|
Goyet Caves
The Goyet Caves (french: Grottes de Goyet) are a series of connected caves located in Wallonia in a limestone cliff about 15 m (50 ft) above the river Samson near the village of Mozet in the Gesves municipality of the Namur province, Belgium. The site is a significant locality of regional Neanderthal and European early modern human occupation, as thousands of fossils and artifacts were discovered that are all attributed to a long and contiguous stratigraphic sequence from 120,000 years ago, the Middle Palaeolithic to less than 5.000 years ago, the late Neolithic. A robust sequence of sediments was identified during extensive excavations by geologist Edouard Dupont, who undertook the first probings as early as 1867. The site was added to the Belgian National Heritage register in 1976. Site Located just south of the ''Goyet Castle'' the caves are essentially long underground galleries, rich in speleothems and carved out of the limestone during millions of years by the waters of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
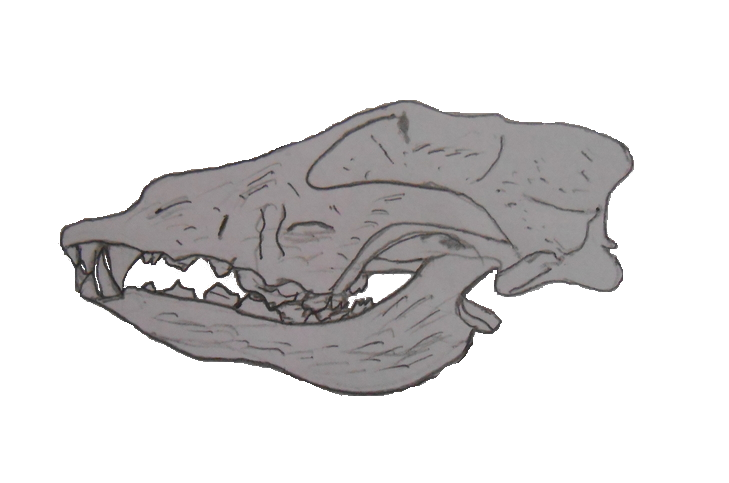
Goyet Cave Canid Skull Full
Goyet may refer to: People Goyet is a French surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Eugène Goyet (1798—1857), French painter, son of Jean-Baptiste Goyet, husband of Zoé Goyet *Jean-Baptiste Goyet (1779—1854), French painter, father of Eugène Goyet *Zoé Goyet (died 8 July 1869), French painter, wife of Eugène Goyet Places *Goyet (place), a hamlet in France *Goyet Caves, located near Goyet, France {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolní Věstonice (archaeology)
Dolní Věstonice (german: Unterwisternitz) is a municipality and village in Břeclav District in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 300 inhabitants. It is known for the eponymous archaeological site. Geography Dolní Věstonice lies on the border between the Mikulov Highlands and Dyje–Svratka Valley. It is located on the shore of the Nové Mlýny reservoirs. The municipality is partly located in the Pálava Protected Landscape Area. The area on the reservoir is protected as the Věstonice Reservoir Nature Reserve. History Prehistoric times Dolní Věstonice is known for the Dolní Věstonice archaeological site. Approximately 25,000 years ago, during the Upper Paleolithic period of the Stone Age, a small settlement of mammoth hunters consisting of huts built with rocks and mammoth bones was founded on the site of what is now Dolní Věstonice. This is the oldest permanent human settlement that has ever been found. Numerous other archaeolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spy Cave
Spy Cave (french: Grotte de Spy) is located in Wallonia near Spy in the municipality of Jemeppe-sur-Sambre, Namur Province, Belgium above the left bank of the Orneau River. Classified as a premier Heritage site of the Walloon Region, the location ranks among the most significant paleolithic sites in Europe. The cave consists of numerous small chambers and corridors.Camille Daujeard, Grégory Abrams, Mietje Germonpré, Jeanne-Marie Le Pape, Alicia Wampach, Kevin Di Modica, Marie-Hélène Moncel "Neanderthal and animal karstic occupations from southern Belgium and south-eastern France: Regional or common features?", ''Quaternary International'' Available online 27 May 2016, doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2016.02.009/ref> Excavations Since the first amateur investigations during the late 19th century numerous amateur and professional archaeologists have carried out excavations and removed all sediment deposits of the cave. In 1886 Neanderthal fossils of excellent quality were discovered, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear DNA
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. It adheres to Mendelian inheritance, with information coming from two parents, one male and one female—rather than matrilineally (through the mother) as in mitochondrial DNA. Structure Nuclear DNA is a nucleic acid, a polymeric biomolecule or biopolymer, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Its structure is a double helix, with two strands wound around each other, a structure first described by Francis Crick and James D. Watson (1953) using data collected by Rosalind Franklin. Each strand is a long polymer chain of repeating nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and an organic base. Nucleotides are distinguished by their bases: purines, large bases that include adenine and guanine; and pyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleolithic in African archeology. The Middle Paleolithic broadly spanned from 300,000 to 30,000 years ago. There are considerable dating differences between regions. The Middle Paleolithic was succeeded by the Upper Paleolithic subdivision which first began between 50,000 and 40,000 years ago. Pettit and White date the Early Middle Paleolithic in Great Britain to about 325,000 to 180,000 years ago (late Marine Isotope Stage 9 to late Marine Isotope Stage 7), and the Late Middle Paleolithic as about 60,000 to 35,000 years ago. According to the theory of the recent African origin of modern humans, anatomically modern humans began migrating out of Africa during the Middle Stone Age/Middle Paleolithic around 125,000 years ago and began to replace e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. This sequencing revealed that the human mtDNA includes 16,569 base pairs and encodes 13 proteins. Since animal mtDNA evolves faster than nuclear genetic markers, it represents a mainstay of phylogenetics and evolutionary biology. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and biogeography. Origin Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA are thought to be of separate evolutionary origin, with the mtDNA being derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleolithic Dog
The Paleolithic dog was a Late Pleistocene canine. They were directly associated with human hunting camps in Europe over 30,000 years ago and it is proposed that these were domesticated. They are further proposed to be either a proto-dog and the ancestor of the domestic dog or an extinct, morphologically and genetically divergent wolf population. Taxonomy One authority has classified the Paleolithic dog as ''Canis c.f. familiaris'' (where c.f. is a Latin term meaning uncertain, as in ''Canis'' believed to be ''familiaris''). Previously in 1969, a study of ancient mammoth-bone dwellings at the Mezine paleolithic site in the Chernigov region, Ukraine uncovered 3 possibly domesticated "short-faced wolves". The specimens were classified as ''Canis lupus domesticus'' (domesticated wolf). Naming In 2002, a study looked at 2 fossil skulls of large canids dated at 16,945 years before present (YBP) that had been found buried 2 metres and 7 metres from what was once a mammoth-bone hut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canidae
Canidae (; from Latin, ''canis'', "dog") is a biological family of dog-like carnivorans, colloquially referred to as dogs, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). There are three subfamilies found within the canid family, which are the extinct Borophaginae and Hesperocyoninae, and the extant Caninae. The Caninae are known as canines, and include domestic dogs, wolves, coyotes, foxes, jackals and other extant and extinct species. Canids are found on all continents except Antarctica, having arrived independently or accompanied human beings over extended periods of time. Canids vary in size from the gray wolf to the fennec fox. The body forms of canids are similar, typically having long muzzles, upright ears, teeth adapted for cracking bones and slicing flesh, long legs, and bushy tails. They are mostly social animals, living together in family units or small groups and behaving cooperatively. Typically, only the dominant pair in a group bree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
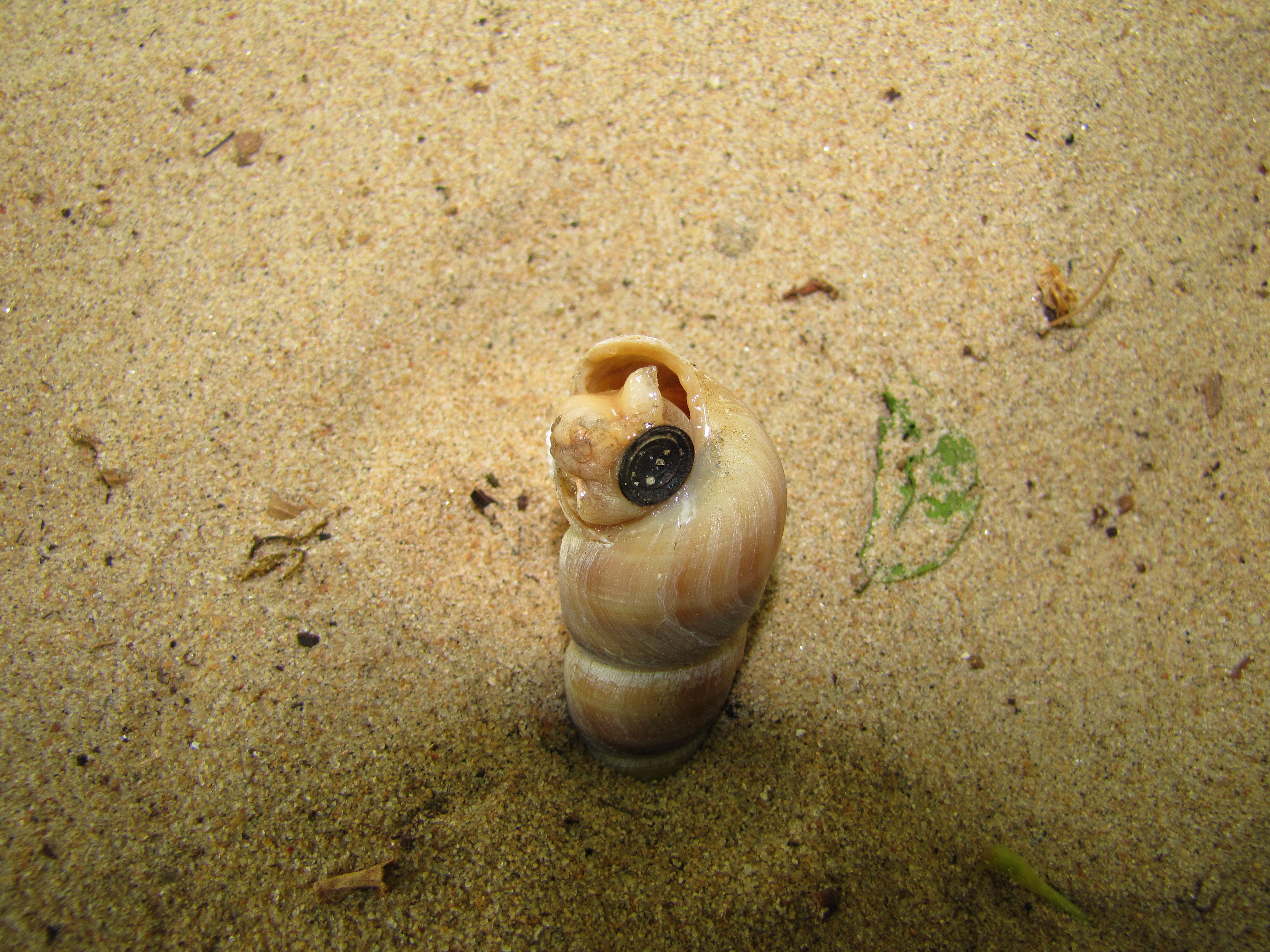
Turritella
''Turritella'' is a genus of medium-sized sea snails with an operculum, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Turritellidae.Vos, C.; Gofas, S. (2013). Turritella Lamarck, 1799. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=138615 on 2013-06-02 They have tightly coiled shells, whose overall shape is basically that of an elongated cone. The name ''Turritella'' comes from the Latin word ''turritus'' meaning "turreted" or "towered" and the diminutive suffix ''-ella''. Species Valid Valid species within the genus ''Turritella'' are listed below. Fossil species are marked with a dagger "†". * ''Turritella acropora'' (Dall, 1889) * '' Turritella albolapis'' Finlay, 1924 * '' Turritella algida'' Melvill & Standen, 1912 * '' Turritella anactor'' Berry, 1957 * ''Turritella annulata'' Kiener, 1843 * † '' Turritella apicalis'' - Pleistocene of Florida * ''Turritella attenuata'' Reeve, 1849 * '' Turritella aurocincta'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panthera Leo Spelaea
''Panthera spelaea'', also known as the Eurasian cave lion, European cave lion or steppe lion, is an extinct ''Panthera'' species that most likely evolved in Europe after the third Cromerian interglacial stage, less than 600,000 years ago. Phylogenetic analysis of fossil bone samples revealed that it was highly distinct and genetically isolated from the modern lion (''Panthera leo'') occurring in Africa and Asia. Analysis of morphological differences and mitochondrial data support the taxonomic recognition of ''Panthera spelaea'' as a distinct species that genetically diverged from the lion about . Nuclear genomic evidence shows a more recent split approximately 500,000 years ago, with no subsequent interbreeding with the ancestors of the modern lion. The oldest known bone fragments were excavated in Yakutia and radiocarbon dated at least 62,400 years old. It became extinct about 13,000 years ago. Taxonomy ''Felis spelaea'' was the scientific name used by Georg August Goldfus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave Bear
The cave bear (''Ursus spelaeus'') is a prehistoric species of bear that lived in Europe and Asia during the Pleistocene and became extinct about 24,000 years ago during the Last Glacial Maximum. Both the word "cave" and the scientific name ''spelaeus'' are used because fossils of this species were mostly found in caves. This reflects the views of experts that cave bears may have spent more time in caves than the brown bear, which uses caves only for hibernation. Taxonomy Cave bear skeletons were first described in 1774 by Johann Friedrich Esper, in his book ''Newly Discovered Zoolites of Unknown Four Footed Animals''. While scientists at the time considered that the skeletons could belong to apes, canids, felids, or even dragons or unicorns, Esper postulated that they actually belonged to polar bears. Twenty years later, Johann Christian Rosenmüller, an anatomist at Leipzig University, gave the species its binomial name. The bones were so numerous that most researcher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Wolf.png)

BisonsPoursuivisParDesLions.jpg)
