|
Gyrinodon
''Gyrinodon'' is an extinct genus of toxodontid notoungulate that lived from the Late Miocene and Early Pliocene in what is now Brazil and Colombia. Description This animal was approximately the size of a modern rhinoceros, and they were similar in build as in appearance. Like most of its close relatives, ''Gyrinodons size was substantially larger than any other mammal in its habitat. The frontal region of the skull passed softly into the anterior portion of the temporal fossa. The postorbital processes were reduced. Unlike some of its relatives, neither the upper edge of the orbit nor the roof of the nasal cavity were swollen. The lateral upper incisors were curved, and formed an arch of 180° or more. The first two upper molars had a small metaloph, while the third molar had a long and concave ectoloph, but was devoid of metaloph. The symphysis of the mandible did not exceed the second lower molar. The third lower molar lacked a second posterior crease in the enamel of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxodontidae
Toxodontidae is an extinct family of notoungulate mammals, known from the Oligocene to the Holocene (11,000 BP) of South America, with one genus, ''Mixotoxodon'', also known from the Pleistocene of Central America and southwestern North America (Texas).E. Lundelius, et al. 2013. The first occurrence of a toxodont (Mammalia, Notoungulata) in the United States. ''Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology'', Vol 33, No 1, pp. 229–23DOI:10.1080/02724634.2012.711405/ref> They somewhat resembled rhinoceroses, and had teeth with high crowns and open roots, suggesting that they often fed on tough pampas grass. However, isotopic analyses have led to the conclusion that the most recent forms were grazing and browsing generalists. Taxonomy The endemic notoungulate and litoptern ungulates of South America have been shown by studies of collagen and mitochondrial DNA sequences to be a sister group to the perissodactyl Odd-toed ungulates, mammals which constitute the taxonomic order Peris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falcontoxodon
''Falcontoxodon'' is an extinct genus of toxodontid notoungulate that lived from the late Pliocene to the Pleistocene in what is now Venezuela. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Chapadmalalan-Uquian Codore Formation, as well as in the more recent Ensenadan San Gregorio Formation. Description The genus ''Falcontoxodon'' was described in 2018 by Carrillo ''et al'' with AMU-CURS 765, an almost complete skull with a well-preserved dentition found in the Algodones Member of the Codore Formation. In the same article, two other specimens assigned to ''Falcontoxodon'' were described from the Vergel Member of the San Gregorio Formation, assigned respectively to ''Falcontoxodon'' aff. ''aguilerai'' and ''Falcontoxodon'' sp. In 2021, an analysis of the San Gregorio Formation by Carrillo-Briceño ''et al'' uncovered thirty-three additional remains, mostly teeth, that were assigned to the genus. The name of the genus, ''Falcontoxodon'', refers to its relative, ''Toxodon'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piauhytherium
''Piauhytherium'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous notoungulate mammal of the family Toxodontidae. It lived during the Late Pleistocene, about 10,000 years ago; fossils have been found in Brazil. The only known species is ''Piauhytherium capivarae''.Guérin, Claude, and Martine Faure. "Un nouveau Toxodontidae (Mammalia, Notoungulata) du Pléistocène supérieur du Nordeste du Brésil." ''Geodiversitas'' 35.1 (2013): 155-205. Description This animal in general terms resembles a hippopotamus, with a big short snout, a massive body and a large head. The skull measured almost in length, which indicates that ''Piauhytherium'' could be as big as a modern black rhinoceros. With regard to its nearest relatives, such as ''Toxodon'', this animal's legs were shorter and thicker, in addition, certain differences in the denture distinguish it from other notoungulates of this period. Classification ''Piauhytherium capivarae'' was described for the first time in 2013, based on a comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixotoxodon
''Mixotoxodon'' ("mixture ''Toxodon''") is an extinct genus of notoungulate of the family Toxodontidae inhabiting South America, Central America and parts of southern North America during the Pleistocene epoch, from 1,800,000—12,000 years ago.''Mixotoxodon'' at .org Description 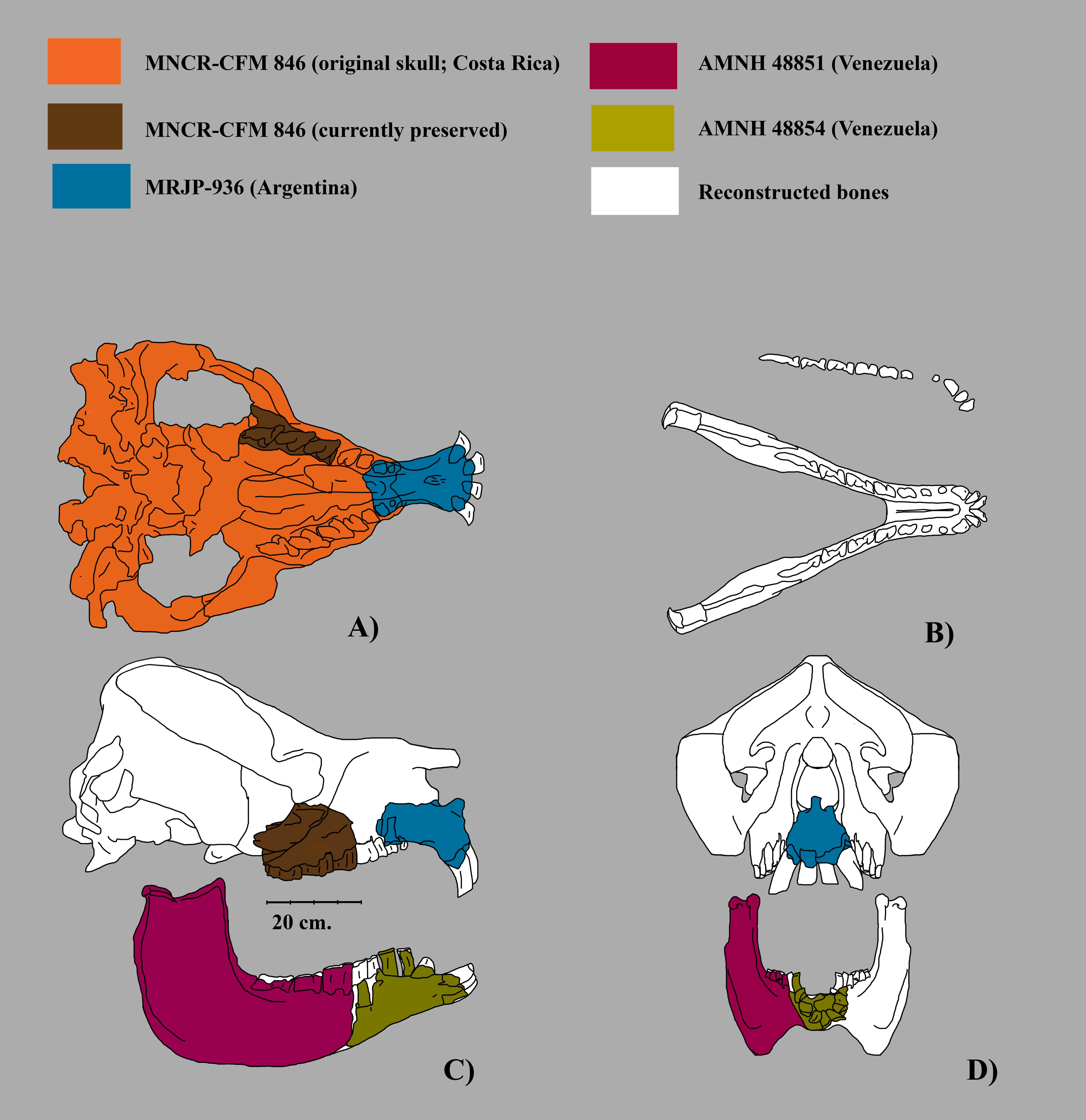
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urumaco Formation
The Urumaco Formation is a formation in Venezuela that includes deposits from the Late Miocene. It is the site of several "giant forms": the turtles, crocodiles, sloths and rodents of Urumaco are among the largest of their groups. Location The Urumaco formation is located in the Urumaco region in the Caribbean coastal Falcón state. The deposits date from 10 to 5.3 million years ago and the Urumaco formation was deposited in an area with large rivers, swamps, estuaries, lagoons and shallow coastal seas. These conditions in the Late Miocene contrast strongly with the current dry environment in the area today. Fauna Cartilaginous fish There are 21 known species of cartilaginous fishes from the Urumaco Formation, belonging to the orders Lamniformes, Carcharhiniformes, Myliobatiformes and Rajiformes. '' Carcharhinus caquetius'' is an endemic species of predator shark from Urumaco. A large number of well-preserved fossils of the sawfish '' Pristis rostra'' have been fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogene Colombia
The Neogene ( ), informally Upper Tertiary or Late Tertiary, is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period Mya. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868). During this period, mammals and birds continued to evolve into modern forms, while other groups of life remained relatively unchanged. The first humans (''Homo habilis'') appeared in Africa near the end of the period. Some continental movements took place, the most significant event being the connection of North and South America at the Isthmus of Panama, late in the Pliocene. This cut off the warm ocean currents from the Pacific to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Colombia
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, Seashell, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in #Resin, amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock stratum, strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogene Brazil
The Neogene ( ), informally Upper Tertiary or Late Tertiary, is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period Mya. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868). During this period, mammals and birds continued to evolve into modern forms, while other groups of life remained relatively unchanged. The first humans ('' Homo habilis'') appeared in Africa near the end of the period. Some continental movements took place, the most significant event being the connection of North and South America at the Isthmus of Panama, late in the Pliocene. This cut off the warm ocean currents from the Pacific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Mammals Of South America
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene Mammals Of South America
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic, Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time scale, which placed the four most recent major glaciations entirely within the Pleistocene, the Pliocene also included the Gelasian Stage, which lasted from 2.588 to 1.806 million years ago, and is now included in the Pleistocene. As with other older geologic periods, the Stratum, geological strata that define the start and end are well identified but the exact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Placental Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxodonts
Toxodontia. Retrieved April 2013. is a suborder of the meridiungulate order Notoungulata. Most of the members of the five included families, including the largest notoungulates, share several dental, auditory and tarsal specializations. The group is named after ''Toxodon'', the first example of the group to be discovered by science. Description Isotemnidae, the oldest and most primitive family of toxodonts, were generally large animals with larger canines than other early notoungulates. The family is probably paraphyletic or polyphyletic since only primitive dental features unite the 12 included genera, such as a complete dentition with unreduced canines and no diastemata in the earliest genera. Likewise, they are only weakly linked to other toxodonts by a few dental features, and their primitive cheek tooth pattern can be basal to all notoungulates except notioprogonians. The oldest of the 12 genera in this family is '' Isotemnus'' known from the Riochican-Casamayoran, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






