|
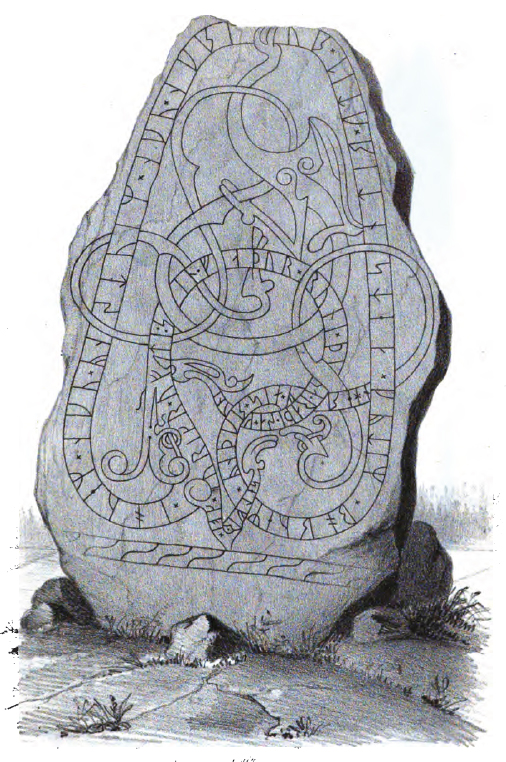
Gök Runestone
The Sigurd stones form a group of eight or nine Swedish runic inscriptions (five or six runestones, two natural rocks, and a baptismal font) and one picture stone that depict imagery from the Germanic heroic legend of Sigurd the dragon slayer. They were made during the Viking Age and constitute the earliest Norse representations of the matter of the Völsung cycle that is the basis of the Middle High German ''Nibelungenlied'' and the Sigurd legends in the ''Poetic Edda'', the ''Prose Edda'', and the ''Völsunga saga''. In addition, the figure of Sigurd sucking the dragon's blood from his thumb appears on several carved stones in parts of Great Britain that were under Norse culture: at Ripon and Kirby Hill, North Yorkshire, at York and at Halton, Lancashire, and carved slates from the Isle of Man, broadly dated , include several pieces interpreted as showing episodes from the Sigurd story. Uppland U 1163 This runestone is in runestone style Pr2. It was found in Drävle, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigurd Runestones
Sigurd ( non, Sigurðr ) or Siegfried (Middle High German: ''Sîvrit'') is a legendary hero of Germanic heroic legend, who killed a dragon and was later murdered. It is possible he was inspired by one or more figures from the Frankish Merovingian dynasty, with Sigebert I being the most popular contender. Older scholarship sometimes connected him with Arminius, victor of the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. He may also have a purely mythological origin. Sigurd's story is first attested on a series of carvings, including runestones from Sweden and stone crosses from the British Isles, dating from the eleventh century. In both the Norse and continental Germanic tradition, Sigurd is portrayed as dying as the result of a quarrel between his wife (Gudrun/Kriemhild) and another woman, Brunhild, whom he has tricked into marrying the Burgundians, Burgundian king Gunther, Gunnar/Gunther. His slaying of a dragon and possession of the hoard of the Nibelungen is also common to both tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a minster, castle, and city walls. It is the largest settlement and the administrative centre of the wider City of York district. The city was founded under the name of Eboracum in 71 AD. It then became the capital of the Roman province of Britannia Inferior, and later of the kingdoms of Deira, Northumbria, and Scandinavian York. In the Middle Ages, it became the northern England ecclesiastical province's centre, and grew as a wool-trading centre. In the 19th century, it became a major railway network hub and confectionery manufacturing centre. During the Second World War, part of the Baedeker Blitz bombed the city; it was less affected by the war than other northern cities, with several historic buildings being gutted and restore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valkyrie
In Norse mythology, a valkyrie ("chooser of the slain") is one of a host of female figures who guide souls of the dead to the god Odin's hall Valhalla. There, the deceased warriors become (Old Norse "single (or once) fighters"Orchard (1997:36) and Lindow (2001:104).). When the are not preparing for the events of Ragnarök, the valkyries bear them mead. Valkyries also appear as lovers of heroes and other mortals, where they are sometimes described as the daughters of royalty, sometimes accompanied by ravens and sometimes connected to swans or horses. Valkyries are attested in the ''Poetic Edda'' (a book of poems compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources), the ''Prose Edda'', the (both by Snorri Sturluson) and the (one of the Sagas of Icelanders), all written—or compiled—in the 13th century. They appear throughout the poetry of skalds, in a 14th-century charm, and in various runic inscriptions. The Old English cognate term appears in several Old E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andvari
In Norse mythology, Andvari ( 12th c. Old Norse: ; "careful one") is a dwarf who lives underneath a waterfall and has the power to change himself into a pike (gedda) at will. Andvari had a magical ring Andvaranaut, which helped him become wealthy. Using a net provided by Ran, Loki catches him as a pike and forces him to give up his gold and Andvaranaut. Andvari cursed the stolen gold which would destroy anyone who possessed it. After the deaths of Brynhild and Sigurd, Gunnar left Andvari's gold in a cave. Years later, Andvari discovered the cave and his lost gold, although his ring was lost forever. In Richard Wagner's cycle of music dramas, ''Der Ring des Nibelungen'', the character Alberich is a combination of Andvari and the character of Alberich from the Nibelungenlied The ( gmh, Der Nibelunge liet or ), translated as ''The Song of the Nibelungs'', is an epic poem written around 1200 in Middle High German. Its anonymous poet was likely from the region of Passau. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lindworm
The lindworm (''worm'' meaning snake), also spelled lindwyrm or lindwurm, is a mythical creature in Northern and Central European folklore living deep in the forest that traditionally has the shape of a giant serpent monster. It can be seen as a sort of dragon. According to legend, everything that lies under the lindworm will increase as the lindworm grows, giving rise to tales of dragons that brood over treasures to become richer. Legend tells of two kinds of lindworm, a good one associated with luck, often a cursed prince who has been transformed into another beast (as in the fairy tale The Frog Prince), and a bad one, a dangerous man-eater which will attack humans on sight. A lindworm may swallow its own tail, turning itself into a rolling wheel, as a method of pursuing fleeing humans. The head of the 16th-century lindworm statue at Lindwurm Fountain () in Klagenfurt, Austria, is modeled on the skull of a woolly rhinoceros found in a nearby quarry in 1335. It has been cited a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Dragon
Dragons are present in Germanic mythology and folklore, where they are often portrayed as large venomous serpents. Especially in later tales, however, they share many common features with other dragons in European mythology. Origin, appearance and terminology In early depictions, as with dragons in other cultures, the distinction between Germanic dragons and regular snakes is blurred, with both being referred to as Old Norse or Old English from Proto-Germanic *wurmiz. ''Wyrm'' has since been borrowed back into Modern English to mean "dragon", while the descendent term ''worm'' remains used in Modern English to refer to dragons, especially those lacking wings. In Fáfnismál, the dragon Fáfnir is described as flightless and snake-like, and is referred to as an . In the later Völsunga saga, however, he has shoulders, suggesting legs, wings or both, and is referred to as both a and an . Similarly, the dragon in Beowulf is referred to as both a and a , although in some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manor House
A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were held the lord's manorial courts, communal meals with manorial tenants and great banquets. The term is today loosely applied to various country houses, frequently dating from the Late Middle Ages, which formerly housed the landed gentry. Manor houses were sometimes fortified, albeit not as fortified as castles, and were intended more for show than for defencibility. They existed in most European countries where feudalism was present. Function The lord of the manor may have held several properties within a county or, for example in the case of a feudal baron, spread across a kingdom, which he occupied only on occasional visits. Even so, the business of the manor was directed and controlled by regular manorial courts, which appointed manorial officials such as the bailiff, granted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Style Pr2
:''The term "runestone style" in the singular may refer to the Urnes style.'' The style or design of runestones varied during the Viking Age. The early runestones were simple in design, but towards the end of the runestone era they became increasingly complex and made by travelling runemasters such as Öpir and Visäte. A categorization of the styles was developed by Anne-Sophie Gräslund in the 1990s. Her systematization is considered to have been a break-through and is today a standard. The styles are RAK, Fp, Pr1, Pr2, Pr3, Pr4 and Pr5, and they cover the period 980-1130, which was the period during which most runestones were made. The styles Pr1 and Pr2 correspond to the Ringerike style, whereas Pr3, Pr4 and Pr5 belong to what is more widely known as the Urnes style.Sawyer 2000:32 Below follows a brief presentation of the various styles by showing sample runestones according to Rundata's annotation. RAK RAK is the oldest style and covers the period 980-1015 AD, but the Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runestone Style
:''The term "runestone style" in the singular may refer to the Urnes style.'' The style or design of runestones varied during the Viking Age. The early runestones were simple in design, but towards the end of the runestone era they became increasingly complex and made by travelling runemasters such as Öpir and Visäte. A categorization of the styles was developed by Anne-Sophie Gräslund in the 1990s. Her systematization is considered to have been a break-through and is today a standard. The styles are RAK, Fp, Pr1, Pr2, Pr3, Pr4 and Pr5, and they cover the period 980-1130, which was the period during which most runestones were made. The styles Pr1 and Pr2 correspond to the Ringerike style, whereas Pr3, Pr4 and Pr5 belong to what is more widely known as the Urnes style.Sawyer 2000:32 Below follows a brief presentation of the various styles by showing sample runestones according to Rundata's annotation. RAK RAK is the oldest style and covers the period 980-1015 AD, but the Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)