|
György Paál
György Paál (Budapest, 1934 – Budapest, 1992) was a Hungarian astronomer and cosmologist. Work In the late 1950s Paál studied the quasar and galaxy cluster distributions. In 1970 from redshift quantization he came up with the idea that the Universe might have nontrivial topological structure. These are the oldest papers that associate real observations with the possibility that our universe could have nontrivial topology. Membership Cosmological Committee of IAU Awards László Detre award. See also * Accelerating universe *Cosmological constant *Dark energy *Redshift quantization *Universe *Shape of the universe In physical cosmology, the shape of the universe refers to both its local and global geometry. Local geometry is defined primarily by its curvature, while the global geometry is characterised by its topology (which itself is constrained by curv ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Paal, Gyorgy 20th-century Hungarian astronomers Cosmologists 1934 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budapest
Budapest is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, most populous city of Hungary. It is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, tenth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the List of cities and towns on the river Danube, second-largest city on the river Danube. The estimated population of the city in 2025 is 1,782,240. This includes the city's population and surrounding suburban areas, over a land area of about . Budapest, which is both a List of cities and towns of Hungary, city and Counties of Hungary, municipality, forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of and a population of 3,019,479. It is a primate city, constituting 33% of the population of Hungary. The history of Budapest began when an early Celts, Celtic settlement transformed into the Ancient Rome, Roman town of Aquincum, the capital of Pannonia Inferior, Lower Pannonia. The Hungarian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
László Detre (astronomer)
László Detre (19 April 1906, Szombathely – 15 October 1974, Budapest) was a Hungarian astronomer well known for his work on variable stars. Detre was the director for many years of the Konkoly Observatory in Budapest (assuming the role in 1943), a professor of Budapest University, and editor of the ''Information Bulletin of Variable Stars'' of the International Astronomical Union. Discovered in 1940, asteroid 1538 Detre is named after him. His two sons were prominent sailors: Szabolcs Detre (father of windsurfer Diána Detre) and Zsolt Detre Zsolt Detre (born March 7, 1947) is a Hungarian sailor. He won the Olympic Bronze Medal in the 1980 Summer Olympics in the Sailing at the 1980 Summer Olympics, Flying Dutchman class along with his brother Szabolcs Detre. Early life His father wa .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Detre, Laszlo 20th-century Hungarian astronomers Members of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences 1906 births 1974 deaths 1974 suicides Suicides in Hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmologists
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the world". In 1731, German philosopher Christian Wolff used the term cosmology in Latin (''cosmologia'') to denote a branch of metaphysics that deals with the general nature of the physical world. Religious or mythological cosmology is a body of beliefs based on mythological, religious, and esoteric literature and traditions of creation myths and eschatology. In the science of astronomy, cosmology is concerned with the study of the chronology of the universe. Physical cosmology is the study of the observable universe's origin, its large-scale structures and dynamics, and the ultimate fate of the universe, including the laws of science that govern these areas. It is investigated by scientists, including astronomers and physicists, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shape Of The Universe
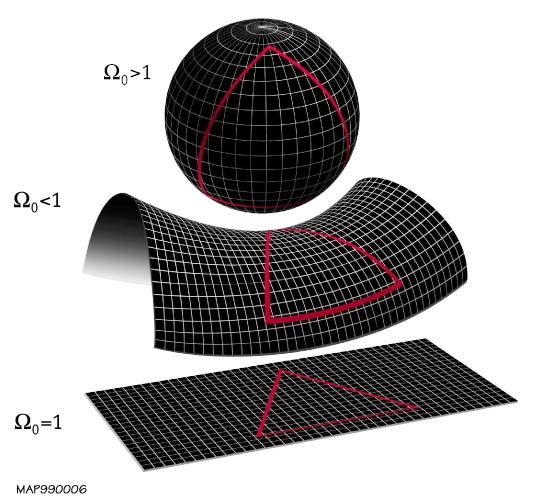
In physical cosmology, the shape of the universe refers to both its local and global geometry. Local geometry is defined primarily by its curvature, while the global geometry is characterised by its topology (which itself is constrained by curvature). General relativity explains how spatial curvature (local geometry) is constrained by gravity. The global topology of the universe cannot be deduced from measurements of curvature inferred from observations within the family of homogeneous general relativistic models alone, due to the existence of locally indistinguishable spaces with varying global topological characteristics. For example; a multiply connected space like a 3 torus has everywhere zero curvature but is finite in extent, whereas a flat simply connected space is infinite in extent (such as Euclidean space). Current observational evidence ( WMAP, BOOMERanG, and Planck for example) imply that the observable universe is spatially flat to within a 0.4% margin of error o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redshift Quantization
Redshift quantization, also referred to as redshift periodicity, redshift discretization, preferred redshifts and redshift-magnitude bands, is the hypothesis that the redshifts of cosmologically distant objects (in particular galaxies and quasars) tend to cluster around multiples of some particular value. In standard inflationary cosmological models, the redshift of cosmological bodies is ascribed to the expansion of the universe, with greater redshift indicating greater cosmic distance from the Earth (see Hubble's law). This is referred to as cosmological redshift and is one of the main pieces of evidence for the Big Bang. Quantized redshifts of objects would indicate, under Hubble's law, that astronomical objects are arranged in a quantized pattern around the Earth. It is more widely posited that the redshift is unrelated to cosmic expansion and is the outcome of some other physical mechanism, referred to as "intrinsic redshift" or "non-cosmological redshift". In 1973, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark Energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is a proposed form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. Its primary effect is to drive the accelerating expansion of the universe. It also slows the rate of structure formation. Assuming that the lambda-CDM model of cosmology is correct, dark energy dominates the universe, contributing 68% of the total energy in the present-day observable universe while dark matter and Baryon#Baryonic matter, ordinary (baryonic) matter contribute 27% and 5%, respectively, and other components such as neutrinos and photons are nearly negligible.Sean Carroll, Ph.D., Caltech, 2007, The Teaching Company, ''Dark Matter, Dark Energy: The Dark Side of the Universe'', Guidebook Part 2. p. 46. Retrieved 7 October 2013, "...dark energy: A smooth, persistent component of invisible energy, thought to make up about 70 percent of the energy density of the universe. Dark energy is smooth because it doesn't accumulate preferentially in galaxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological Constant
In cosmology, the cosmological constant (usually denoted by the Greek capital letter lambda: ), alternatively called Einstein's cosmological constant, is a coefficient that Albert Einstein initially added to his field equations of general relativity. He later removed it; however, much later it was revived to express the energy density of space, or vacuum energy, that arises in quantum mechanics. It is closely associated with the concept of dark energy. Einstein introduced the constant in 1917. to counterbalance the effect of gravity and achieve a static universe, which was then assumed. Einstein's cosmological constant was abandoned after Edwin Hubble confirmed that the universe was expanding. From the 1930s until the late 1990s, most physicists agreed with Einstein's choice of setting the cosmological constant to zero. That changed with the discovery in 1998 that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, implying that the cosmological constant may have a positive valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acta Physica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae
Acta or ACTA may refer to: Institutions * Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Agreement, an intellectual property trade agreement * Administrative Council for Terminal Attachments, a standards organization for terminal equipment such as registered jacks * Alameda Corridor Transportation Authority, in southern California * American Council of Trustees and Alumni, an education organization * Atlantic County Transportation Authority, a transportation agency in Atlantic County, New Jersey * Australian Community Television Alliance, an industry association representing community television licensees in Australia Science and technology * Acta, the transactions (proceedings) of an academic field, a learned society, or an academic conference * Acta (software), early outliner software * Activin A, mammalian protein * ACTA1, actin alpha 1 (skeletal muscle), human protein * ACTA2, actin alpha 2 (smooth muscle), human protein * Actin assembly-inducing protein, motility protein in the bacterium ''Listeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian People
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common culture, language and history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric branch of the Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty and Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, and Austria. In addition, significant groups of people with Hungarian ancestry live in various other parts of the world, most of them in the United States, Canada, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Chile, Brazil, Australia, and Argentina, and therefore constitute the Hungarian diaspora (). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'' is the peer review, peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' cover the full range of List of academ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |