|
Greater Armenia
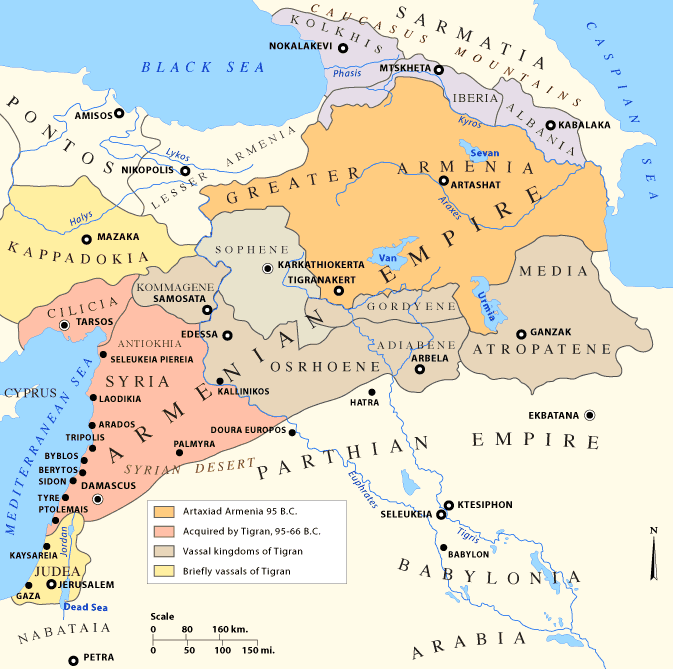
Greater Armenia ( hy, Մեծ Հայք, translit=Mets Hayk) is the name given to the Armenian state that emerged on the Armenian Highlands during the reign of King Artaxias I at the turn of the 2nd century BC. The term was used to refer principally to the fifteen provinces that made up Armenian kingdoms throughout the classical, late antique, and medieval periods by contemporary Armenian and non-Armenian authors alike. Extent Though its borders were never exactly defined, Greater Armenia usually referred to the stretch of land beginning from the Euphrates River to the west, the region of Artsakh and parts of what are now Azerbaijan and Iranian Azerbaijan to the east, parts of the modern state of Georgia to the north, with its southern boundary rounding the northern tip of Mesopotamia. The Romans referred to it in Latin as ''Armenia Maior'' while the Greek-speaking peoples called it ''Armenia Megale'' (), to differentiate it from Lesser Armenia (''Pok'r Hayk′'', in Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maps Of The Armenian Empire Of Tigranes
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, other countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. They also form a significant diaspora (), with Greek communities established around the world.. Greek colonies and communities have been historically established on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea, but the Greek people themselves have always been centered on the Aegean and Ionian seas, where the Greek language has been spoken since the Bronze Age.. Until the early 20th century, Greeks were distributed between the Greek peninsula, the western coast of Asia Minor, the Black Sea coast, Cappadocia in central Anatolia, Egypt, the Balkans, Cyprus, and Constantinople. Many of these regions coincided to a large extent with the borders of the Byzantine Empire of the late 11th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenia (other)
Armenia is a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia. Armenia may also refer to: Places Historical * Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic (1922–1991), a former republic of USSR * First Republic of Armenia (1918–1920) * Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), a kingdom from 331 BC to 428 AD * Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, a state along the coast of the Mediterranean around the time of the Crusades * Armenia (East Syriac diocese), a diocese of the Church of the East Colombia * Armenia, Colombia, a city in Quindío Department * Armenia, Antioquia, a municipality in Antioquia Department United States * Armenia, Wisconsin * Armenia Township, Bradford County, Pennsylvania * Little Armenia, Los Angeles * Armenia Gardens Estates, Tampa, Florida Honduras * Armenia Bonito, Atlántida, Atlántida Department * Nueva Armenia, a municipality in department of Francisco Morazán Other places * Armenian Highlands, a plateau in Asia sometimes known as Armenia * Armenia, Belize, in Cayo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Hewsen
Robert H. Hewsen (May 20, 1934 – November 17, 2018) was an American historian and professor of history at Rowan University. He was an expert on the ancient history of the South Caucasus. Hewsen is the author of ''Armenia: A Historical Atlas'' (2001), a major reference book, acclaimed as an important achievement in Armenian studies. Biography Hewsen was born Robert H. Hewsenian in New York City in 1934 to Armenian American parents. He spent seven years in Europe with the US Air Force and studying. He received his B.A. in history from the University of Maryland and his Ph.D. from Georgetown University in 1967. The same year he joined the history department of Rowan University, where he taught Byzantine and Russian history for more than 30 years. After retiring from Rowan University in July 1999, Professor Hewsen lectured at University of Chicago, Columbia University, California State University, Fresno and University of California, Los Angeles. Professor Hewsen was also the co-fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nina Garsoïan
Nina G. Garsoïan (April 11, 1923 – August 14, 2022) was a French-born American historian specializing in Armenian and Byzantine history. In 1969 she became the first female historian to get tenure at Columbia University and, subsequently, became the first holder of Gevork M. Avedissian Chair in Armenian History and Civilization at Columbia. From 1977 to 1979, she served as dean of the Graduate School of Princeton University. Biography Nina G. Garsoïan was born in Paris on April 11, 1923, to Armenian parents from Nakhichevan-on-Don (Rostov-on-Don) and Tbilisi. She moved to New York in 1933. She received a Bachelor of Arts in classical archaeology from Bryn Mawr College in 1943 and both Master of Arts degree and PhD from Columbia University in Byzantine, Near Eastern, and Armenian history. She received Fulbright Fellowship to study at the Mekhitarist monastery of San Lazzaro degli Armeni on San Lazzaro Island in Venice. Garsoïan began teaching at Smith College in 1956 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Adontz
Nicholas Adontz (, ''Nikoghayos Adonts’'', also spelled Adonts; ; January 10, 1871 – January 27, 1942) was an Armenian historian, specialist of Byzantine and Armenian studies, and philologist. Yuzbashyan, Karen. s.v. Adonts', Nikoghayos Gevorki. Armenian Soviet Encyclopedia. Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences, 1974, vol. 1, p. 77. Adontz was the author of ''Armenia in the Period of Justinian'', a highly influential work and landmark study on the social and political structures of early Medieval Armenia. Biography Early life Adontz was born Nikoghayos Ter-Avetikian () in the village of Brnakot in Sisian, which was then part of the Zangezur ''uezd'' of the Elisabethpol Governorate (modern Syunik). His family traced its roots to an eighteenth-century Armenian military figure and close ally of David Bek named Ter-Avetik. Yuzbashyan, Karen. "Nikoghayos Adonts'i gitakan zharangut'yune" he intellectual legacy of Nikoghayos Adonts ''Patma-Banasirakan Handes'' 4 (1962): pp. 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the '' Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography (Ptolemy)
The ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Γεωγραφικὴ Ὑφήγησις, ''Geōgraphikḕ Hyphḗgēsis'', "Geographical Guidance"), also known by its Latin names as the ' and the ', is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, compiling the geographical knowledge of the 2nd-century Roman Empire. Originally written by Claudius Ptolemy in Greek at Alexandria around AD 150, the work was a revision of a now-lost atlas by Marinus of Tyre using additional Roman and Persian gazetteers and new principles. Its translation into Arabic in the 9th century and Latin in 1406 was highly influential on the geographical knowledge and cartographic traditions of the medieval Caliphate and Renaissance Europe. Manuscripts Versions of Ptolemy's work in antiquity were probably proper atlases with attached maps, although some scholars believe that the references to maps in the text were later additions. No Greek manuscript of the ''Geography'' survives from earlier than the 13th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emirate Of Armenia
Arminiya, also known as the Ostikanate of Arminiya ( hy, Արմինիա ոստիկանություն, ''Arminia vostikanut'yun'') or the Emirate of Armenia ( ar, إمارة أرمينيا, ''imārat Arminiya''), was a political and geographic designation given by the Muslim Arabs to the lands of Greater Armenia, Caucasian Iberia, and Caucasian Albania, following their conquest of these regions in the 7th century. Though the caliphs initially permitted an Armenian prince to represent the province of ''Arminiya'' in exchange for tribute and the Armenians' loyalty during times of war, Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan introduced direct Arab rule of the region, headed by an ''ostikan'' with his capital in Dvin. According to the historian Stephen H. Rapp in the third edition of the ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'': History Early period: the Arab conquest of Armenia The details of the early conquest of Armenia by the Arabs are uncertain, as the various Arabic sources conflict with the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Kingdom Of Cilicia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia (Middle Armenian: , '), also known as Cilician Armenia ( hy, Կիլիկեան Հայաստան, '), Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia ( hy, Կիլիկիայի հայկական իշխանութիւն), was an Armenians, Armenian state formed during the High Middle Ages by Armenian refugees fleeing the Seljuk Empire, Seljuk invasion of Armenia., pp. 630–631. Located outside the Armenian Highlands and distinct from the Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Kingdom of Armenia of classical antiquity, antiquity, it was centered in the Cilicia region northwest of the Gulf of Alexandretta. The kingdom had its origins in the principality founded c. 1080 by the Rubenid dynasty, an alleged offshoot of the larger Bagratuni dynasty, which at various times had held the throne of Armenia. Their capital was originally at Tarsus (city), Tarsus, and later became Sis (ancient city), Sis. Cilicia wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Armenian Soviet Encyclopedia'' ( hy, Հայկական սովետական հանրագիտարան, ''Haykakan sovetakan hanragitaran''; ASE) publishing house was established in 1967 as a department of the Institute of History of the Armenian Academy of Sciences under the presidency of Viktor Hambardzumyan (1908–1996), co-edited by Abel Simonyan (1922–1994) and Makich Arzumanyan (1919–1988). In 1988–1999 the editor-in-chief was Konstantin Khudaverdyan (1929–1999) and since 1999 Hovhannes Aivazyan. It produced the ''Soviet Armenian Encyclopedia'' (also rendered ''Armenian Soviet Encyclopedia''; '' hy, Հայկական Սովետական Հանրագիտարան'', ', ''russian: Армя́нская сове́тская энциклопе́дия'', ' ) from 1974–1986. The AE publishing house also edited a children's encyclopedia, ''Who is it? What is it?'' ( hy, italic=yes, Ո՞վ է, Ի՞նչ է) in 4 volumes (1984–87), the ''Russian-Armenian Polytechnical Dic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suren Yeremyan
Suren Tigrani Yeremian ( hy, Սուրեն Տիգրանի Երեմյան; russian: Сурен Тигранович Еремян; – 17 December 1992) was a Soviet and Armenian historian and cartographer who specialized in the study of the early formation of the Armenian nation, pre-medieval Armenia, and the Caucasus. He devoted nearly thirty years of his scholarly efforts in reconstructing the ''Ashkharhatsuyts'', a seventh-century atlas commonly attributed to Anania Shirakatsi.See the "Preface" and "Introduction" in Robert Hewsen's ''The Geography of Ananias of Širak: Asxarhacoyc, the Long and the Short Recensions''. Wiesbaden: Dr. Ludwig Reichert, 1992, . Biography Early life and education Yeremian was born into a family of laborers in Tiflis, in 1908 and attended a local Russian school. Presidency of the Armenian Academy of the Sciences, Institute of History. "S. T. Yeremian," ''Patma-Banasirakan Handes'' 135-136 (1992), pp. 255-256. Mahé, Jean-Pierre. "In Memoriam: Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)

