|
HMS Prize (Q Ship)
HMS ''Prize '' was a schooner converted to a Q ship during the First World War and commanded by Lieutenant William Sanders of the Royal Naval Reserve. Originally a German vessel called ''Else'', she was captured by the Royal Navy in the first days of the First World War. In April 1917 she was commissioned into the Royal Navy as a Q ship with the name HMS ''First Prize'', later to be shortened to HMS ''Prize''. During her first patrol, ''Prize'' was involved in an engagement with a U-boat, for which Sanders received the Victoria Cross while the rest of the crew were also awarded various medals. ''Prize'' was destroyed by a torpedo on 13 August 1917, with all crew lost. History A steel-hulled three-masted schooner, ''Else'' was built in Groningen, Holland, by the firm E. V. Smit & Zoon in 1901 for a German ship owner. Displacing 277 tons, she had an overall length of with a beam of . Her draught was . Her home port was Leer, near Emden. On 4 August 1914, the day on which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q Ship
Q-ships, also known as Q-boats, decoy vessels, special service ships, or mystery ships, were heavily armed merchant ships with concealed weaponry, designed to lure submarines into making surface attacks. This gave Q-ships the chance to open fire and sink them. The use of Q-ships contributed to the abandonment of cruiser rules restricting attacks on unarmed merchant ships and to the shift to unrestricted submarine warfare in the 20th century. They were used by the British Royal Navy and the German ''Kaiserliche Marine'' during the First World War and by the Royal Navy, the ''Kriegsmarine'', and the United States Navy during the Second World War (1939–45). Etymology Short for Queenstown in Ireland, as Haulbowline Dockyard in Cork Harbour was responsible for the conversion of many mercantile steamers to armed decoy ships in World War One, although the majority appear to have been converted in larger navy yards such as Devonport. Early uses of the concept In the 1670s, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship's hull is the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull (keel). The draught of the vessel is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if deployed. Draft determines the minimum depth of water a ship or boat can safely navigate. The related term air draft is the maximum height of any part of the vessel above the water. The more heavily a vessel is loaded, the deeper it sinks into the water, and the greater its draft. After construction, the shipyard creates a table showing how much water the vessel displaces based on its draft and the density of the water (salt or fresh). The draft can also be used to determine the weight of cargo on board by calculating the total displacement of water, accounting for the content of the ship's bunkers, and using Archimedes' principle. The closely related term "trim" is defined as the difference between the forward and aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
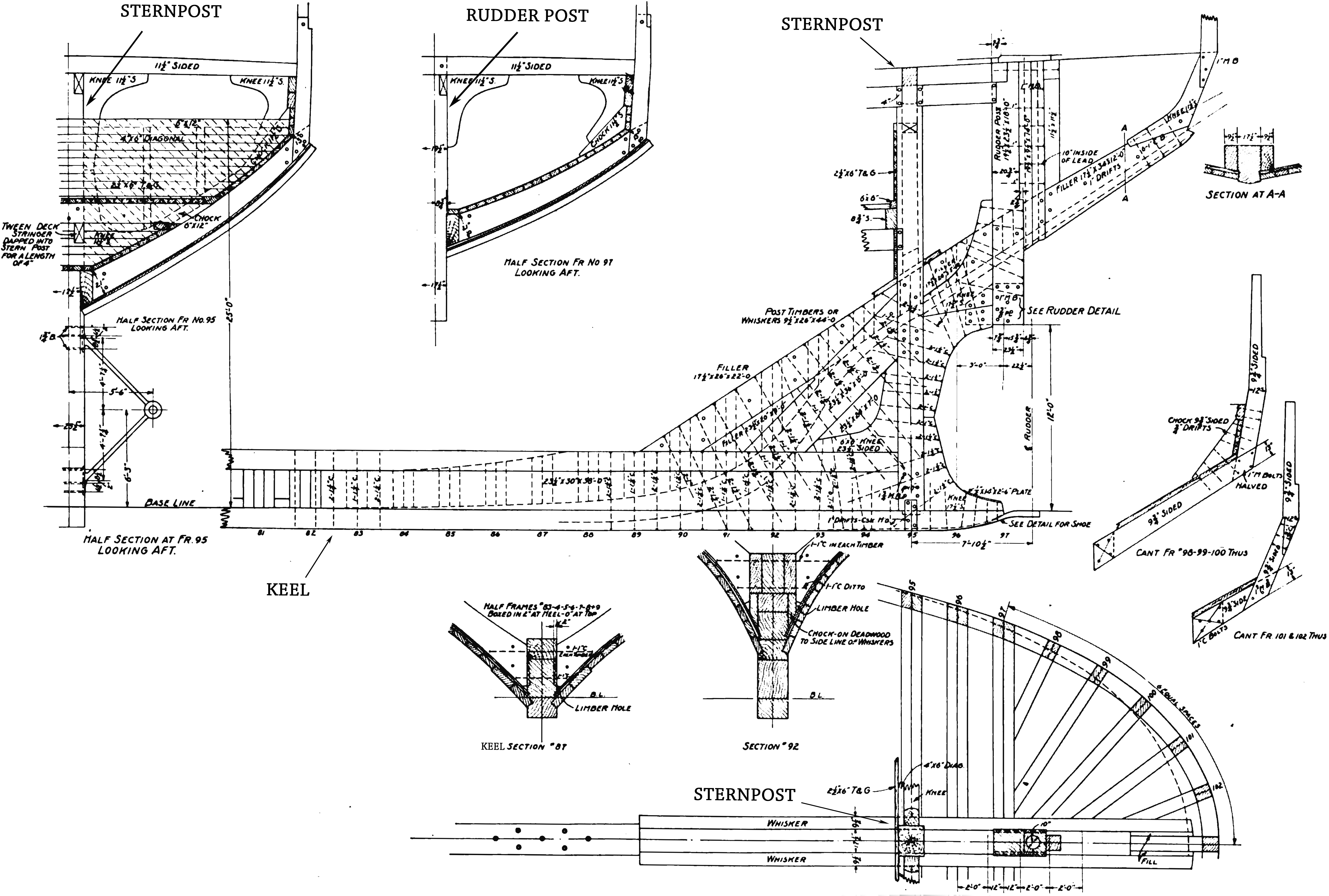
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bow (ship)
The bow () is the forward part of the hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern. Prow may be used as a synonym for bow or it may mean the forward-most part of the bow above the waterline. Function A ship's bow should be designed to enable the hull to pass efficiently through the water. Bow shapes vary according to the speed of the boat, the seas or waterways being navigated, and the vessel's function. Where sea conditions are likely to promote pitching, it is useful if the bow provides reserve buoyancy; a flared bow (a raked stem with flared topsides) is ideal to reduce the amount of water shipped over the bow. Ideally, the bow should reduce the resistance and should be tall enough to prevent water from regularly washing over the top of it. Large commercial barges on inland waterways rarely meet big waves and may have remarkably little freeboard at the bow, whereas fast military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WE Sanders
In Modern English, ''we'' is a plural, first-person pronoun. Morphology In Standard Modern English, ''we'' has six distinct shapes for five word forms: * ''we'': the nominative (subjective) form * ''us'' and ': the accusative (objective; also called the ' oblique'.) form * ''our:'' the dependent genitive (possessive) form *''ours:'' the independent genitive (possessive) form * ''ourselves'': the reflexive form There is also a distinct determiner ''we'' as in ''we humans aren't perfect'', which some people consider to be just an extended use of the pronoun. History ''We'' has been part of English since Old English, having come from Proto-Germanic *''wejes'', from PIE *''we''-. Similarly, ''us'' was used in Old English as the accusative and dative plural of ''we'', from PIE *''nes''-. The following table shows the old English first-person plural and dual pronouns: By late Middle English the dual form was lost and the dative and accusative had merged. The ''ours'' genitiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swansea
Swansea (; cy, Abertawe ) is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Swansea ( cy, links=no, Dinas a Sir Abertawe). The city is the twenty-fifth largest in the United Kingdom. Located along Swansea Bay in southwest Wales, with the principal area covering the Gower Peninsula, it is part of the Swansea Bay region and part of the historic county of Glamorgan; also the ancient Welsh commote of Gŵyr. The principal area is the second most populous local authority area in Wales with an estimated population of 246,563 in 2020. Swansea, along with Neath and Port Talbot, forms the Swansea Urban Area with a population of 300,352 in 2011. It is also part of the Swansea Bay City Region. During the 19th-century industrial heyday, Swansea was the key centre of the copper-smelting industry, earning the nickname ''Copperopolis''. Etymologies The Welsh name, ''Abertawe'', translates as ''"mouth/es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for the command of the Royal Navy until 1964, historically under its titular head, the Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (later Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of the Admiralty and Marine Affairs administered the Royal Navy of the Kingdom of England, which merged with the Royal Scots Navy and the absorbed the responsibilities of the Lord High Admiral of the Kingdom of Scotland with the unification of the Kingdom of Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garthwaite Baronets
The Garthwaite Baronetcy, of Durham, is a title in the Baronetage of the United Kingdom. It was created on 19 May 1919 for William Garthwaite. He was a shipowner and sugar planter and provided valuable service to the Admiralty during the First World War World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin .... As of 2010 the title is held by his grandson, the third Baronet, who succeeded his father in 1993. His daughter is the journalist Rosie Garthwaite. Garthwaite baronets, of Durham (1919) *Sir William Garthwaite, 1st Baronet (1874–1956) *Sir William Garthwaite, 2nd Baronet (1906–1993) *Sir (William) Mark Charles Garthwaite, 3rd Baronet (born 1946) Notes References *Kidd, Charles, Williamson, David (editors). ''Debrett's Peerage and Baronetage'' (1990 edition). New York: St M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prize (law)
In admiralty law prizes are equipment, vehicles, vessels, and cargo captured during armed conflict. The most common use of ''prize'' in this sense is the capture of an enemy ship and her cargo as a prize of war. In the past, the capturing force would commonly be allotted a share of the worth of the captured prize. Nations often granted letters of marque that would entitle private parties to capture enemy property, usually ships. Once the ship was secured on friendly territory, she would be made the subject of a prize case: an ''in rem'' proceeding in which the court determined the status of the condemned property and the manner in which the property was to be disposed of. History and sources of prize law In his book ''The Prize Game'', Donald Petrie writes, "at the outset, prize taking was all smash and grab, like breaking a jeweler's window, but by the fifteenth century a body of guiding rules, the maritime law of nations, had begun to evolve and achieve international recogn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falmouth, Cornwall
Falmouth ( ; kw, Aberfala) is a town, civil parish and port on the River Fal on the south coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It has a total resident population of 21,797 (2011 census). Etymology The name Falmouth is of English origin, a reference to the town's situation on the mouth of the River Fal. The Cornish language name, ' or ', is of identical meaning. It was at one time known as ''Pennycomequick'', an Anglicisation of the Celtic ''Pen-y-cwm-cuic'' "head of the creek"; this is the same as Pennycomequick, a district in Plymouth. History Early history In 1540, Henry VIII built Pendennis Castle in Falmouth to defend Carrick Roads. The main town of the district was then at Penryn. Sir John Killigrew created the town of Falmouth shortly after 1613. In the late 16th century, under threat from the Spanish Armada, the defences at Pendennis were strengthened by the building of angled ramparts. During the Civil War, Pendennis Castle was the second to las ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several roles. The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hundred years, has changed its meaning over time. During the Age of Sail, the term ''cruising'' referred to certain kinds of missions—independent scouting, commerce protection, or raiding—fulfilled by frigates or sloops-of-war, which functioned as the ''cruising warships'' of a fleet. In the middle of the 19th century, ''cruiser'' came to be a classification of the ships intended for cruising distant waters, for commerce raiding, and for scouting for the battle fleet. Cruisers came in a wide variety of sizes, from the medium-sized protected cruiser to large armored cruisers that were nearly as big (although not as powerful or as well-armored) as a pre-dreadnought battleship. With the advent of the dreadnought battleship before World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |