|
Grypsera
Grypsera (: from Low German ''Grips'' meaning "intelligence", "cleverness"; also ''drugie życie'', literally "second life" in Polish) is a distinct nonstandard dialect or prison slang of the Polish language, used traditionally by recidivist prison inmates. It evolved in the 19th century in the areas of Congress Poland: it is said to have originated in Gęsiówka, a prison in Warsaw. The basic substrate of the dialect is Polish, but there are many notable influences (mostly lexical) from other languages used in Polish lands at that time, most notably Yiddish and German, but also some Lithuanian, Ukrainian, Russian, Greek and Latin. It was also heavily influenced by various regional dialects of the Polish language, most notably the Bałak jargon of Lwów and the Warsaw dialect. Initially, it served the role of a cant, or "secret language", but in the late 19th century, it became a standard sociolect of criminals. Grypsera is constantly evolving to maintain the status of a langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Dialect
The Warsaw subdialect ( pl, gwara warszawska ), or Warsaw dialect ( pl, dialekt warszawski), is a regional subdialect of the Masovian dialect of the Polish language, centered on the city of Warsaw. It evolved as late as the 18th century, under notable influence of several languages spoken in the city. After the destruction of Warsaw in the aftermath of the Warsaw Uprising of 1944 the subdialect has been in decline. It is estimated that in modern times it is almost extinct as the native language and is preserved mostly in literary works. Classification The Warsaw dialect is composed mostly of the Polish language substratum, with notable (mostly lexical) influences from the Masovian dialect of Polish, as well as Russian, German, Yiddish and other languages. The dialect was composed of a variety of different class dialects: the language of the suburbs differed from the language of the city centre and each professional group used its own version of the dialect, slightly different fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cant (language)
A cant is the jargon or language of a group, often employed to exclude or mislead people outside the group.McArthur, T. (ed.) ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (1992) Oxford University Press It may also be called a cryptolect, argot, pseudo-language, anti-language or secret language. Each term differs slightly in meaning; their use is inconsistent. Etymology There are two main schools of thought on the origin of the word ''cant'': * In linguistics, the derivation is normally seen to be from the Irish word (older spelling ), "speech, talk", or Scottish Gaelic . It is seen to have derived amongst the itinerant groups of people in Ireland and Scotland, who hailed from both Irish/Scottish Gaelic and English-speaking backgrounds, ultimately developing as various creole languages. However, the various types of cant (Scottish/Irish) are mutually unintelligible. The Irish creole variant is simply termed " the Cant". Its speakers from the Irish Traveller community know it a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by the Polish diaspora. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (''ą'', ''ć'', ''ę'', ''ł'', ''ń'', ''ó'', ''ś'', ''ź'', ''ż'') to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet, although they are not used in native words. The traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low German
: : : : : (70,000) (30,000) (8,000) , familycolor = Indo-European , fam2 = Germanic , fam3 = West Germanic , fam4 = North Sea Germanic , ancestor = Old Saxon , ancestor2 = Middle Low German , dia1 = West Low German , dia2 = East Low German , iso2 = nds , iso3 = nds , iso3comment = (Dutch varieties and Westphalian have separate codes) , lingua = 52-ACB , map = Nds Spraakrebeet na1945.svg , mapcaption = Present day Low German language area in Europe. , glotto = lowg1239 , glottoname = Low German , notice = IPA Low German or Low Saxon (in the language itself: , and other names; german: Plattdeutsch, ) is a West Germanic language variety spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern part of the Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the First language, native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. Besides Russia itself, Russian is an official language in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely as a lingua franca throughout Ukraine, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. It was the De facto#National languages, ''de facto'' language of the former Soviet Union,1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 and continues to be used in public life with varying proficiency in all of the post-Soviet states. Russian has over 258 million total speakers worldwide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syllable
A syllable is a unit of organization for a sequence of speech sounds typically made up of a syllable nucleus (most often a vowel) with optional initial and final margins (typically, consonants). Syllables are often considered the phonological "building blocks" of words. They can influence the rhythm of a language, its prosody, its poetic metre and its stress patterns. Speech can usually be divided up into a whole number of syllables: for example, the word ''ignite'' is made of two syllables: ''ig'' and ''nite''. Syllabic writing began several hundred years before the first letters. The earliest recorded syllables are on tablets written around 2800 BC in the Sumerian city of Ur. This shift from pictograms to syllables has been called "the most important advance in the history of writing". A word that consists of a single syllable (like English ''dog'') is called a monosyllable (and is said to be ''monosyllabic''). Similar terms include disyllable (and ''disyllabic''; also '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Vowel
A nasal vowel is a vowel that is produced with a lowering of the soft palate (or velum) so that the air flow escapes through the nose and the mouth simultaneously, as in the French vowel or Amoy []. By contrast, oral vowels are produced without nasalization. Nasalized vowels are vowels under the influence of neighbouring sounds. For instance, the [] of the word ''hand'' is affected by the following nasal consonant. In most languages, vowels adjacent to nasal consonants are produced partially or fully with a lowered velum in a natural process of assimilation and are therefore technically nasal, but few speakers would notice. That is the case in English: vowels preceding nasal consonants are nasalized, but there is no phonemic distinction between nasal and oral vowels, and all vowels are considered phonemically oral. The nasality of nasal vowels, however, is a distinctive feature of certain languages. In other words, a language may contrast oral vowels and nasalized vowels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociolect
In sociolinguistics, a sociolect is a form of language ( non-standard dialect, restricted register) or a set of lexical items used by a socioeconomic class, profession, an age group, or other social group. Sociolects involve both passive acquisition of particular communicative practices through association with a local community, as well as active learning and choice among speech or writing forms to demonstrate identification with particular groups. The term ''sociolect'' might refer to socially-restricted dialects, but it is sometimes also treated as equivalent with the concept of register, or used as a synonym for jargon and slang. Individuals who study sociolects are called sociolinguists. Sociolinguists study language variation. Sociolinguists define a sociolect by examining the social distribution of specific linguistic terms. For example, a sociolinguist would examine the use of the second person pronoun "you" for its use within the population. If one distinct social grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lviv
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukraine. It was named in honour of Leo, the eldest son of Daniel, King of Ruthenia. Lviv emerged as the centre of the historical regions of Red Ruthenia and Galicia in the 14th century, superseding Halych, Chełm, Belz and Przemyśl. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia from 1272 to 1349, when it was conquered by King Casimir III the Great of Poland. From 1434, it was the regional capital of the Ruthenian Voivodeship in the Kingdom of Poland. In 1772, after the First Partition of Poland, the city became the capital of the Habsburg Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria. In 1918, for a short time, it was the capital of the West Ukrainian People's Republic. Between the wars, the city was the centre of the Lwów Voivodeship in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bałak Jargon
Bałak (; often mistakenly called ''bałach'') is a jargon or a sociolect spoken by the commoners of the city of Lwów (modern Lviv, Ukraine). A distinct part of the Lwów dialect of the Polish language, it consists of a Lesser Poland Polish language substratum with a variety of borrowings from German, Yiddish, Ukrainian and other languages. Following the post–World War II expulsion of Poles from Lwów, ''bałak'' was gradually replaced with standard Polish among both the Polish minority still living in Lwów and the descendants of the expelees. The name for the sociolect was coined after the verb ''bałakać'' (to speak) or ''balakaty'' (to speak in Ukrainian), a local counterpart of the standard Polish verb ''mówić''. See also * Balachka * Lwów subdialect The Lwów dialect ( pl, gwara lwowska, ua, Львівська говірка, translit=L’vivs’ka hovirka) is a subdialect (''gwara'') of the Polish language characteristic of the inhabitants of the city of Lviv ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
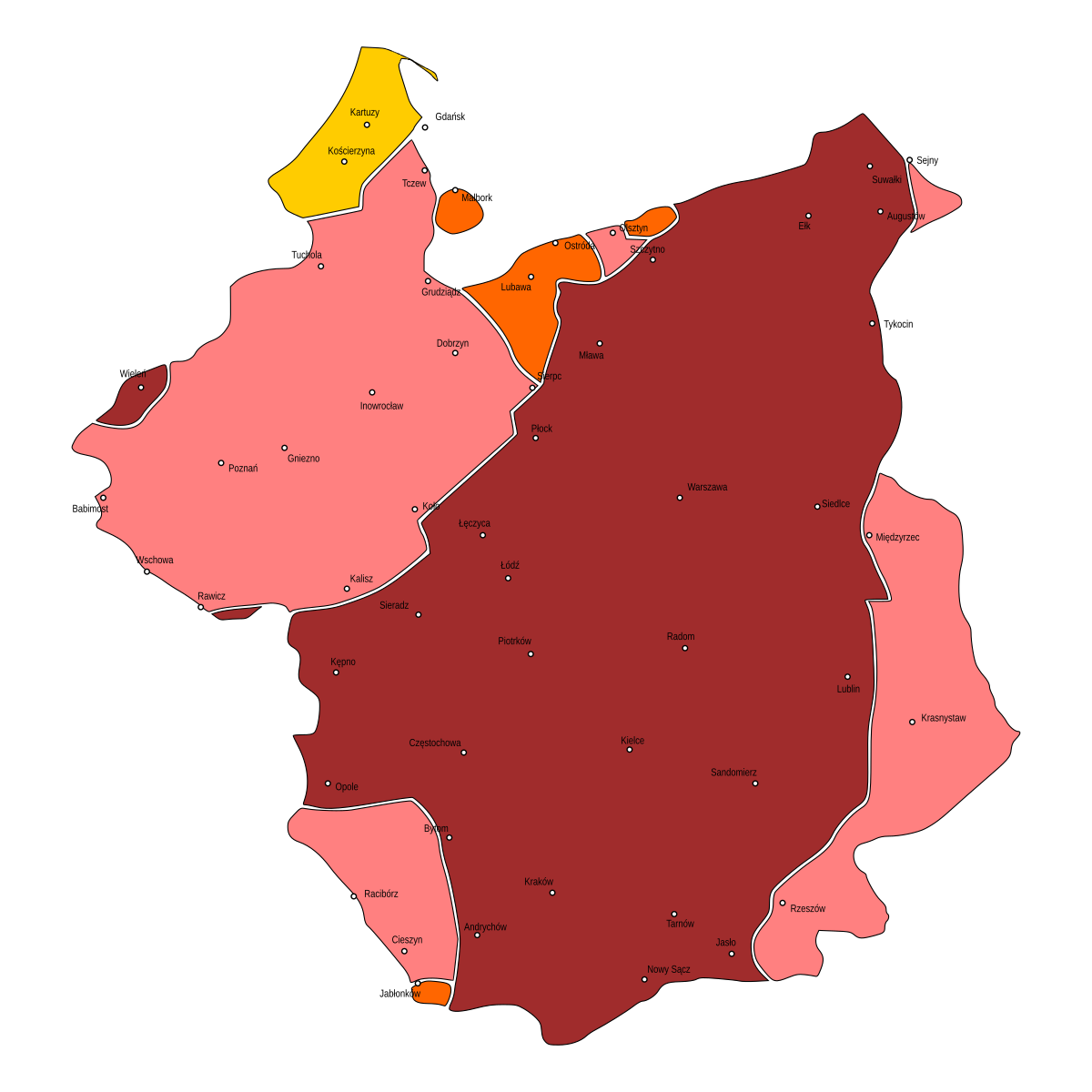
Dialects Of Polish
Polish dialects are regional vernacular varieties of the Polish language. Four major dialect groups are typically recognized, each primarily associated with a particular geographical region, and often further subdivided into subdialectal groups (termed ''gwara'' in Polish).Roland Sussex and Paul Cubberley (2006). ''The Slavic Languages''. Cambridge University Press. P. 530.Robert A. Rothstein (1994). "Polish". ''The Slavonic Languages'', edited by Bernard Comrie and Greville G. Corbett. Routledge. Pp. 754–756. They are: * Greater Polish, spoken in the west * Lesser Polish, spoken in the south and southeast * Masovian, spoken throughout the central and eastern parts of the country * Silesian spoken in the southwest (sometimes also considered a separate language, see comment below) The regional differences correspond mainly to old ethnic or tribal divisions from around a thousand years ago. As a result of 19th century measures taken by occupying powers, of expulsions plus o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |