|
Gothic Tribes
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. In his book ''Getica'' (c. 551), the historian Jordanes writes that the Goths originated in southern Scandinavia, but the accuracy of this account is unclear. A people called the ''Gutones''possibly early Gothsare documented living near the lower Vistula River in the 1st century, where they are associated with the archaeological Wielbark culture. From the 2nd century, the Wielbark culture expanded southwards towards the Black Sea in what has been associated with Gothic migration, and by the late 3rd century it contributed to the formation of the Chernyakhov culture. By the 4th century at the latest, several Gothic groups were distinguishable, among whom the Thervingi and Greuthungi were the most powerful. During this time, Wulfila began t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grande Ludovisi Altemps Inv8574 (cropped)
Grande means "wikt:large, large" or "great (other), great" in many of the Romance languages. It may also refer to: Places *Grande, Germany, a municipality in Germany *Grande Communications, a telecommunications firm based in Texas *Grande-Rivière (other) *Arroio Grande (other) *Boca grande (other) *Campo Grande (other) *El Grande, a German-style board game *Loma Grande (other) *Lucida Grande, a humanist sans-serif typeface *María Grande, a village and municipality in Entre Ríos Province in northeastern Argentina *Mojón Grande, a village and municipality in Misiones Province in northeastern Argentina *Playa Grande (other) *Ribeira Grande (other) *Rio Grande (other) *Salto Grande (other) *Valle Grande (other) *Várzea Grande (other) *Villa Grande (other) *Casa Grande Ruins National Monument *Casas Grandes *Mesa Grande *Pueblo Grande de Nevada *Pueblo Grande Ruin a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time; the Huns' arrival is associated with the migration westward of an Iranian people, the Alans. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, and by 430, they had established a vast, if short-lived, dominion in Europe, conquering the Goths and many other Germanic peoples living outside of Roman borders and causing many others to flee into Roman territory. The Huns, especially under their King Attila, made frequent and devastating raids into the Eastern Roman Empire. In 451, they invaded the Western Roman province of Gaul, where they fought a combined army of Romans and Visigoths at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, and in 452, they invaded Italy. After the death of Attila in 453, the Huns ceased to be a major thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty ( ar, ٱلْأُمَوِيُّون, ''al-ʾUmawīyūn'', or , ''Banū ʾUmayyah'', "Sons of Umayyah"). Uthman ibn Affan (r. 644–656), the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member of the clan. The family established dynastic, hereditary rule with Muawiya ibn Abi Sufyan, long-time governor of Greater Syria, who became the sixth caliph after the end of the First Fitna in 661. After Mu'awiyah's death in 680, conflicts over the succession resulted in the Second Fitna, and power eventually fell into the hands of Marwan I from another branch of the clan. Greater Syria remained the Umayyads' main power base thereafter, with Damascus serving as their capital. The Umayyads continued the Muslim conquests, incorpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umayyad Conquest Of Hispania
The Umayyad conquest of Hispania, also known as the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom, was the initial expansion of the Umayyad Caliphate over Hispania (in the Iberian Peninsula) from 711 to 718. The conquest resulted in the decline of the Visigothic Kingdom and the establishment of the Umayyad Wilayah of Al-Andalus. During the caliphate of the sixth Umayyad caliph al-Walid I (), forces led by Tariq ibn Ziyad disembarked in early 711 in Gibraltar at the head of an army consisting of Berbers from north Africa. After defeating the Visigothic king Roderic at the decisive Battle of Guadalete, Tariq was reinforced by an Arab force led by his superior ''wali'' Musa ibn Nusayr and continued northward. By 717, the combined Arab-Berber force had crossed the Pyrenees into Septimania. They occupied further territory in Gaul until 759. Background The historian al-Tabari transmits a tradition attributed to the Caliph Uthman who stated that the road to Constantinople was throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic War (535–554)
The Gothic War between the Eastern Roman Empire during the reign of Emperor Justinian I and the Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy took place from 535 to 554 in the Italian Peninsula, Dalmatia, Sardinia, Sicily and Corsica. It was one of the last of the many Gothic Wars against the Roman Empire. The war had its roots in the ambition of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Emperor Justinian I to recover the provinces of the former Western Roman Empire, which the Romans had lost to invading barbarian tribes in the previous century, during the Migration Period. The war followed the Eastern Roman reconquest of the province of Africa from the Vandals. Historians commonly divide the war into two phases: * From 535 to 540: ending with the fall of the Ostrogothic capital Ravenna and the apparent reconquest of Italy by the Byzantines. * From 540/541 to 553: a Gothic revival under Totila, suppressed only after a long struggle by the Byzantine general Narses, who also repelled an invasion in 554 by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the capital of the Ostrogothic Kingdom until it was re-conquered in 540 by the Byzantine Empire. Afterwards, the city formed the centre of the Byzantine Exarchate of Ravenna until the last exarch was executed by the Lombards in 751. Although it is an inland city, Ravenna is connected to the Adriatic Sea by the Candiano Canal. It is known for its well-preserved late Roman and Byzantine architecture, with eight buildings comprising the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Early Christian Monuments of Ravenna". History The origin of the name ''Ravenna'' is unclear. Some have speculated that "Ravenna" is related to "Rasenna" (or "Rasna"), the term that the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans used for themselves, but there is no agreement on this point. Ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
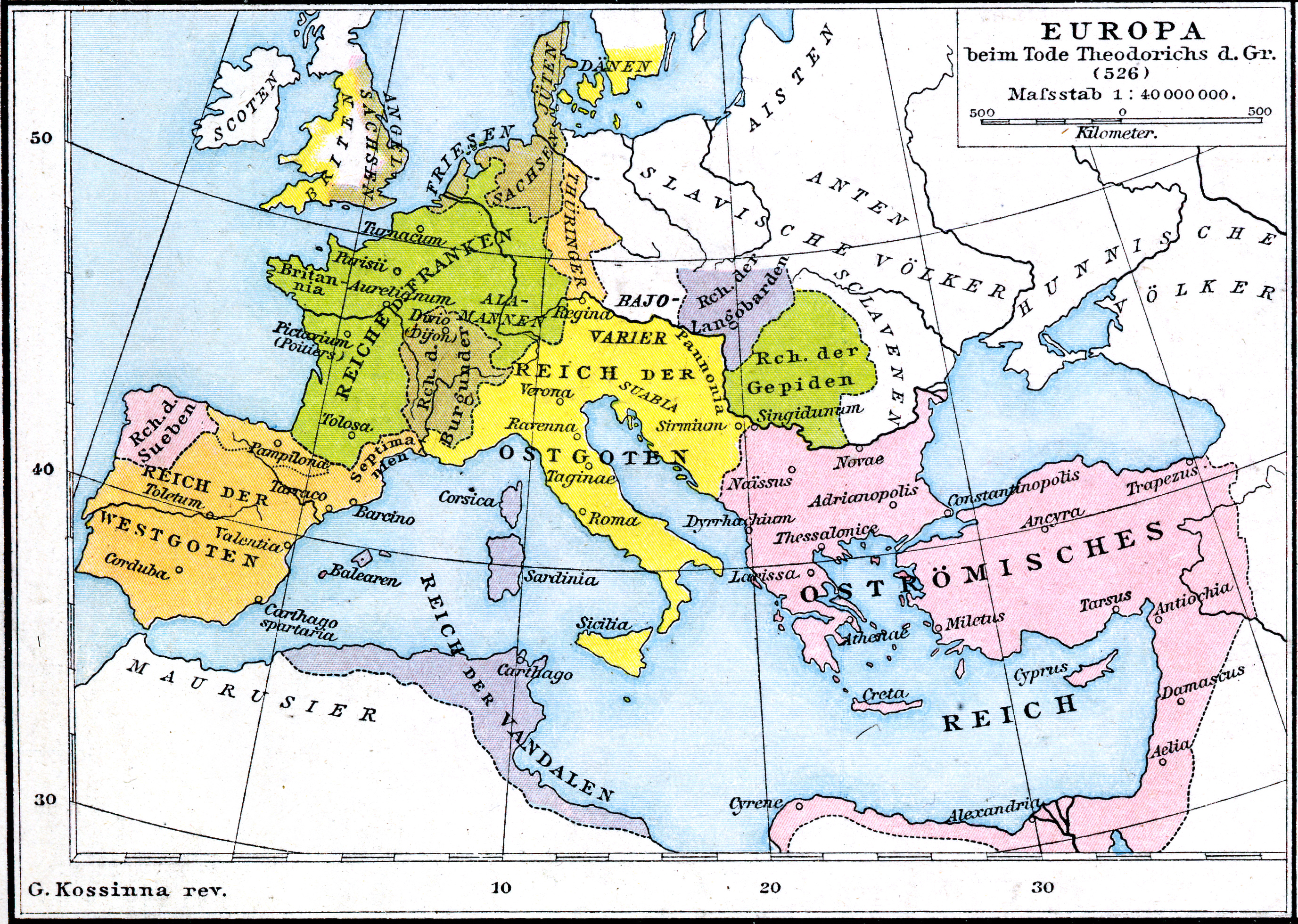
Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), existed under the control of the Germanic peoples, Germanic Ostrogoths in Italian peninsula, Italy and neighbouring areas from 493 to 553. In Italy, the Ostrogoths led by Theodoric the Great killed and replaced Odoacer, a Germanic soldier, erstwhile-leader of the ''foederati'' in Northern Italy, and the ''de facto'' Kingdom of Odoacer, ruler of Italy, who had deposed the last emperor of the Western Roman Empire, Romulus Augustulus, in 476. Under Theodoric, its first king, the Ostrogothic kingdom reached its zenith, stretching from modern southern France in the west to the modern western Serbia in the southeast. Most of the social institutions of the late Western Roman Empire were preserved during his rule. Theodoric called himself ''Gothorum Romanorumque rex'' ("King of the Goths and Romans"), demonstrating his desire to be a leader for both peoples. Starting in 535, the Byzantine Empire invaded Italy under Justinian I. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician of the Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Western Roman Emperor in all but name, since he ruled large parts of the former Western Roman Empire, had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497, and was referred to by the title ''augustus'' by some of his subjects. As a young child of an Ostrogothic nobleman, Theodoric was taken as a hostage to Constantinople, where he spent his formative years and received an East Roman education (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century, having crossed the Lower Danube. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under the influence of the Amal dynasty, the family of Theodoric the Great. After the death of Attila and collapse of the Hunnic empire represented by the Battle of Nedao in 453, the Amal family began to form their kingdom in Pannonia. Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Zeno (emperor), Emperor Zeno played these Pannonian Goths off against the Thracian Goths, but instead the two groups united after the death of the Thracian leader Theoderic Strabo and his son Recitach. Zeno then backed Theodori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toledo, Spain
Toledo ( , ) is a city and municipality of Spain, capital of the province of Toledo and the ''de jure'' seat of the government and parliament of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Castilla–La Mancha. Toledo was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1986 for its extensive monumental and cultural heritage. Located on the banks of the Tagus in central Iberian Peninsula, Iberia, Toledo is known as the "City of the Three Cultures" for the cultural influences of Christians, Muslims, and Jews throughout its history. It was the capital, from 542 to 725 CE, of the Visigothic kingdom, which followed the fall of the Roman Empire. Toledo was also the location of historic events such as the Councils of Toledo and was labelled the "Imperial City" due to the fact that it was the main venue of the court of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in Spain. The city, seat of a powerful archdiocese for much of its history, has a Gothic Cathedral, the ''Cathedral of Toledo, Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic peoples, Germanic successor states to the Western Roman Empire, it was originally created by the settlement of the Visigoths under King Wallia in the province of Gallia Aquitania in southwest Gaul by the Roman government and then extended by conquest over all of Hispania. The Kingdom maintained independence from the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire, whose attempts to re-establish Roman authority in Hispania were only partially successful and short-lived. The Visigoths were Romanization (cultural), romanized central Europeans who had moved west from the Danube, Danube Valley. They became foederati of Rome, and wanted to restore the Roman order against the hordes of Vandals, Alans and Suebi. The Fall of the Western Roman Empire, Western Roman Empire fell in 47 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)
.png)
24.jpg)