|
Gnadensee
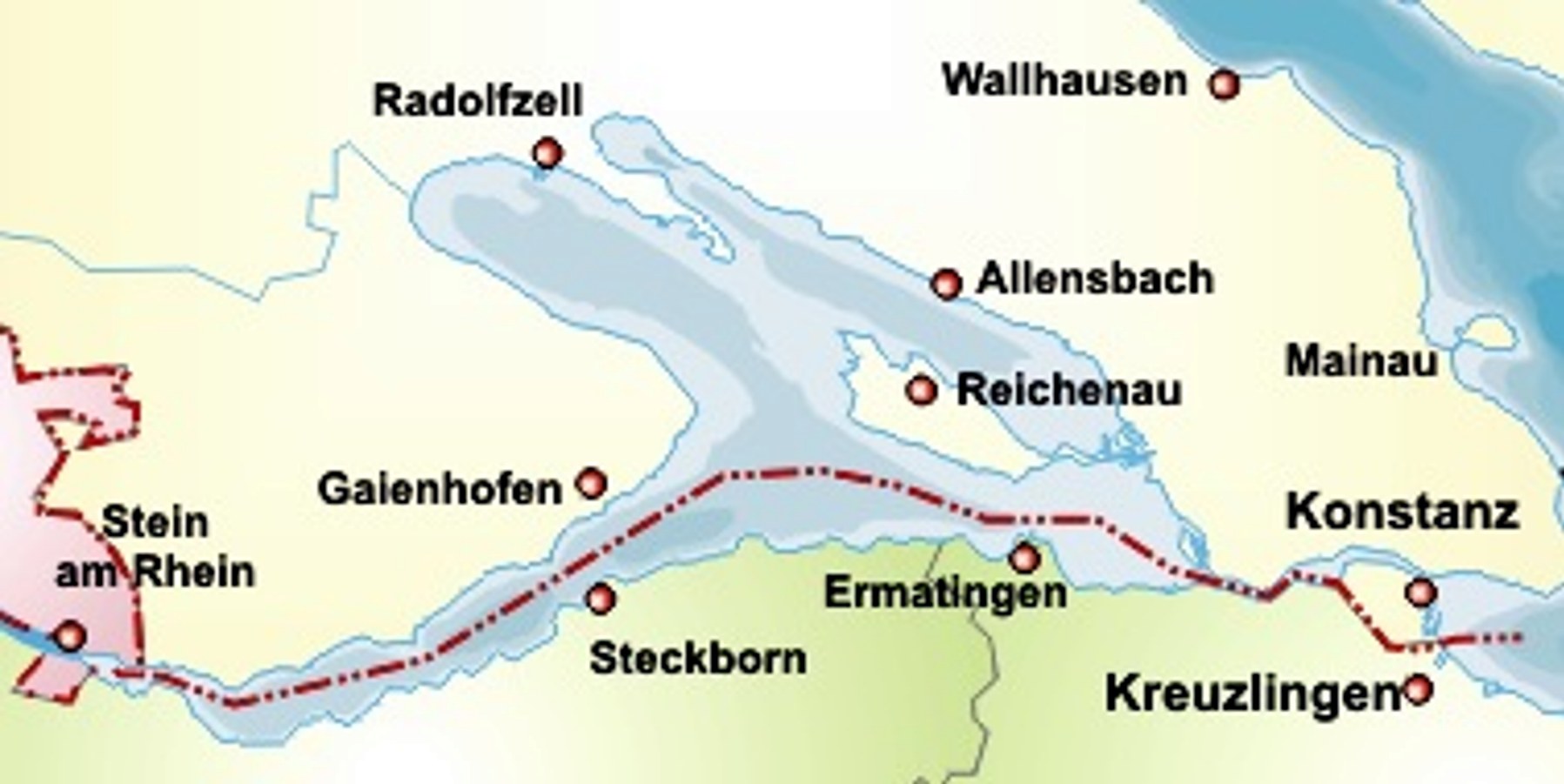
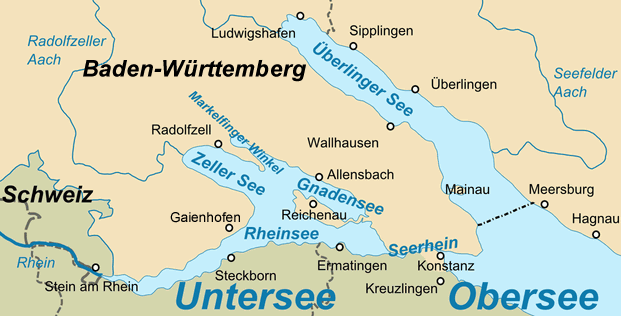
The Gnadensee is part of Lower Lake Constance (german: Untersee), the western part of the lake. Description The Gnadensee lies between Allensbach in the north and the island of Reichenau in the south. In the west it extends to the Mettnau peninsula (Radolfzell) and its eastern end borders on the Wollmatinger Ried Nature Reserve and the Reichenaudamm with its prominent avenue of poplars. The extremely small part in the northwest is called the Markelfinger Winkel. Together with the latter it has an area of 13 square kilometres. It reaches a maximum depth of 19 metres. Name The name of the Gnadensee probably dates to the period when the local judiciary was based on the island of Reichenau. If an accused person was found guilty and sentenced to death, the execution could not take place on the island. It had to be carried out on the mainland as the whole island was holy ground. As a result, the convict was taken by boat to the mainland in the direction of present-day Allensbach, in o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Lake Constance
The Untersee (German for ''Lower Lake''), also known as Lower Lake Constance, is the smaller of the two lakes that together form Lake Constance and forms part of the boundary between Switzerland and Germany. Geography The Lower Lake Constance measures and is situated about lower than the Obersee. The Romans called it ''Lacus Acronius''. In the Middle Ages, the Upper Lake was called ''Bodamicus Lacus'', or ''Bodensee'' in German. At some point in time, this term began to include the Lower Lake, and a new term "Upper Lake" (in German: '' Obersee''), was introduced for the larger lake. The main tributaries are the Seerhein and Radolfzeller Aach. The landscape surrounding the Untersee is very diverse. The Untersee contains two islands: Reichenau and Werd (near the transition to the High Rhine). In the northeast is found the peninsula Bodanrück; in the northwest, the Hegau lowlands with the peninsula Mettnau; in the west, the peninsula Höri, with a mountain called Schiener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wollmatinger Ried
The nature reserve of Wollmatinger Ried – Untersee – Gnadensee is a protected area on the shores of Lake Constance in Germany. It has an area of 767 hectares and is the largest and most important nature reserve on the German side of Lake Constance. It is rich in plant and animal species and extends from the banks of the Seerhein river west of Constance via the causeway to the Island of Reichenau in the Untersee to the eastern Gnadensee near Allensbach-Hegne. The nearby offshore islands of Triboldingerbohl (Langenrain) and Mittler or Langbohl (Kopf) are part of the reserve. Literature * Sources nabu-wollmatingerried.de: Das Wollmatinger Ried* Regierungspräsidium Freiburg Freiburg im Breisgau (; abbreviated as Freiburg i. Br. or Freiburg i. B.; Low Alemannic: ''Friburg im Brisgau''), commonly referred to as Freiburg, is an independent city in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With a population of about 230,000 (as o ...: Faltblatt zum Naturschutzgebiet Wollmatinger Ried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markelfinger Winkel
The Markelfinger Winkel is the part of Lake Constance between the upper part of the Mettnau Peninsula and Markelfingen. It is the northwestern continuation of the Gnadensee The Gnadensee is part of Lower Lake Constance (german: Untersee), the western part of the lake. Description The Gnadensee lies between Allensbach in the north and the island of Reichenau in the south. In the west it extends to the Mettnau peninsu ... and its parent lake, the Untersee ("Lower Lake Constance"). It has an area of around one square kilometre. (map) References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheinsee
{{infobox body of water , name = Rheinsee , image = Ermatingen.jpg , caption = View of the Rheinsee near Ermatingen , location = Baden-Württemberg , coordinates = {{coord, 47, 39, 45, N, 08, 57, 37, E, type:landmark_region:DE-BW, format=dms, display=inline,title , pushpin_map = Germany , inflow = Seerhein , outflow = High Rhine (''Hochrhein'') , islands = , cities = , elevation = {{convert, 395, m , area = , length = {{convert, 20, km , width = , depth = , max-depth = {{convert, 45, m , volume = , shore = The Rhine leaves that part of Lake Constance known as the Upper Lake or Obersee as the Seerhein near Konstanz. After six kilometres it forms the Rheinsee, through which the river current flows. At its outflow is the island of Werd with its Franciscan monastery. The Rheinsee, together with the Zeller See and the Gnadensee, which surround the island of Reichenau, form the Untersee. The latter, together with the Seerhein, are considered part of Lake Const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Of Reichenau
Reichenau Island () is an island in Lake Constance in Southern Germany. It lies almost due west of the city of Konstanz, between the Gnadensee and the Untersee, two parts of Lake Constance. With a total land surface of and a circumference of , the island is long and wide at its greatest extent. The highest point, the Hochwart, stands some above the lake surface and above mean sea level. Reichenau is connected to the mainland by a causeway, completed in 1838, which is intersected between the ruins of Schopflen Castle and the eastern end of Reichenau Island by a -wide and long waterway, the Bruckgraben. A low road bridge allows the passage of ordinary boats but not of sailing-boats. In 724, the first monastery was built on the island by the bishop Pirmin, and Reichenau quickly developed into an influential religious, cultural, and intellectual center. During the Early and High Middle Ages, the Reichenau Abbey was one of the significant monasteries across the Frankish Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a total area of nearly , it is the third-largest German state by both area (behind Bavaria and Lower Saxony) and population (behind North Rhine-Westphalia and Bavaria). As a federated state, Baden-Württemberg is a partly-sovereign parliamentary republic. The largest city in Baden-Württemberg is the state capital of Stuttgart, followed by Mannheim and Karlsruhe. Other major cities are Freiburg im Breisgau, Heidelberg, Heilbronn, Pforzheim, Reutlingen, Tübingen, and Ulm. What is now Baden-Württemberg was formerly the historical territories of Baden, Prussian Hohenzollern, and Württemberg. Baden-Württemberg became a state of West Germany in April 1952 by the merger of Württemberg-Baden, South Baden, and Württemberg-Hohenzollern. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allensbach
Allensbach is a municipality in the district of Konstanz in Baden-Württemberg in Germany. Allensbach is located between Konstanz and Radolfzell on Lake Constance. Notable institution Allensbach is known for being the home of the Institut für Demoskopie Allensbach (also known as Allensbach Institute), one of the best known opinion-polling organizations in Germany. World heritage site It is home to one or more prehistoric pile-dwelling (or stilt house) settlements that are part of the, added in 2011, Prehistoric Pile dwellings around the Alps UNESCO World Heritage Site A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h .... References Konstanz (district) {{Konstanz-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mettnau
Mettnau is a peninsula, located east of the town of Radolfzell in the western part of Lake Constance. It lies between the '' Markelfingen corner'' in the north and the '' Zeller See'' in the south and has a length of 3.5 kilometers and a width of up to 800 meters, a size of 140 hectares.NABU Mettnau. A large part of the peninsula is a nature reserve. The Nature Reserve Mettnau includes a small island name Love Island. It is managed by Naturschutzbund Deutschland on behalf of the Regierungsbezirk of Freiburg. A spa is located on the island, and a field station of the Bird observatory Radolfzell. Nature Reserve The nature reserve of Mettnau was established in 1926 by the town of Radolfzell, but only expanded to its current size of 140 hetctaresin 1984. A pond was accidentally created when the peninsula was used as a landfill. The pond is independent of fluctuations in the water of Lake Constance, making it an attractive place for hatching Hatching (french: hachure) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radolfzell
Radolfzell am Bodensee is a town in Germany at the western end of Lake Constance approximately 18 km northwest of Konstanz. It is the third largest town, after Constance and Singen, in the district of Konstanz, in Baden-Württemberg. Radolfzell is a well-known health care town (Mettnau) and an important railway junction of the High Rhine Railway and the Hegau-Ablach Valley Railway (leading to the Stahringen–Friedrichshafen railway). In 1990 Radolfzell was named the Federal Environment Capital City of Germany. History This town developed out of a monastery founded in 826 AD as a "cell" under Bishop Radolf of Verona. The town belonged to the Abbey of Reichenau, then to the house of Habsburg for a long time, and for 40 years was a Free Imperial City. In the centre is the gothic Cathedral of our Dear Lady, dating from the 15th century and decorated in the baroque style in the 18th. One particularly beautiful feature is the Rosary altar by the Zürn brothers and the Master ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law in legal cases. Definition The judiciary is the system of courts that interprets, defends, and applies the law in the name of the state. The judiciary can also be thought of as the mechanism for the resolution of disputes. Under the doctrine of the separation of powers, the judiciary generally does not make statutory law (which is the responsibility of the legislature) or enforce law (which is the responsibility of the executive), but rather interprets, defends, and applies the law to the facts of each case. However, in some countries the judiciary does make common law. In many jurisdictions the judicial branch has the power to change laws through the process of judicial review. Courts with judicial review power may annul the laws and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary, Mother Of God
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jews, Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Saint Joseph, Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is a central figure of Christianity, venerated under titles of Mary, various titles such as virgin or queen, many of them mentioned in the Litany of Loreto. The Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern and Oriental Orthodox, Church of the East, Catholic, Anglican, and Lutheran churches believe that Mary, as mother of Jesus, is the Theotokos, Mother of God. Other Protestant views on Mary vary, with some holding her to have considerably lesser status. The New Testament of the Holy Bible, Bible provides the earliest documented references to Mary by name, mainly in the canonical Gospels. She is described as a young virgin who was chosen by God in Christianity, God to annunciation, conceive Jesus through the Holy Spirit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsis (linguistics)
In linguistics, ellipsis (from el, ἔλλειψις, ''élleipsis'' 'omission') or an elliptical construction is the omission from a clause of one or more words that are nevertheless understood in the context of the remaining elements. There are numerous distinct types of ellipsis acknowledged in theoretical syntax. Theoretical accounts of ellipsis seek to explain its syntactic and semantic factors, the means by which the elided elements are recovered, and the status of the elided elements. Theoretical accounts of ellipsis can vary greatly depending in part upon whether a constituency-based or a dependency-based theory of syntactic structure is pursued. Background Varieties of ellipsis have long formed a basis of linguistic theory that addresses basic questions of form–meaning correspondence: in particular, how the usual mechanisms of grasping a meaning from a form may be bypassed or supplanted via elliptical structures. In generative linguistics, the term ''ellipsis'' has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |