|
HMS Nassau (1866)
Six ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Nassau'', after King William III who was of the House of Orange-Nassau, with the County of Nassau The County of Nassau was a German state within the Holy Roman Empire and later part of the German Confederation. Its ruling dynasty, the male line of which is now extinct, was the House of Nassau. Origins Nassau, originally a county, developed ... being a subsidiary holding of that family: * was a 4-gun fluyt captured from the Netherlands, Dutch in 1672 and given away later that year. * was an 80-gun third-rate ship of the line launched in 1699 and wrecked in 1706. * was a 70-gun third-rate ship of the line launched in 1706, rebuilt in 1740 and sold in 1770. * was a 64-gun third-rate ship of the line launched in 1785. She was converted into a 36-gun troopship in 1799 and was wrecked later that year. * HDMS Holsteen, HMS ''Nassau'' was a 64-gun third rate originally named HMS ''Holstein'', which the British captured at the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William III Of England
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 16508 March 1702), also widely known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of County of Holland, Holland, County of Zeeland, Zeeland, Lordship of Utrecht, Utrecht, Guelders, and Lordship of Overijssel, Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from the 1670s, and King of England, Monarchy of Ireland, Ireland, and List of Scottish monarchs, Scotland from 1689 until his death in 1702. As King of Scotland, he is known as William II. He is sometimes informally known as "King Billy" in Ireland and Scotland. His victory at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690 is The Twelfth, commemorated by Unionism in the United Kingdom, Unionists, who display Orange Order, orange colours in his honour. He ruled Britain alongside his wife and cousin, Queen Mary II, and popular histories usually refer to their reign as that of "William and Mary". William was the only child of William II, Prince of Orange, and Mary, Princess Royal an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau (Dutch: ''Huis van Oranje-Nassau'', ) is the current reigning house of the Netherlands. A branch of the European House of Nassau, the house has played a central role in the politics and government of the Netherlands and Europe especially since William the Silent organised the Dutch Revolt against Spanish rule, which after the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) led to an independent Dutch state. Several members of the house served during this war and after as stadtholder ("governor"; Dutch: ''stadhouder'') during the Dutch Republic. However, in 1815, after a long period as a republic, the Netherlands became a monarchy under the House of Orange-Nassau. The dynasty was established as a result of the marriage of Henry III of Nassau-Breda from Germany and Claudia of Châlon-Orange from French Burgundy in 1515. Their son René of Chalon inherited in 1530 the independent and sovereign Principality of Orange from his mother's brother, Philibert of Châlon. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Nassau
The County of Nassau was a German state within the Holy Roman Empire and later part of the German Confederation. Its ruling dynasty, the male line of which is now extinct, was the House of Nassau. Origins Nassau, originally a county, developed on the lower Lahn river in what is known today as Rhineland-Palatinate. The town of Nassau was founded in 915. Dudo of Laurenburg held Nassau as a fiefdom as granted by the Bishopric of Worms. His son, Rupert, built the Nassau Castle there around 1125, declaring himself "Count of Nassau". This title was not officially acknowledged by the Bishop of Worms until 1159 under the rule of Rupert's son, Walram. By 1159, the County of Nassau effectively claimed rights of taxation, toll collection, and justice, at which point it can be considered to become a state. The Nassauers held the territory between the Taunus and the Westerwald at the lower and middle Lahn. By 1128, they acquired the bailiwick of the Bishopric of Worms, which had numero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluyt
A fluyt (archaic Dutch: ''fluijt'' "flute"; ) is a Dutch type of sailing vessel originally designed by the shipwrights of Hoorn as a dedicated cargo vessel. Originating in the Dutch Republic in the 16th century, the vessel was designed to facilitate transoceanic delivery with the maximum of space and crew efficiency. Unlike rivals, it was not built for conversion in wartime to a warship, so it was cheaper to build and carried twice the cargo, and could be handled by a smaller crew. Construction by specialized shipyards using new tools made it half the cost of rival ships. These factors combined to sharply lower the cost of transportation for Dutch merchants, giving them a major competitive advantage. The fluyt was a significant factor in the 17th-century rise of the Dutch seaborne empire. In 1670 the Dutch merchant marine totalled 568,000 tons of shipping—about half the European total. Ship design The standard fluyt design minimized or completely eliminated its armaments to max ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
) , anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau") , image_map = , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands , established_title = Before independence , established_date = Spanish Netherlands , established_title2 = Act of Abjuration , established_date2 = 26 July 1581 , established_title3 = Peace of Münster , established_date3 = 30 January 1648 , established_title4 = Kingdom established , established_date4 = 16 March 1815 , established_title5 = Liberation Day (Netherlands), Liberation Day , established_date5 = 5 May 1945 , established_title6 = Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Kingdom Charter , established_date6 = 15 December 1954 , established_title7 = Dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, Caribbean reorganisation , established_date7 = 10 October 2010 , official_languages = Dutch language, Dutch , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = , languages2_type = Reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Years of experience proved that the third rate ships embodied the best compromise between sailing ability (speed, handling), firepower, and cost. So, while first-rates and second-rates were both larger and more powerful, third-rate ships were the optimal configuration. Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Of The Line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactic known as the line of battle, which depended on the two columns of opposing warships maneuvering to volley fire with the cannons along their broadsides. In conflicts where opposing ships were both able to fire from their broadsides, the opponent with more cannons firingand therefore more firepowertypically had an advantage. Since these engagements were almost invariably won by the heaviest ships carrying more of the most powerful guns, the natural progression was to build sailing vessels that were the largest and most powerful of their time. From the end of the 1840s, the introduction of steam power brought less dependence on the wind in battle and led to the construction of screw-driven wooden-hulled ships of the line; a number of purely sail-powered ships were converted to this propulsion mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troopship
A troopship (also troop ship or troop transport or trooper) is a ship used to carry soldiers, either in peacetime or wartime. Troopships were often drafted from commercial shipping fleets, and were unable land troops directly on shore, typically loading and unloading at a seaport or onto smaller vessels, either tenders or barges. Attack transports, a variant of ocean-going troopship adapted to transporting invasion forces ashore, carry their own fleet of landing craft. Landing ships beach themselves and bring their troops directly ashore. History Ships to transport troops were used in Antiquity. Ancient Rome used the navis lusoria, a small vessel powered by rowers and sail, to move soldiers on the Rhine and Danube. The modern troopship has as long a history as passenger ships do, as most maritime nations enlisted their support in military operations (either by leasing the vessels or by impressing them into service) when their normal naval forces were deemed insufficient fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
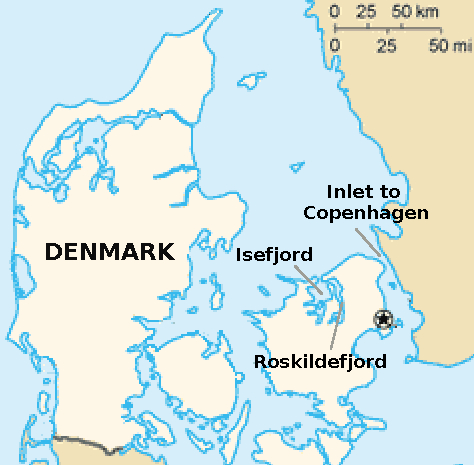
HDMS Holsteen
''Holsteen'' was a 60-gun ship of the line in the Royal Dano-Norwegian Navy. She was commissioned in 1775 and the British Royal Navy captured her in the Battle at Copenhagen Roads on 2 April 1801. The British renamed the ship HMS ''Holstein'', and later HMS ''Nassau''. She participated in one major battle during the Gunboat War and was sold in 1814. Design ''Holsteen'' was the name ship of her class of three vessels. The Danish naval builder, Frederik Michael Krabbe, was the chief designer and builder for the Danish navy. She was a foot narrower than the otherwise identical ''Oldenborg''-class vessels. Danish service In 1775 ''Holsteen'' fitted out during a voyage to Norway, where she was used as a command ship for the ships laid up in Trosvik (near the mouth of the Oslo Fjord), before she returned to Copenhagen in 1776. From 25 May 1776 to 16 July 1780 ''Holsteen'' sailed to Lisbon, the Gold Coast, and Cape Town. On her return in July 1780, she performed guardship duties i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Copenhagen (1801)
The Battle of Copenhagen of 1801 (Danish: ''Slaget på Reden''), also known as the First Battle of Copenhagen to distinguish it from the Second Battle of Copenhagen in 1807, was a naval battle in which a British fleet fought and defeated a smaller force of the Dano-Norwegian Navy anchored near Copenhagen on 2 April 1801. The battle came about over British fears that the powerful Danish fleet would ally with France, and a breakdown in diplomatic communications on both sides. As the British ships entered the harbour of the Danish fleet, several of its ships stationed in the city's inlet forming a blockade. The Danish fleet defended the capital with these ships and bastions on both sides of the harbour inlet. It was the second attempt by the British to try to prevent a Franco-Danish alliance, as the British had already entered Øresund with a fleet in August 1800, in order to persuade Denmark not to ally with France. The Danes agreed to the British terms upon hearing news of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies. History Pre-steam era In the age of sail, a gunboat was usually a small undecked vessel carrying a single smoothbore cannon in the bow, or just two or three such cannons. A gunboat could carry one or two masts or be oar-powered only, but the single-masted version of about length was most typical. Some types of gunboats carried two cannons, or else mounted a number of swivel guns on the railings. The small gunboat had advantages: if it only carried a single cannon, the boat could manoeuvre in shallow or restricted areas – such as rivers or lakes – where larger ships could sail only with difficulty. The gun that such boats carried could be quite heavy; a 32-pounder for instance. As such boats were cheap and quick to build, naval forces favoured swarm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)