|
Greenfield, IN
Greenfield is a city in and the county seat of Hancock County, Indiana, Hancock County, Indiana, United States, and a part of the Indianapolis metropolitan area. The population was 20,602 at the 2010 census, and an estimated 23,006 in 2019. It lies in Center Township, Hancock County, Indiana, Center Township. Greenfield was a stop along the Pittsburgh, Cincinnati, Chicago and St. Louis Railroad that connected Pittsburgh to Chicago and St. Louis. History Hancock County was created on March 1, 1828, and named for John Hancock, the first person to sign the United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence. The town of Greenfield was chosen as the county seat on April 11, 1828. The Commissioners announced, "The seat of Justice of Hancock County shall be known and designated by the name and title of Greenfield." The population of the county at that time was 400. Early settlers built along the two creeks which flow south through Center Township, which includes Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indianapolis Metropolitan Area
Indianapolis–Carmel–Anderson or Indianapolis metropolitan area is an 11-county metropolitan area in the U.S. state of Indiana, as defined by the Office of Management and Budget. The metropolitan area is situated in Central Indiana, within the American Midwest. The metropolitan area is centered on the capital and most populous city of Indiana, Indianapolis. Indianapolis–Carmel–Anderson is the 32nd most populous metropolitan area in the United States and largest in the state of Indiana. As of 2020, the population was 2,111,040. Indianapolis also anchors the larger Indianapolis–Carmel–Muncie combined statistical area (CSA), the 26th most populated, with 2,457,286. The Indianapolis metropolitan area is part of the Great Lakes Megalopolis, which contains an estimated 59 million people. Metropolitan areas In the 2020 Census, there were 2,111,040 people residing in the MSA. The racial demographics were 69.6% White, 15.0% Black or African-American, 0.4% American Indian or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boomtown
A boomtown is a community that undergoes sudden and rapid population and economic growth, or that is started from scratch. The growth is normally attributed to the nearby discovery of a precious resource such as gold, silver, or oil, although the term can also be applied to communities growing very rapidly for different reasons, such as a proximity to a major metropolitan area, huge construction project, or attractive climate. First boomtowns Early boomtowns, such as Leeds, Liverpool, and Manchester, experienced a dramatic surge in population and economic activity during the Industrial Revolution at the turn of the 19th century. In pre-industrial England these towns had been relative backwaters, compared to the more important market towns of Bristol, Norwich, and York, but they soon became major urban and industrial centres. Although these boomtowns did not directly owe their sudden growth to the discovery of a local natural resource, the factories were set up there to take a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, and helium are also usually present. Natural gas is colorless and odorless, so odorizers such as mercaptan (which smells like sulfur or rotten eggs) are commonly added to natural gas supplies for safety so that leaks can be readily detected. Natural gas is a fossil fuel and non-renewable resource that is formed when layers of organic matter (primarily marine microorganisms) decompose under anaerobic conditions and are subjected to intense heat and pressure underground over millions of years. The energy that the decayed organisms originally obtained from the sun via photosynthesis is stored as chemical energy within the molecules of methane and other hydrocarbons. Natural gas can be burned fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
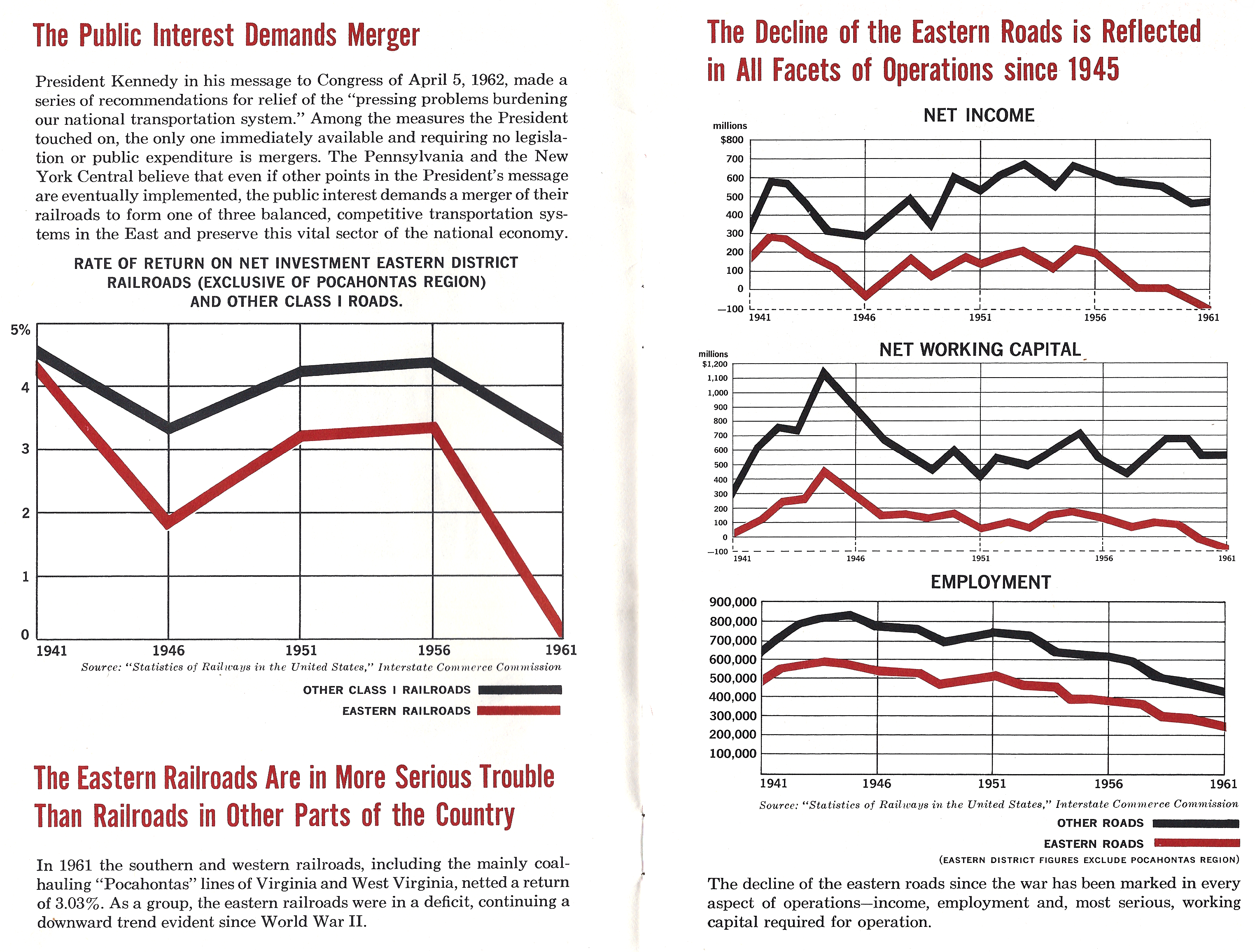
Penn Central Transportation Company
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American class I railroad that operated from 1968 to 1976. Penn Central combined three traditional corporate rivals (the Pennsylvania, New York Central and the New York, New Haven and Hartford railroads), all united by heavy service into the New York metropolitan area and (to a lesser extent) New England and Chicago. The new company failed barely two years after formation, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history at the time. The Penn Central's railroad assets were nationalized into Conrail along with the other bankrupt northeastern roads; its real estate and insurance holdings successfully reorganized into American Premier Underwriters. History Pre-merger The Penn Central railroad system developed in response to challenges facing northeastern American railroads during the late 1960s. While railroads elsewhere in North America drew revenues from long-distance shipments of commodities suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
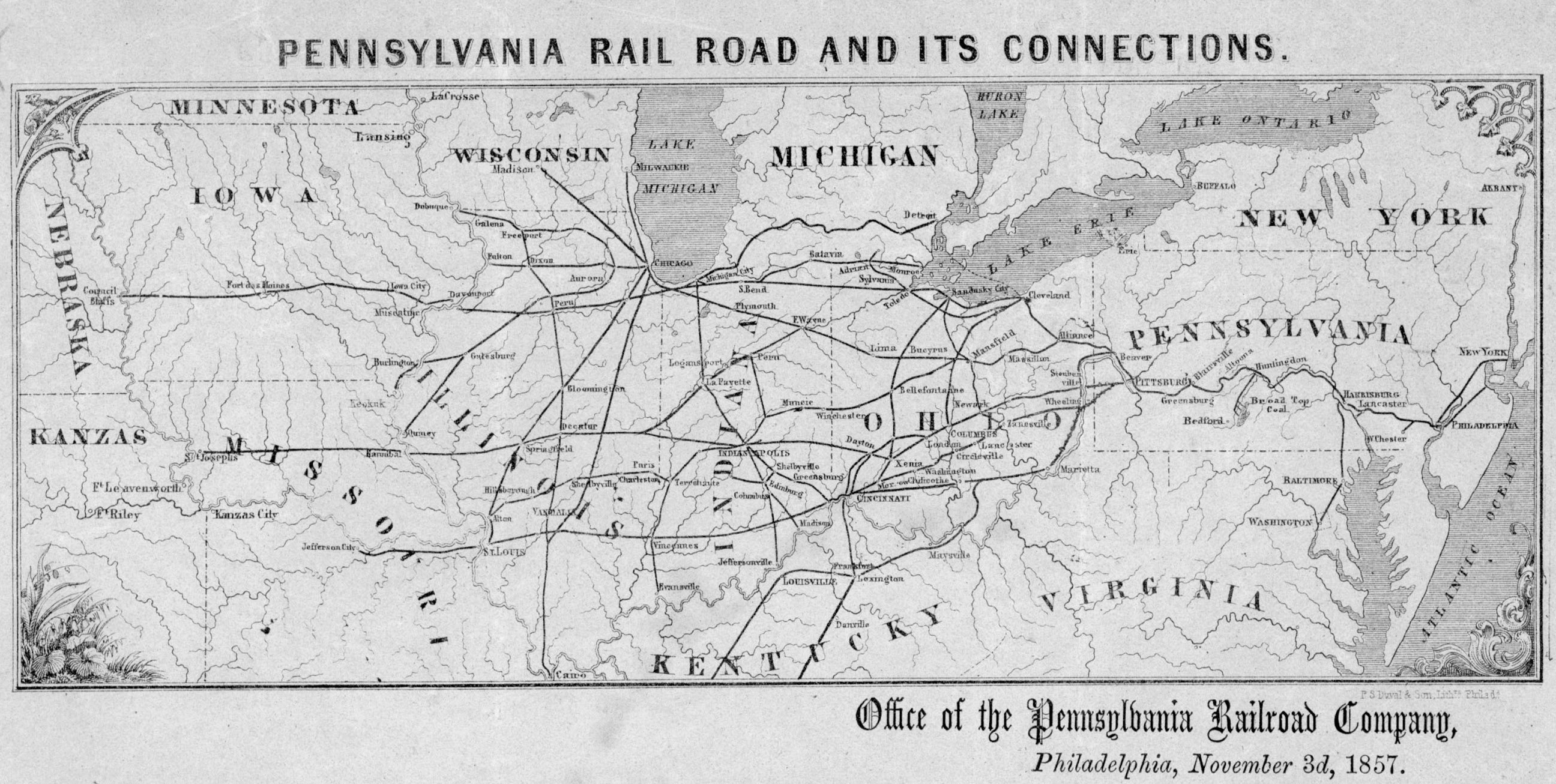
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named for the commonwealth in which it was established. By 1882, Pennsylvania Railroad had become the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Its budget was second only to the U.S. government. Over the years, it acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Hamilton County. Settled in 1788, the city is located at the northern side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio rivers, the latter of which marks the state line with Kentucky. The city is the economic and cultural hub of the Cincinnati metropolitan area. With an estimated population of 2,256,884, it is Ohio's largest metropolitan area and the nation's 30th-largest, and with a city population of 309,317, Cincinnati is the third-largest city in Ohio and 64th in the United States. Throughout much of the 19th century, it was among the top 10 U.S. cities by population, surpassed only by New Orleans and the older, established settlements of the United States eastern seaboard, as well as being the sixth-most populous city from 1840 until 1860. As a rivertown crossroads at the junction of the North, South, East, and West, Cincinnati developed with fewer immigrants and less influence from Europe than Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Road
The National Road (also known as the Cumberland Road) was the first major improved highway in the United States built by the Federal Government of the United States, federal government. Built between 1811 and 1837, the road connected the Potomac River, Potomac and Ohio Rivers and was a main transport path to the Western United States, West for thousands of settlers. When improved in the 1830s, it became the second U.S. road surfaced with the macadam process pioneered by Scotsman John Loudon McAdam. Construction began heading west in 1811 at Cumberland, Maryland, on the Potomac River. After the panic of 1837, Financial Panic of 1837 and the resulting economic depression, congressional funding ran dry and construction was stopped at Vandalia, Illinois, the then-capital of Illinois, northeast of St. Louis, Missouri, St. Louis across the Mississippi River. The road has also been referred to as the Cumberland Turnpike, the Cumberland–Brownsville Turnpike (or Road or Pike), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gristmill
A gristmill (also: grist mill, corn mill, flour mill, feed mill or feedmill) grinds cereal grain into flour and Wheat middlings, middlings. The term can refer to either the Mill (grinding), grinding mechanism or the building that holds it. Grist is grain that has been separated from its chaff in preparation for grinding. History Early history The Greek geographer Strabo reports in his ''Geography'' a water-powered grain-mill to have existed near the palace of king Mithradates VI Eupator at Cabira, Asia Minor, before 71 BC. The early mills had horizontal paddle wheels, an arrangement which later became known as the "Water wheel#Vertical axis, Norse wheel", as many were found in Scandinavia. The paddle wheel was attached to a shaft which was, in turn, attached to the centre of the millstone called the "runner stone". The turning force produced by the water on the paddles was transferred directly to the runner stone, causing it to grind against a stationary "Mill machinery#Wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Declaration Of Independence
The United States Declaration of Independence, formally The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen States of America, is the pronouncement and founding document adopted by the Second Continental Congress meeting at Pennsylvania State House (later renamed Independence Hall) in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, on July 4, 1776. Enacted during the American Revolution, the Declaration explains why the Thirteen Colonies at war with the Kingdom of Great Britain regarded themselves as thirteen independent sovereign states, no longer subject to British colonial rule. With the Declaration, these new states took a collective first step in forming the United States of America and, de facto, formalized the American Revolutionary War, which had been ongoing since April 1775. The Declaration of Independence was signed by 56 of America's Founding Fathers, congressional representatives from New Hampshire, Massachusetts Bay, Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Connecticut, New York, New Jer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hancock
John Hancock ( – October 8, 1793) was an American Founding Father, merchant, statesman, and prominent Patriot of the American Revolution. He served as president of the Second Continental Congress and was the first and third Governor of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. He is remembered for his large and stylish signature on the United States Declaration of Independence, so much so that the term ''John Hancock'' or ''Hancock'' has become a nickname in the United States for one's signature. He also signed the Articles of Confederation, and used his influence to ensure that Massachusetts ratified the United States Constitution in 1788. Before the American Revolution, Hancock was one of the wealthiest men in the Thirteen Colonies, having inherited a profitable mercantile business from his uncle. He began his political career in Boston as a protégé of Samuel Adams, an influential local politician, though the two men later became estranged. Hancock used his wealth to support t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will , image_map = , map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = State , subdivision_type2 = Counties , subdivision_name1 = Illinois , subdivision_name2 = Cook and DuPage , established_title = Settled , established_date = , established_title2 = Incorporated (city) , established_date2 = , founder = Jean Baptiste Point du Sable , government_type = Mayor–council , governing_body = Chicago City Council , leader_title = Mayor , leader_name = Lori Lightfoot ( D) , leader_title1 = City Clerk , leader_name1 = Anna Valencia ( D) , unit_pref = Imperial , area_footnotes = , area_tot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


(cropped).jpg)
