king of Chu, King Huai II, promised that whoever invaded Guanzhong first would rule the region. In late 207 the Chu rebel Liu Bang became the first anti-Qin rebel to enter the Guanzhong region, capturing the Qin capital Xianyang and receiving the surrender of Ziying, the last king of Qin. He also won the support of the people of Guanzhong by abolishing the harsh Qin laws and by forbidding his troops from killing and robbing the locals. For these reasons, Liu Bang had a strong claim to Guanzhong, which was grain-rich, populous, easily defensible and ideal for expansion into China's Central Plain. However, the Chu rebel Xiang Yu, the most powerful rebel warlord at the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanzhong
Hanzhong (; abbreviation: Han) is a prefecture-level city in the southwest of Shaanxi province, China, bordering the provinces of Sichuan to the south and Gansu to the west. The founder of the Han dynasty, Liu Bang, was once enfeoffed as the king of the Hanzhong region after overthrowing the Qin dynasty. During the Chu-Han contention, Liu Bang shortened his title to the King of Han (), and later used it as the name of his imperial dynasty. In this way, Hanzhong was responsible for the naming of the Han dynasty, which was later hailed as the first golden age in imperial Chinese history and lends its name to the principal ethnic group in China. Hanzhong is located at the modern headwater of the Han River, the largest tributary of the Yangtze River. Hanzhong city covers and is centered around the Hantai District. The prefecture-level city consists of two urban district and nine rural counties. As of the 2020 census, its population was 3,211,462, of whom 1,084,448 lived in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chu (state)
Chu, or Ch'u in Wade–Giles romanization, (, Hanyu Pinyin: Chǔ, Old Chinese: ''*s-r̥aʔ'') was a Zhou dynasty vassal state. Their first ruler was King Wu of Chu in the early 8th century BCE. Chu was located in the south of the Zhou heartland and lasted during the Spring and Autumn period. At the end of the Warring States period it was destroyed by the Qin in 223 BCE during the Qin's wars of unification. Also known as Jing () and Jingchu (), Chu included most of the present-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan, along with parts of Chongqing, Guizhou, Henan, Anhui, Jiangxi, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai. For more than 400 years, the Chu capital Danyang was located at the junction of the Dan and Xi Rivers near present-day Xichuan County, Henan, but later moved to Ying. The house of Chu originally bore the clan name Nai ( OC: /*rneːlʔ/) which was later written as Mi ( OC: /*meʔ/). They also bore the lineage name Yan ( OC: /*qlamʔ/, /*qʰɯːm/) which would later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the Sichuan Basin and the easternmost part of the Tibetan Plateau between the Jinsha River on the west, the Daba Mountains in the north and the Yungui Plateau to the south. Sichuan's capital city is Chengdu. The population of Sichuan stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai to the northwest, Gansu to the north, Shaanxi to the northeast, Chongqing to the east, Guizhou to the southeast, Yunnan to the south, and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the west. In antiquity, Sichuan was the home of the ancient states of Ba and Shu. Their conquest by Qin strengthened it and paved the way for Qin Shi Huang's unification of China under the Qin dynasty. During the Three Kingdoms era, Liu Bei's state of Shu was based in Sichuan. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighteen Kingdoms
The historiographical term "Eighteen Kingdoms" ( zh, t=十八國), also translated to as "Eighteen States", refers to the eighteen ''fengjian'' states in China created by military leader Xiang Yu in 206 BCE, after the collapse of the Qin dynasty.林达礼,中华五千年大事记, 台南大孚书局, 1982, p. 56 The establishment and abolishment of the Eighteen Kingdoms marked the beginning and end of a turbulent interregnum known as the Chu-Han Contention. The details of the feudal division are as follows: The Eighteen Kingdoms were short-lived: almost immediately rebellion broke out in Qi, after which Tian Rong conquered Jiaodong and Jibei, reuniting the old Qi state. Meanwhile, Xiang Yu had Emperor Yi of Chu and King Han Cheng of Hán killed. Thereafter, Liu Bang of Hàn conquered the lands of the Three Qins, thereby formally starting the Chu–Han Contention. Following many battles and changing alliances, Hàn defeated Chu and subdued all other kingdoms, where Liu Bang a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiahou Ying
Xiahou Ying (died 172 BC), posthumously known as Marquis Wen of Ruyin, was a Chinese official who served as Minister Coachman () during the early Han dynasty. He served under Liu Bang (Emperor Gaozu), the founding emperor of the Han dynasty, and fought on Liu Bang's side during the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC) against Liu Bang's rival, Xiang Yu. He is also sometimes referred to as the Duke of Teng in historical records. Early life Xiahou Ying was from Pei County in present-day Jiangsu. He started his career as a minor officer in charge of horses, chariots and carriages in the county office. Whenever he passed by Sishui Village (), one of the villages in Pei County, he would visit his friend Liu Bang, a low-ranking officer in the village, and spend a long time chatting with him. On one occasion, Liu Bang played a prank on Xiahou Ying and caused him to be injured. The county magistrate found out about the incident and ordered an investigation. Under the law of the Qin d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Bang
Emperor Gaozu of Han (256 – 1 June 195 BC), born Liu Bang () with courtesy name Ji (季), was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning in 202–195 BC. His temple name was "Taizu" while his posthumous name was Emperor Gao, or Gaodi; "Gaozu of Han", derived from the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', is the common way of referring to this sovereign even though he was not accorded the temple name "Gaozu", which literally means "High Founder". Liu Bang was one of the few dynasty founders in Chinese history who was born into a peasant family. Prior to coming to power, Liu Bang initially served for the Qin dynasty as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. With the First Emperor's death and the Qin Empire's subsequent political chaos, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became an anti-Qin rebel leader. He won the race against fellow rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin Dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first Dynasties in Chinese history, dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin (state), Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), the Qin dynasty arose as a fief of the Western Zhou and endured for over five centuries until 221 BCE when it founded its brief empire, which lasted only until 206 BCE. It often causes confusion that the ruling family of the Qin kingdom (what is conventionally called a "dynasty") ruled for over five centuries, while the "Qin Dynasty," the conventional name for the first Chinese empire, comprises the last fourteen years of Qin's existence. The divide between these two periods occurred in 221 BCE when King Zheng of Qin declared himself the Qin Shi Huang, First Emperor of Qin, though he had already been king of Qin since 246 BCE. Qin was a minor power for the early centuries of its existence. The streng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiang Liang
Xiang Liang (died 208 BC) was a military leader who led a rebellion against the Qin dynasty. Early life Xiang Liang was from Xiaxiang (下相; present-day Suqian, Jiangsu) and was a descendant of a family who served the Chu state in the Warring States period. Xiang Liang's father, , was a famous general who led the Chu army to resist the invading Qin forces led by Wang Jian, and was killed in action in 223 BC when Qin annexed Chu. After the fall of Chu, Xiang Liang and his brothers became commoners and lived under Qin rule for years. When Xiang Liang's elder brother Xiang Chao () died, Xiang Liang took Xiang Chao's son, Xiang Yu, under his care. Xiang Liang doted on Xiang Yu and had his nephew instructed in scholarly arts and swordsmanship, but Xiang Yu did not master what he was taught and Xiang Liang was very displeased with him.Sima Qian. ''Records of the Grand Historian'', Volume 7, Biography of Xiang Yu. When Xiang Yu expressed interest in military strategy, Xiang Liang t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
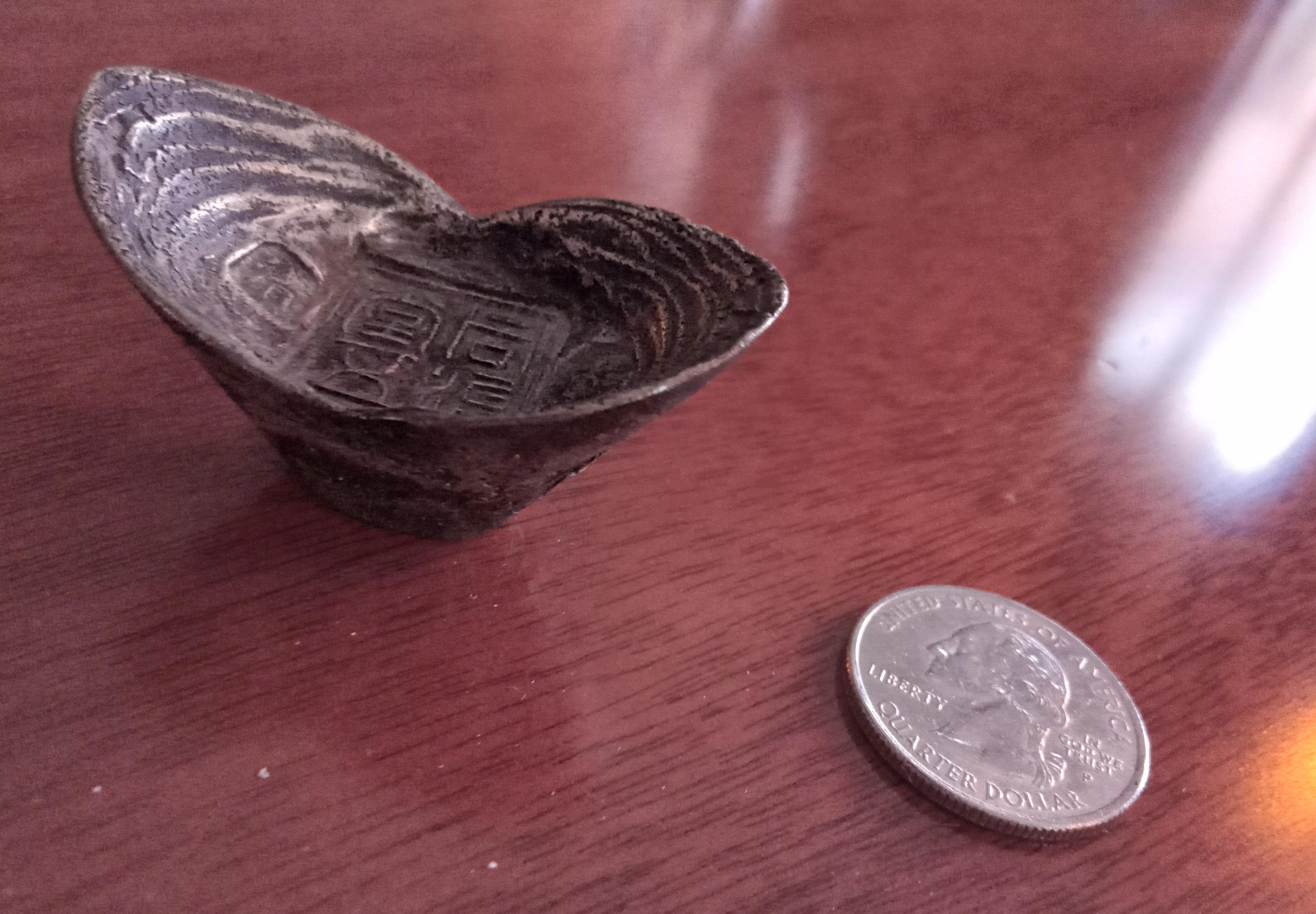
Tael
Tael (),"Tael" entry at the . also known as the tahil and by , can refer to any one of several used in and |
.jpg)