|
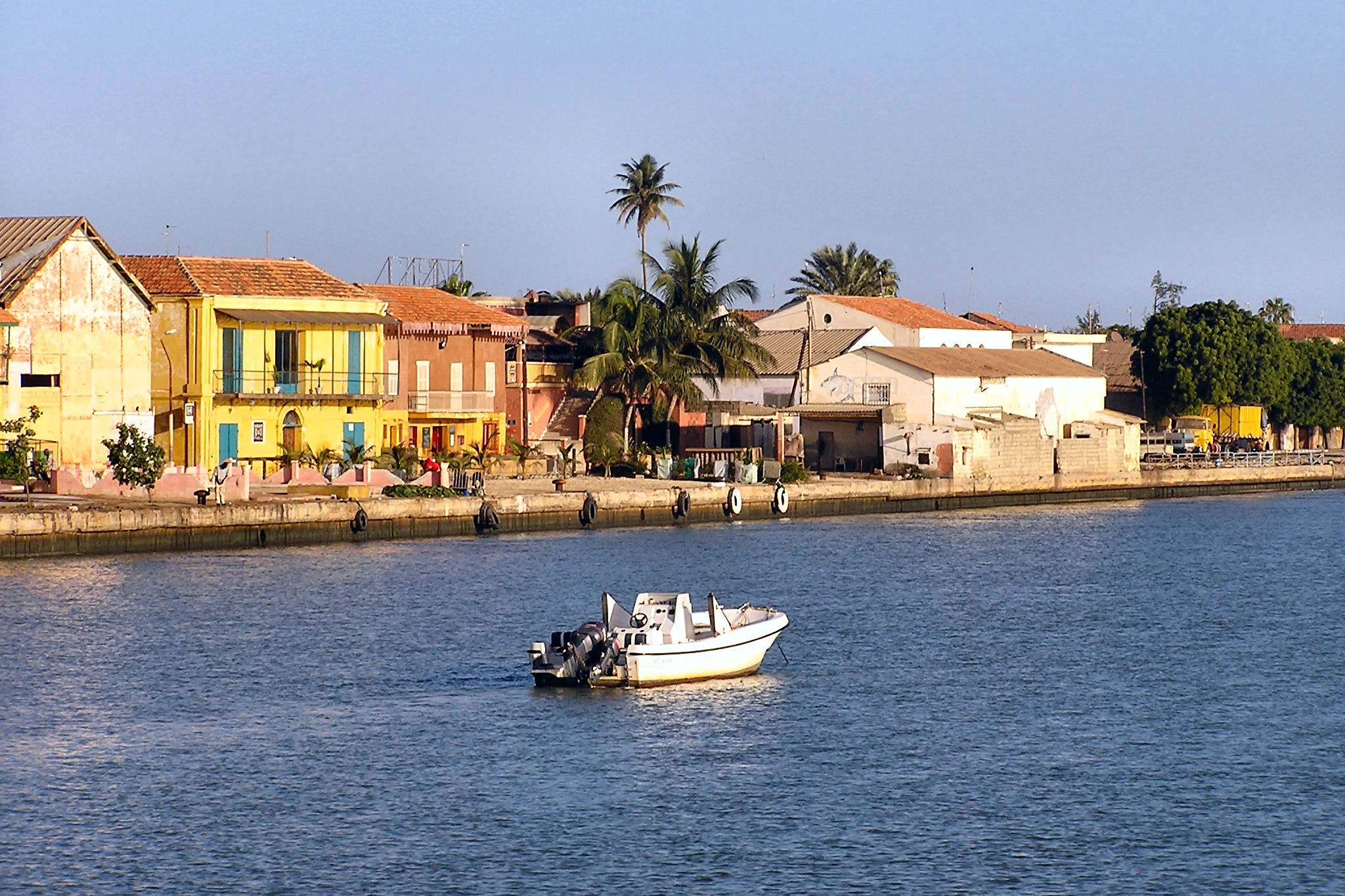
Gorée
(; "Gorée Island"; ) is one of the 19 (i.e. districts) of the city of Dakar, Senegal. It is an island located at sea from the main harbour of Dakar (), famous as a destination for people interested in the Atlantic slave trade. Its population as of the 2013 census was 1,680 inhabitants, giving a density of , which is only half the average density of the city of Dakar. Gorée is both the smallest and the least populated of the 19 of Dakar. Other important centres for the slave trade from Senegal were further north, at Saint-Louis, Senegal, or to the south in the Gambia, at the mouths of major rivers for trade.''Les Guides Bleus: Afrique de l'Ouest'' (1958 ed.), p. 123 It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and was one of the first 12 locations in the world to be designated as such in 1978. The name is a corruption of its original Dutch language, Dutch name Goeree, named after the Dutch island of Goeree-Overflakkee, Goeree. The island was also known as Palma, or in Portuguese. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Senegal, largest city of Senegal. The Departments of Senegal, department of Dakar has a population of 1,278,469, and the population of the Dakar metropolitan area was at 4.0 million in 2023. Dakar is situated on the Cap-Vert peninsula, the westernmost point of mainland Africa. Cap-Vert was colonized by the Portuguese people, Portuguese in the early 15th century. The Portuguese established a presence on the island of Gorée off the coast of Cap-Vert and used it as a base for the Atlantic slave trade. Kingdom of France, France took over the island in 1677. Following the abolition of the slave trade and French annexation of the mainland area in the 19th century, Dakar grew into a major regional port and a major city of the French colonial empire. In 1902, Dakar replaced Saint-Louis, Senegal, Saint-Louis as the capital of French West Africa. From 1959 to 1960, Dakar was the capital of the short-lived Mali Federation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea to Guinea–Senegal border, the southeast and Guinea-Bissau to Guinea-Bissau–Senegal border, the southwest. Senegal nearly surrounds The Gambia, a country occupying a narrow sliver of land along the banks of the Gambia River, which separates Senegal's southern region of Casamance from the rest of the country. It also shares a maritime border with Cape Verde. Senegal's capital is Dakar. Senegal is the westernmost country in the mainland of the Old World, or Afro-Eurasia. It owes its name to the Senegal River, which borders it to the east and north. The climate is typically Sahelian, though there is a wet season, rainy season. Senegal covers a land area of almost and has a population of around 18 million. The state is a Presidential system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
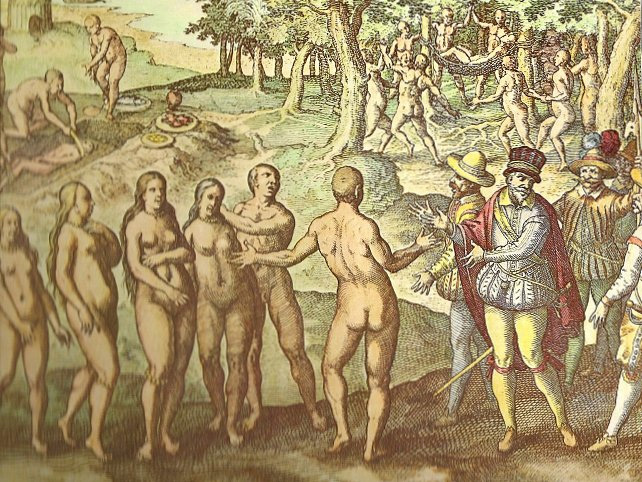
Atlantic Slave Trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Passage. Europeans established a coastal slave trade in the 15th century and trade to the Americas began in the 16th century, lasting through the 19th century. The vast majority of those who were transported in the transatlantic slave trade were from Central Africa and West Africa and had been sold by West African slave traders to European slave traders, while others had been captured directly by the slave traders in coastal raids. European slave traders gathered and imprisoned the enslaved at slave fort, forts on the African coast and then brought them to the Americas. Some Portuguese and Europeans participated in slave raids. As the National Museums Liverpool explains: "European traders captured some Africans in raids along the coast, but bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goeree-Overflakkee
Goeree-Overflakkee () is the southernmost river delta, delta island of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of South Holland, Netherlands. It is separated from Voorne-Putten and Hoeksche Waard by the Haringvliet, from the mainland of North Brabant by the Volkerak, and from Schouwen-Duiveland by Lake Grevelingen. Since 2013, Goeree-Overflakkee has also been a municipality consisting, from west to east, of the former municipalities of Goedereede, Dirksland, Middelharnis, and Oostflakkee. The largest towns are Sommelsdijk, Middelharnis, Ouddorp, and Dirksland. Despite being part of the province of South Holland, the island's scenery and dialect are more closely related to Zeeland than to Holland. On the island they speak a form of Zeelandic, namely in the west and in the east. History The island was detached from the mainland when the Haringvliet formed as a result of two major flooding events. The first was in 1216, which breached the dunes of Voorne-Putten, Voorne and cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Louis, Senegal
Saint-Louis () or Saint Louis (), is the capital of Senegal's Saint-Louis Region. Located in the northwest of Senegal, near the mouth of the Senegal River, and north of Senegal's capital city Dakar. It had a population of 254,171 in 2023. Saint-Louis was the capital of the French colony of Senegal from 1673 until 1902 and French West Africa from 1895 until 1902, when the capital was moved to Dakar. From 1920 to 1957, it also served as the capital of the neighboring colony of Mauritania. The town was an important economic center during the period of French West Africa, but it is less important now. Nonetheless, it still has important industries, including tourism, a commercial center, sugar production, and fishing. The tourism industry is in part due to the city being listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2000. However, the city is also Climate change vulnerability, vulnerable to climate change—where sea level rise is expected to threaten the city center and potentially damag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afonso De Albuquerque
Afonso de Albuquerque, 1st Duke of Goa ( – 16 December 1515), was a Portuguese general, admiral, statesman and ''conquistador''. He served as viceroy of Portuguese India from 1509 to 1515, during which he expanded Portuguese influence across the Indian Ocean and built a reputation as a fierce and skilled military commander. Albuquerque advanced the three-fold Portuguese grand scheme of combating Islam, spreading Christianity, and securing the trade of spices by establishing a Portuguese Asian empire. Among his achievements, Albuquerque managed to conquer Goa and was the first European of the Renaissance to raid the Persian Gulf, and he led the first voyage by a European fleet into the Red Sea. He is generally considered a highly effective military commander, and "probably the greatest naval commander of the age", given his successful strategy of attempting to close all the Indian Ocean naval passages to the Atlantic, Red Sea, Persian Gulf, and to the Pacific, transforming it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
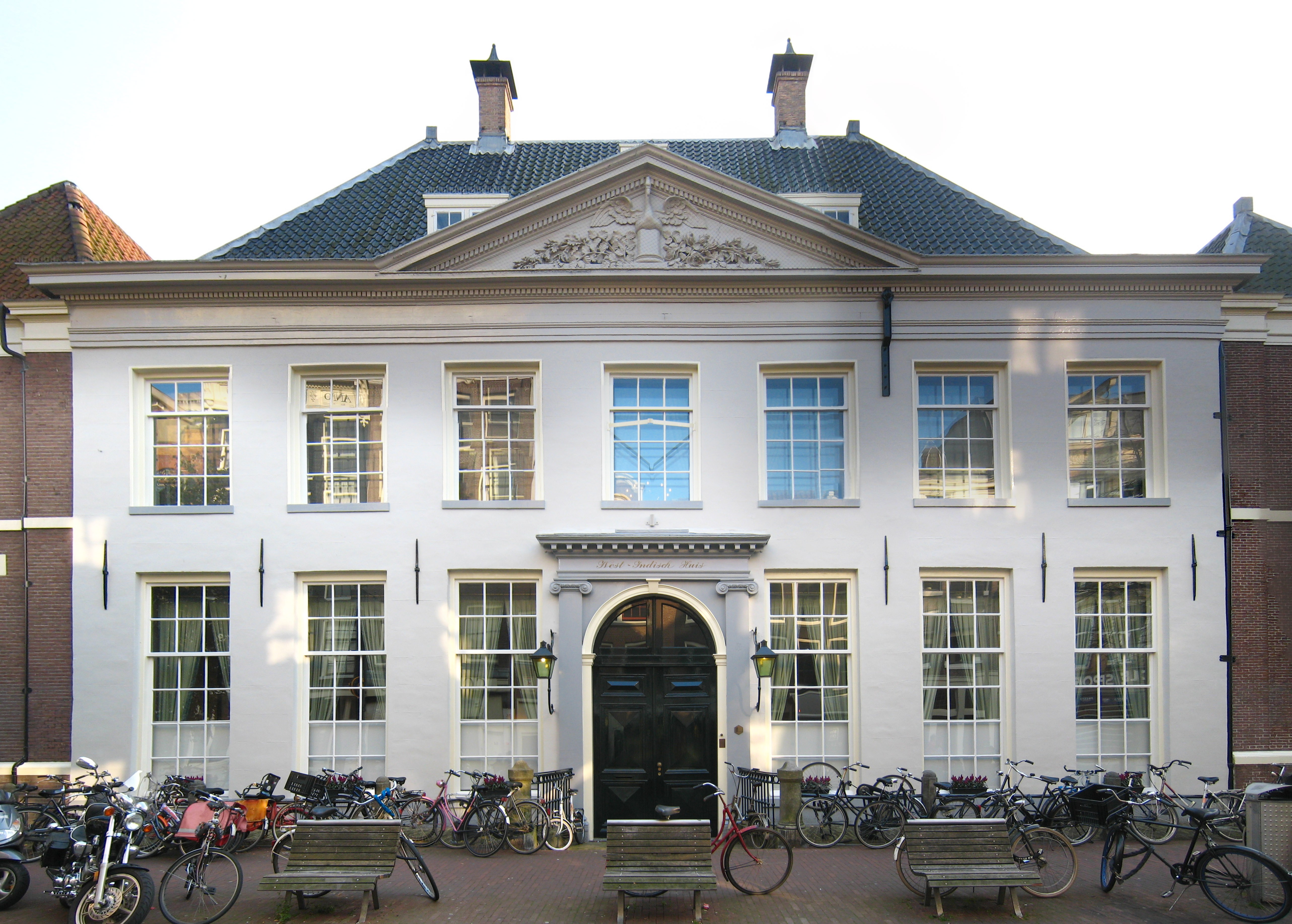
Dutch West India Company
The Dutch West India Company () was a Dutch chartered company that was founded in 1621 and went defunct in 1792. Among its founders were Reynier Pauw, Willem Usselincx (1567–1647), and Jessé de Forest (1576–1624). On 3 June 1621, it was granted a :wikisource:Charter of the Dutch West India Company, charter for a trade monopoly in the Dutch West Indies by the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands and given jurisdiction over Dutch participation in the Atlantic slave trade, Brazil, the Caribbean, and North America. The area where the company could operate consisted of West Africa (between the Tropic of Cancer and the Cape of Good Hope) and the Americas, which included the Pacific Ocean and ended east of the Maluku Islands, according to the Treaty of Tordesillas. The intended purpose of the charter was to eliminate competition, particularly Spanish or Portuguese, between the various trading posts established by the merchants. The company became instrumental in the largely eph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfert Dapper
Olfert Dapper (January 1636 – 29 December 1689) was a Dutch physician and writer who wrote books about world history and geography although he never travelled outside the Netherlands. Biography Olfert Dapper was born in January 1636 in the Jordaan in Amsterdam. On 6 January 1636, he was baptized in the Lutheran church in Amsterdam. In 1663 wrote a book on the history of Amsterdam. His '' Description of Africa'' (1668) is a key text for African studies. His book "is one of the most authoritative 17th-century accounts on Africa published in Dutch. Translations appeared in English, French, and German. Dapper never travelled outside the Netherlands but used reports by Jesuit missionaries and Dutch explorers. Within a few years, he published about China, India, Persia, Georgia and Arabia. His books became well-known in his own time. The fine plates include views of Algiers, Benin, Cairo, Cape Town, Valletta, Marrakesh, St. Helena, Tangier, Tripoli and Tunis, as well as animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Ethnic Groups
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common ancestry, language, faith, historical continuity, etc. There are no universally accepted and precise definitions of the terms "ethnic group" and "nationality", but in the context of European ethnography in particular, the terms ''ethnic group'', ''people'', ''nationality'' and ''ethno-linguistic group'' are used as mostly synonymous. Preference may vary in usage with respect to the situation specific to the individual countries of Europe, and the context in which they may be classified by those terms. The total number of national minority populations in Europe is estimated at 105 million people, or 14% of 770 million Europeans in 2002.Christoph Pan, Beate Sibylle Pfeil (2002), Minderheitenrechte in Europa. Handbuch der europäischen Volksgruppen', Braumüller, (Google Books, snippet view). Als2006 rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tristão Da Cunha
Tristão da Cunha (sometimes misspelled Tristão d'Acunha; ; c. 1460 – c. 1540) was a Portuguese explorer and naval commander. In 1514, he served as ambassador from King Manuel I of Portugal to Pope Leo X, leading a luxurious embassy presenting in Rome the new conquests of Portugal. He later became a member of the Portuguese privy council. Italian Wars Da Cunha was born in Portugal, c. 1460. He served in the Third Italian War under Castilian general Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba, participating in the Battle of Cerignola and being entasked with hosting the funeral of the fallen French general, Louis d'Armagnac, Duke of Nemours. He was also in command of Roca Guillerma, between Gaeta and Salerno, where he was briefly captured by the French army in a betrayal of the local nobility. Da Cunha was later freed. After returning to Portugal, he was nominated as first viceroy of Portuguese India in 1504, but could not take up this post owing to a temporary blindness. 1506 voy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amerigo Vespucci
Amerigo Vespucci ( , ; 9 March 1454 – 22 February 1512) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Florence for whom "Naming of the Americas, America" is named. Vespucci participated in at least two voyages of the Age of Discovery between 1497 and 1504, first on behalf of Spain (14991500) and then for Portugal (15011502). In 1503 and 1505, two booklets were published under his name containing colourful descriptions of these explorations and other voyages. Both publications were extremely popular and widely read throughout much of Europe. Historians still dispute the authorship and veracity of these accounts, but they were instrumental in raising awareness of the discoveries and enhancing the reputation of Vespucci as an explorer and navigator. Vespucci claimed to have understood in 1501 that Brazil was part of a fourth continent unknown to Europeans, which he called the "New World" (Mundus Novus). The claim inspired cartographer Martin Waldseemüller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
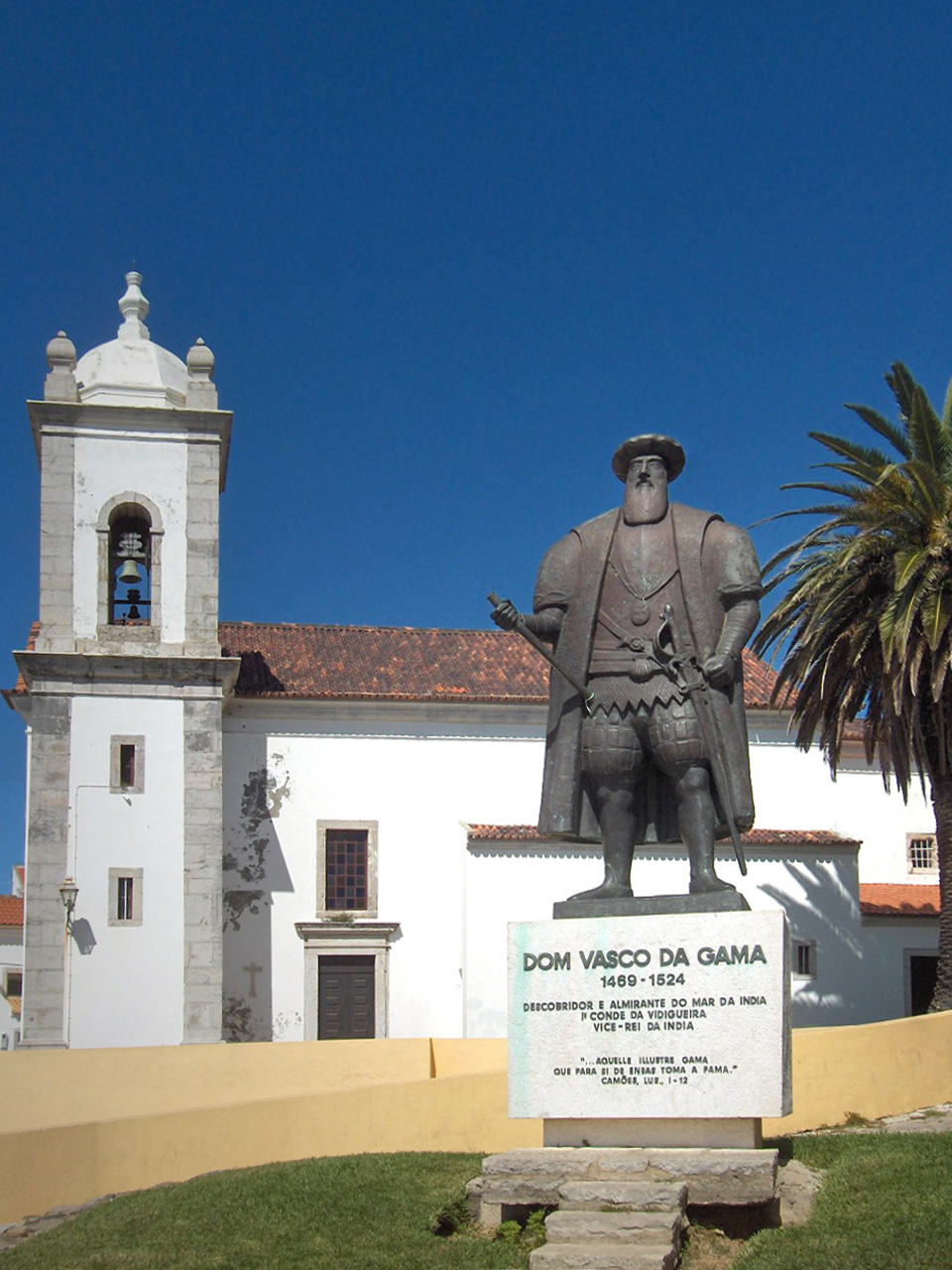
Vasco Da Gama
Vasco da Gama ( , ; – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and nobleman who was the Portuguese discovery of the sea route to India, first European to reach India by sea. Da Gama's first voyage (1497–1499) was the first to link Europe and Asia using an Cape Route, ocean route that rounded the southern tip of Africa. This route allowed the Portuguese to avoid sailing across the highly disputed Mediterranean Sea and traversing the dangerous Arabian Peninsula, Arabian Peninsula. A milestone in Portuguese maritime exploration, this voyage marked the beginning of a sea-based phase of international trade and an age of global imperialism. The Portuguese later established a Portuguese Empire, long-lasting colonial empire along the route from Africa to Asia. The outward and return voyages constituted the longest known ocean voyages ever completed. Sailors had been trying to reach the Indies for decades, with thousands of lives and dozens of vessels lost in shipwrecks and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |