|
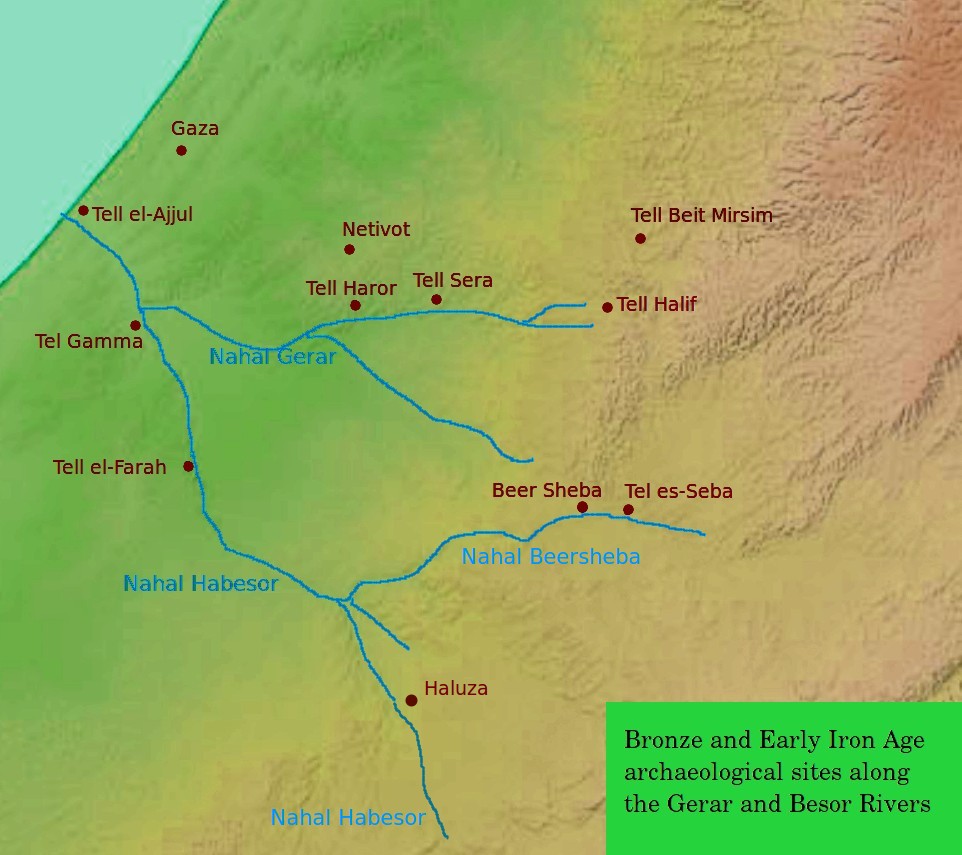
Haluza
The ancient city of Halasa or Chellous ( gr, Χελλοὺς), Elusa () in the Byzantine period, was a city in the Negev near present-day Kibbutz Mash'abei Sadeh that was once part of the Nabataean Incense Route. It lay on the route from Petra to Gaza.Carta's Official Guide to Israel, 1983. Today it is known as Haluza ( he, חלוצה), and during periods of Arab habitation it was known as al-Khalūṣ ( ar, الخلوص; Early Muslim period) and Al-Khalasa (; 20th century). In the 5th century it was surrounded by vineyards and was famous for its wines. Due to its historic importance, UNESCO declared Haluza a World Heritage Site along with Mamshit, Avdat and Shivta. Name in ancient sources The city is called 'Chellous' (Χελλοὺς) in the Greek text of Judith, i, 9 (seJdt 1:9in NABRE), a work probably dating to the 1st century BCE. It is also mentioned in the 2nd century CE by Ptolemy, Peutinger's Table, Stephanus Byzantius (fl. 6th century; as being formerly in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shivta
Shivta ( he, שבטה), originally Sobata ( gr, Σόβατα) or Subeita ( ar, شبطا), is an ancient city in the Negev Desert of Israel located 43 kilometers southwest of Beersheba. Shivta was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in June 2005, as part of the Incense Route and the Desert Cities of the Negev, together with Haluza/Elusa, Avdat and Mamshit/Mampsis. The name Shivta is a modern Hebraization, given by the Negev Naming Committee in the early 1950s. The Greek name Sobata was mentioned in the Nessana papyri. History Long considered a classical Nabataean town on the ancient spice route, archaeologists are now considering the possibility that Shivta was a Byzantine agricultural colony and a way station for pilgrims en route to the Saint Catherine's Monastery in the Sinai Peninsula. A few Roman-period ruins have been discovered, but most of the archaeological findings date to the Byzantine period. Shivta's water supply was based on surface runoff collected in large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamshit
Mampsis (Medieval Greek: Μάμψις) or Memphis (Ancient Greek: Μέμφις), today Mamshit ( he, ממשית), Arabic Kurnub, is a former Nabataean caravan stop and Byzantine city. In the Nabataean period, Mampsis was an important station on the Incense Road, connecting Southern Arabia through Edom, the Arabah and Ma'ale Akrabim, to the Mediterranean ports, as well as to Jerusalem via Beersheba and Hebron. The city covers and is the smallest but best restored ancient city in the Negev Desert. The once-luxurious houses feature unusual architecture not found in any other Nabataean city. The reconstructed city gives the visitor a sense of how Mampsis once looked. Entire streets have survived intact, and there are also large groups of Nabataean buildings with open rooms, courtyards, and terraces. The stones are carefully chiseled and the arches that support the ceiling are remarkably well constructed. The Incense Route - Desert Cities in the Negev, including Mampsis, Haluza, Avda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Khalasa
Al-Khalasa ( ar, الخلصة, al-Khalasah; he, אל-ח'אלצה, ''al-Khalatsah''), was a Palestinian village, located 23 kilometers southwest of the town of Beersheba. The village stood at the site of an ancient town from the Nabatean, Roman, Byzantine, and the beginning of the Early Muslim period. The ancient city, founded by the Nabateans, is known from Greek and Roman sources as "Halasa" or "Chellous", and later as "Elusa", one of the Byzantine administrative centers in the Negev Desert. Still important in the century of the Muslim conquest, it was deserted not long after. The site was repopulated by Bedouin in the early twentieth century, after western archaeologists took an interest in it. In October 1948, it was captured by Israel during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. The population of al-Khalasa is unknown, but all of the inhabitants were Muslims, from the al-Azizma tribe. History Nabataean, Roman, and Byzantine periods The ancient site was founded by the Nabateans, proba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' ( grc, Ναβατηνή, translit=Nabatēnḗ) to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BCE,Taylor, Jane (2001). ''Petra and the Lost Kingdom of the Nabataeans''. London: I.B.Tauris. pp. 14, 17, 30, 31. . Retrieved 8 July 2016. with their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by contemporary Greco-Roman accounts, the Nabataeans were annexed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southern end is the Gulf of Aqaba and the resort city and port of Eilat. It contains several development towns, including Dimona, Arad and Mitzpe Ramon, as well as a number of small Bedouin towns, including Rahat and Tel Sheva and Lakiya. There are also several kibbutzim, including Revivim and Sde Boker; the latter became the home of Israel's first Prime Minister, David Ben-Gurion, after his retirement from politics. Although historically part of a separate region (known during the Roman period as Arabia Petraea), the Negev was added to the proposed area of Mandatory Palestine, of which large parts later became Israel, on 10 July 1922, having been conceded by British representative St John Philby "in Trans-Jordan's name". Despite this, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataeans
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic language, Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabian Peninsula, Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Petra, Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' ( grc, Ναβατηνή, translit=Nabatēnḗ) to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BCE,Taylor, Jane (2001). ''Petra and the Lost Kingdom of the Nabataeans''. London: I.B.Tauris. pp. 14, 17, 30, 31. . Retrieved 8 July 2016. with Nabataean Kingdom, their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avdat
Avdat ( he, עבדת, ar, عبدة, ''Abdah''), also known as Abdah and Ovdat and Obodat, is a site of a ruined Nabataean city in the Negev desert in southern Israel. It was the most important city on the Incense Route after Petra, between the 1st century BCE and the 7th century CE. It was founded in the 3rd century BCE, and inhabited by Nabataeans, Romans, Byzantines, and during the early Islamic period.Yedioth Ahronoth (6 October 2009)"Avdat National Park vandalized" Retrieved on April 3, 2012. Avdat was a seasonal camping ground for Nabataean caravans travelling along the early Petra–Gaza road (Darb es-Sultan) in the 3rd – late 2nd century BCE. The city's original name was changed to Avdat in honor of Nabataean King Obodas I, who, according to tradition, was revered as a deity and was buried there. History Before the end of the 1st century BCE a temple platform (the acropolis) was created along the western edge of the plateau. Recent excavations have shown that the town c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incense Route
The Incense Trade Route was an ancient network of major land and sea trading routes linking the Mediterranean world with eastern and southern sources of incense, spices and other luxury goods, stretching from Mediterranean ports across the Levant and Egypt through Northeastern Africa and Arabia to India and beyond. These routes collectively served as channels for the trading of goods such as Arabian frankincense and myrrh; Indian spices, precious stones, pearls, ebony, silk and fine textiles; and from the Horn of Africa, rare woods, feathers, animal skins, Somali frankincense, gold, and slaves. The incense land trade from South Arabia to the Mediterranean flourished between roughly the 3rd century BC and the 2nd century AD. Early history The Egyptians had traded in the Red Sea, importing spices, gold and exotic wood from the "Land of Punt" and from Arabia.Rawlinson 2001: 11–12 Indian goods were brought in Arabian and Indian vessels to Aden. Rawlinson identifies the long-debat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mashabei Sadeh
Mashabei Sadeh ( he, מַשְׁאַבֵּי שָׂדֶה) is a kibbutz in southern Israel. Located in the Negev desert, it falls under the jurisdiction of Ramat HaNegev Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The kibbutz was established in 1947 in the Halutza dunes, and was originally known as Mashabim (Hebrew: משאבים, lit. ''Resources''). During the 1948 Arab-Israeli War the kibbutz was attacked by the Egyptian army, but was retained by Israel. After the war ended it relocated to its present site. It was renamed Mashabei Sadeh in honour of Palmach leader Yitzhak Sadeh who died in 1952. File:חלוצה - הקמת ישוב חדש בנגב-JNF012130.jpeg, Halutza 1947 File:משאבים - מראה כללי-JNF001053.jpeg, Halutza 1947 Economy Apart from agriculture (field crops, poultry and dairy), the kibbutz breeds shrimp using special aquaculture techniques. It is also the only kibbutz in Israel to breed the Australian fish Barramundi The barramundi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern District (Israel)
The Southern District ( he, מחוז הדרום, ''Meḥoz HaDarom''; ar, لواء الجنوب) is one of Israel's six administrative districts, the largest in terms of land area but the most sparsely populated. It covers most of the Negev desert, as well as the Arava valley. The population of the Southern District is 1,086,240 and its area is 14,185 km2. Its population is 79.66% Jewish and 12.72% Arab (mostly Muslim), with 7.62% of other origins. The district capital is Beersheba, while the largest city is Ashdod. Beersheba's dormitory towns of Omer, Meitar, and Lehavim are affluent on an Israel scale, while the development towns of Dimona, Sderot, Netivot, Ofakim, and Yeruham and the seven Bedouin cities are lower on the socio-economic scale. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Judith
The Book of Judith is a deuterocanonical book, included in the Septuagint and the Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Christian Old Testament of the Bible, but excluded from the Hebrew canon and assigned by Protestants to the apocrypha. It tells of a Jewish widow, Judith, who uses her beauty and charm to destroy an Assyrian general and save Israel from oppression. The surviving Greek manuscripts contain several historical anachronisms, which is why some Protestant scholars now consider the book non-historical: a parable, a theological novel, or perhaps the first historical novel. The name Judith (), meaning "Praised" or "Jewess", is the feminine form of Judah. Historical context Original language It is not clear whether the Book of Judith was originally written in Hebrew or in Greek. The oldest existing version is in the Septuagint, and might either be a translation from Hebrew or composed in Greek. Details of vocabulary and phrasing point to a Greek text written in a language m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NABRE
The New American Bible Revised Edition (NABRE) is an English-language Catholic translation of the Bible, the first major update in 20 years to the New American Bible (NAB), which was translated by members of the Catholic Biblical Association and originally published in 1970. Released on March 9, 2011, the NABRE consists of the 1986 revision of the NAB New Testament with a fully revised Old Testament approved by the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops in 2010. Approved for private use and study by Catholics, the NABRE has not received approval for Catholic liturgical use. Although the revised Lectionary based on the original New American Bible is still the sole translation approved for use at Mass in the dioceses of the United States, the NABRE New Testament is currently being revised so that American Catholics can read the same Bible translation in personal study and devotion that they hear in Mass. The use of NABRE has received strong criticism from conservative Cathol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)