|
Toxodonts
Toxodontia. Retrieved April 2013. is a suborder of the meridiungulate order Notoungulata. Most of the members of the five included families, including the largest notoungulates, share several dental, auditory and tarsal specializations. The group is named after ''Toxodon'', the first example of the group to be discovered by science. Description Isotemnidae, the oldest and most primitive family of toxodonts, were generally large animals with larger canines than other early notoungulates. The family is probably paraphyletic or polyphyletic since only primitive dental features unite the 12 included genera, such as a complete dentition with unreduced canines and no diastemata in the earliest genera. Likewise, they are only weakly linked to other toxodonts by a few dental features, and their primitive cheek tooth pattern can be basal to all notoungulates except notioprogonians. The oldest of the 12 genera in this family is ''Isotemnus'' known from the Riochican-Casamayoran, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleurostylodon
''Pleurostylodon'' is an extinct Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ... genus of Notoungulata, notoungulate belonging to the family Isotemnidae. It lived during the Middle Eocene, in what is now Argentina. Description This genus is known from numerous remains, mainly cranial, allowing to reconstruct its morphology. It was approximately the size of a sheep, with an appearance evocating a tapir or a boar. ''Pleurostylodon'' had a large skull, widening in the orbital arch area, and narrowing in the posterior area of the muzzle, whose terminal part was enlarged and had small incisors ; there was no diastema after the canines. The muzzle was shorter than in more derived and specialized toxodonts such as ''Adinotherium'', and the occipital area was narrower. Several characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotemnus
''Isotemnus'' is an extinct genus of notoungulata, notoungulate belonging to the family Isotemnidae. It lived from the Late Paleocene to the Middle Eocene of what is now Argentina. Description This genus was smaller than ''Thomashuxleya'' and ''Periphragnis'', and did not exceed 50 kilograms in weight. Its build was comparable to a modern peccary, with a body relatively massive and strong and sturdy legs. Compared to other Eocene notoungulates, like basal Notohippidae and Notostylopidae, ''Isotemnus'' had an humerus whose distal part had a high medial trochlear crest, while the bicipital radial tuberosity was almost unexistant. The astragalus had a broad and low trochlea with a short neck. The calcaneus had rectangular fibular facets, and an unusually thick sustentaculum. Several of the distinctive anatomical leg characteristics of ''Isotemnus'' could be due to its smaller size ; ''Periphragnis'' and ''Thomashuxleya'', while very similar, had different characteristics. Classif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixotoxodon
''Mixotoxodon'' ("mixture ''Toxodon''") is an extinct genus of notoungulate of the family Toxodontidae inhabiting South America, Central America and parts of southern North America during the Pleistocene epoch, from 1,800,000—12,000 years ago.''Mixotoxodon'' at .org Description 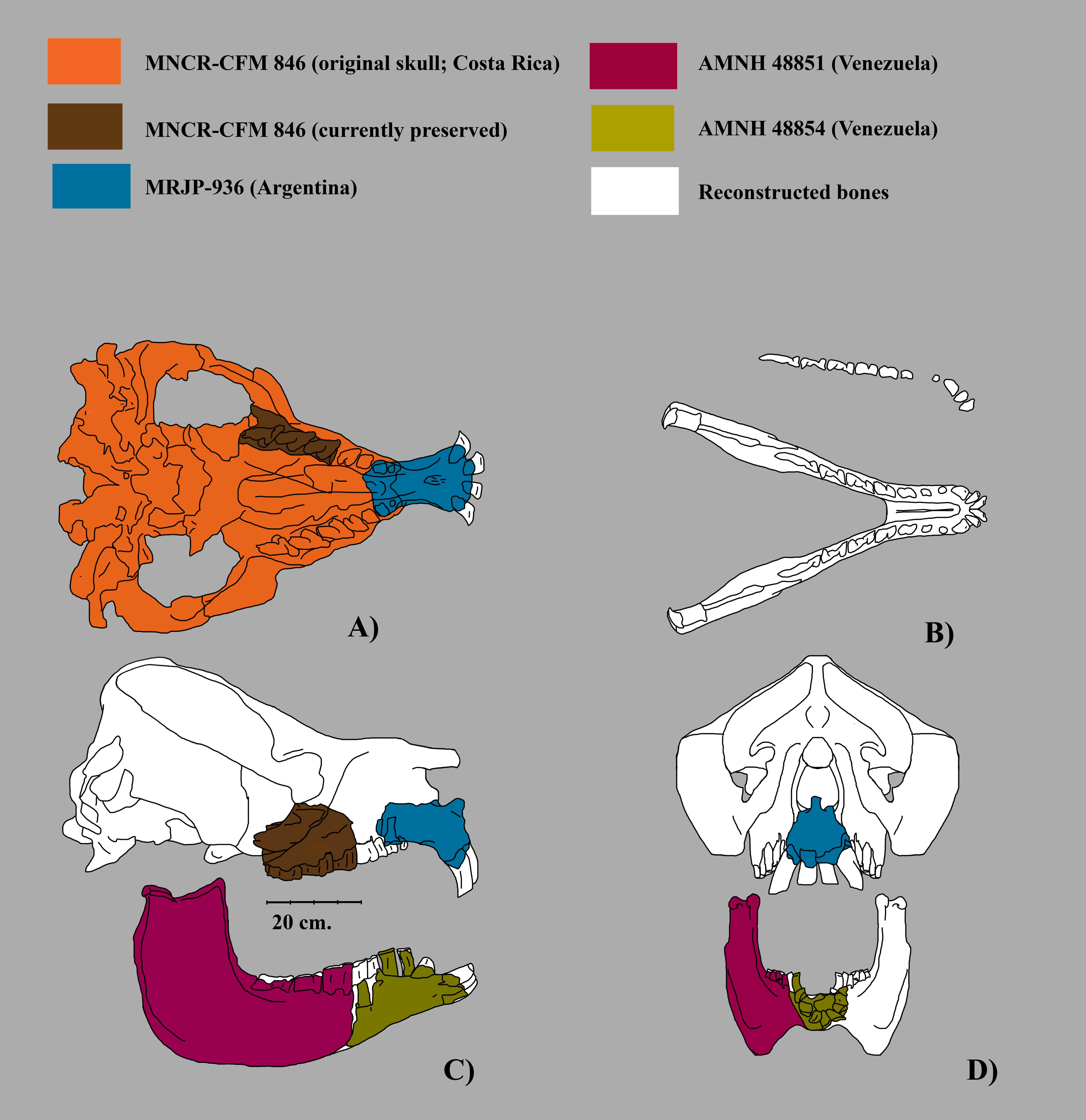
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casamayoran
The Casamayoran ( es, Casamayorense) age is a period of geologic time (50.0–48.0 Ma) within the Early Eocene epoch of the Paleogene, used more specifically within the South American land mammal age (SALMA) classification. It follows the Itaboraian and precedes the Mustersan age. Several astrapotherian mammals are known from this period, such as ''Antarctodon'' and ''Albertogaudrya'' from Antarctica and Argentina, respectively. ''Albertogaudrya'' and '' Scaglia'' were the size of a sheep or a small tapir, hence among the larger mammals in South America at this time.Rose, 2006, p.236 Etymology This age is named after the Casamayor Formation of the Golfo San Jorge Basin The Golfo San Jorge Basin ( es, Cuenca del Golfo San Jorge) is a hydrocarbon-rich sedimentary basin located in eastern Patagonia, Argentina. The basin covers the entire San Jorge Gulf and an inland area west of it, having one half located in Santa .... Formations Fossils References Bibliography ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachydont
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinmiguelia
''Martinmiguelia'' is an extinct genus of Notoungulate, belonging to the family Leontiniidae. It lived during the Middle Eocene, and its fossil remains were found in South America. Description This animal is only known from skull and mandible remains, and it probably shared similarities with later and better known leontiniids, such as ''Scarrittia''. It was smaller-sized than those derived genera, approximately the size of a sheep. ''Martinmiguelia'' was characterized by an archaic dental formula, with a complete dentition (three incisors, one canine, four premolars and three molars) and a quasi-absence of diastema, except for small spaces around the small-sized canines. The molars and premolars were low-crowned (brachydont), a primitive condition for leontinnids. The upper incisors were canine-like and possessed labial girdles, and the second upper incisor was larger than the others. Classification ''Martinmiguelia fernandezi'' was first described in 1995, based on fossils fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cementum
Cementum is a specialized calcified substance covering the root of a tooth. The cementum is the part of the periodontium that attaches the teeth to the alveolar bone by anchoring the periodontal ligament.Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 170. Structure The cells of cementum are the entrapped cementoblasts, the cementocytes. Each cementocyte lies in its lacuna, similar to the pattern noted in bone. These lacunae also have canaliculi or canals. Unlike those in bone, however, these canals in cementum do not contain nerves, nor do they radiate outward. Instead, the canals are oriented toward the periodontal ligament and contain cementocytic processes that exist to diffuse nutrients from the ligament because it is vascularized. After the apposition of cementum in layers, the cementoblasts that do not become entrapped in cementum line up along the cemental surface along the length of the outer covering of the perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santacrucian
The Santacrucian age is a period of geologic time (17.5 – 16.3 Ma) within the Early Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically with SALMA classification in South America. It follows the Colhuehuapian and precedes the Friasian age. Etymology The age is named after the Santa Cruz Formation in the Austral/Magallanes Basin of southern Patagonia Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and gl ..., Argentina and Chile. Formations Fossils References Bibliography ;Santa Cruz Formation * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ;Aisol Formation * * ;Cantaure Formation * ;Castillo Formation * * * * * ;Cerro Boleadores Formation * ;Chaguaramas Formation * ;Chilcatay Formation * * * * ;Cura-Mallín Group * * * ;Gran Bajo del Gualich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurygenium
''Eurygenium'' is an extinct genus of notoungulate belonging to the family Notohippidae. It lived during the Late Oligocene in what is today South America. Description It was a medium-sized mammal ; the best known species, ''Eurygenium pacegnum'', was approximately 80 centimeters long and weighed 10 kilograms. Its body was relatively compact, with more robust legs than its relatives, such as '' Rhynchippus''; unlike the latter, however, ''Eurygenium'' had tetradactyls forelegs and a third trochanter near the femoral midline. The skull of ''Eurygenium'' was characterized by a short and broad muzzle, with strong and laterally expanded zygomatic arches. The dentition was devoid of diastema. As in all Notohippidae, premolars and molars had a very high crown (hypsodont). The upper premolars lacked an anterolingual cingulum, while the posterolingual cingulum was reduced. The lower incisors cingulum was reduced or absent, while the lower premolars and molars had a dimple at the trigon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchippus
''Rhynchippus'' ("Snout Horse") is an extinct genus of notoungulate mammals from the Late Oligocene ( Deseadan in the SALMA classification) of South America. The genus was first described by Florentino Ameghino in 1897 and the type species is ''R. equinus'', with lectotype MACN A 52–31. Fossils of ''Rhynchippus'' have been found in the Agua de la Piedra and Sarmiento Formations of Argentina, the Salla and Petaca Formations of Bolivia, the Tremembé Formation of Brazil,''Rhynchippus'' at Fossilworks.org and the Moquegua Formation of |
Deseadan
The Deseadan ( es, Deseadense) age is a period of geologic time (29.0–21.0 Ma) within the Oligocene epoch of the Paleogene to the Early Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification of South America. It follows the Tinguirirican and precedes the Colhuehuapian age. Etymology The age is named after the Deseado Formation of the Deseado Massif in eastern Patagonia, Argentina. Formations Fossils Correlations The Deseadan South American land mammal age (SALMA) is equivalent to the Arikareean in the North American land mammal age (NALMA) and the Harrisonian in the 2000 version of the classification. It overlaps with the Hsandagolian The Hsandagolian age is a period of geologic time (33.9 – 23.03 Ma) within the Oligocene epoch of the Paleogene used more specifically with Asian Land Mammal Ages. It follows the Kekeamuan and precedes the Tabenbulakian age. The Ulangochuian ... of Asia and the MP 25 zone of Europe, the Waitaki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mustersan
The Mustersan age is a period of geologic time (48.0–42.0 Ma) within the Eocene epoch of the Paleogene, used more specifically within the South American land mammal age (SALMA) classification. It follows the Casamayoran and precedes the Divisaderan age.Mustersan at .orgWoodburne et al., 2013 Etymology This age is named after Lake Musters in the |

