|
Global Drifter Program
The Global Drifter Program (GDP) (formerly known as the Surface Velocity Program (SVP)) was conceived by Prof. Peter Niiler, with the objective of collecting measurements of surface ocean currents, sea surface temperature and sea-level atmospheric pressure using drifters. It is the principal component of the Global Surface Drifting Buoy Array, a branch of NOAA's Global Ocean Observations and a scientific project of the Data Buoy Cooperation Panel (DBCP). The project originated in February 1979 as part of the TOGA/Equatorial Pacific Ocean Circulation Experiment (EPOCS) and the first large-scale deployment of drifters was in 1988 with the goal of mapping the tropical Pacific Ocean's surface circulation. The current goal of the project is to use 1250 satellite-tracked surface drifting buoys to make accurate and globally dense in-situ observations of mixed layer currents, sea surface temperature, atmospheric pressure, winds and salinity, and to create a system to process the dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
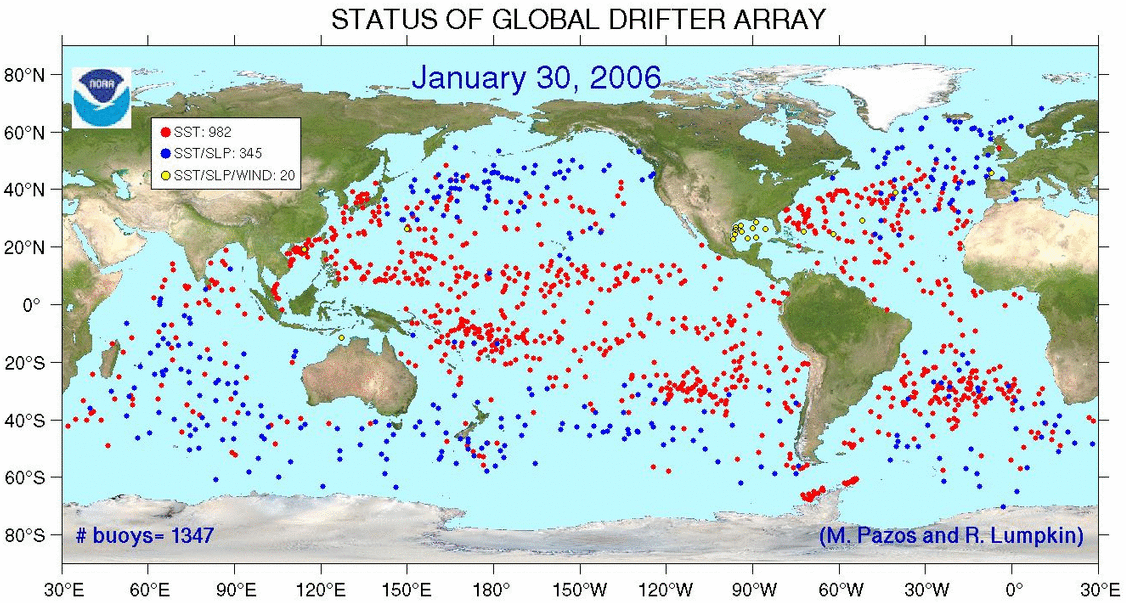
Status Of Global Drifter Array
Status (Latin plural: ''statūs''), is a state, condition, or situation, and may refer to: * Status (law) ** City status ** Legal status, in law ** Political status, in international law ** Small entity status, in patent law ** Status conference ** Status crime * Marital status * Observer status, in international organizations * Senior status * Social status, in sociology ** Achieved status ** Ascribed status ** Master status ** Socioeconomic status ** Sociometric status ** Status attainment ** Status offense ** Status shift * Status brand, in marketing * Status constructus, a noun form * Status match, in frequent-flyer loyalty programs * Status quo * Status symbol Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Status'', a magazine edited by Igor Cassini * Recurring status, in acting * Status effect, in gaming Computing * Exit status, in computer science * Process states (Process Status) * Status bar, in user interface design * Status message (instant messaging) * Statu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal to ‰). Salinity is an important factor in determining many aspects of the chemistry of natural waters and of biological processes within it, and is a thermodynamic state variable that, along with temperature and pressure, governs physical characteristics like the density and heat capacity of the water. A contour line of constant salinity is called an ''isohaline'', or sometimes ''isohale''. Definitions Salinity in rivers, lakes, and the ocean is conceptually simple, but technically challenging to define and measure precisely. Conceptually the salinity is the quantity of dissolved salt content of the water. Salts are compounds like sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and sodium bicarbonate which dissolve into ions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Oceanographic And Meteorological Laboratory
The Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (AOML), a federal research laboratory, is part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research (OAR), located in Miami in the United States. AOML's research spans tropical cyclone and hurricanes, coastal ecosystems, oceans and human health, climate studies, global carbon systems, and ocean observations. It is one of seven NOAA Research Laboratories (RLs). AOML’s organizational structure consists of an Office of the Director and three scientific research divisions. The Office of the Director oversees the Laboratory’s scientific programs, as well as its financial, administrative, computer, outreach/education, and facility management services. Research programs are augmented by Cooperative Institutes, such as the Cooperative Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Studies (CIMAS), a joint enterprise with the University of Miami’s Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmosphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmond Tutu Deploys A Drifter
Desmond or Desmond's may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Desmond'' (novel), 1792 novel by Charlotte Turner Smith * '' Desmond's'', 1990s British television sitcom Ireland * Kingdom of Desmond, medieval Irish kingdom * Earl of Desmond, Irish aristocratic title * Desmond Rebellions, Irish rebellions during the 16th century led by the Earl of Desmond Science and technology * DESMOND (diabetes) (Diabetes Education and Self Management for Ongoing and Newly Diagnosed), a UK NHS diabetes education programme * Desmond (software), molecular dynamics simulation software * Storm Desmond, a windstorm in Britain and Ireland in 2015 Other uses * Desmond (name) Desmond is a given name and a surname, derived from the Irish place-name ''Desmond'', an anglicization of the Irish ''Deas-Mhumhna'' ("South Munster"). The Irish peerages of Ormonde, Desmond, and Thomond represented the old sub-kingdoms of East ..., a common given name and surname * Desmond (horse) (1896-1913), Thoroughbred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climatology
Climatology (from Greek , ''klima'', "place, zone"; and , '' -logia'') or climate science is the scientific study of Earth's climate, typically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years. This modern field of study is regarded as a branch of the atmospheric sciences and a subfield of physical geography, which is one of the Earth sciences. Climatology now includes aspects of oceanography and biogeochemistry. The main methods employed by climatologists are the analysis of observations and modelling of the physical processes that determine the climate. The main topics of research are the study of climate variability, mechanisms of climate changes and modern climate change. Basic knowledge of climate can be used within shorter term weather forecasting, for instance about climatic cycles such as the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), the Madden–Julian oscillation (MJO), the North Atlantic oscillation (NAO), the Arctic oscillation (AO), the Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamics; plate tectonics and the geology of the sea floor; and fluxes of various chemical substances and physical properties within the ocean and across its boundaries. These diverse topics reflect multiple disciplines that oceanographers utilize to glean further knowledge of the world ocean, including astronomy, biology, chemistry, climatology, geography, geology, hydrology, meteorology and physics. Paleoceanography studies the history of the oceans in the geologic past. An oceanographer is a person who studies many matters concerned with oceans, including marine geology, physics, chemistry and biology. History Early history Humans first acquired knowledge of the waves and currents of the seas and oceans in pre-historic times. Observations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments. Biologists are able to study life at multiple levels of organization, from the molecular biology of a cell to the anatomy and physiology of plants and animals, and evolution of populations.Based on definition from: Hence, there are multiple subdisciplines within biology, each defined by the nature of their research questions and the tools that they use. Like other scientists, biologists use the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their spatial scale, their speed and direction, the forces that cause them, the regions in which they occur, and their effect. Winds have various asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearn P
Pearn is a surname. Notable people with this surname include: * Cole Pearn (born 1982), Canadian driver * Inez Pearn (1913–1976), British novelist * Jon Pearn, English house music producer * Kris Pearn, Canadian animation director * Mark Pearn (born 1977), English field hockey player * Nancy Pearn, founder of Pearn, Pollinger & Higham * Perry Pearn Perry Pearn (born June 6, 1951) is a Canadian professional ice hockey coach. He is a former assistant coach in the National Hockey League, most recently with the Vancouver Canucks. In 2022, he became the head coach of the Japanese national ice ho ... (born 1951), Canadian ice hockey coach As a given name * Pearn P. Niiler (1937–2010), American oceanographer {{surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 760mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes—the Earth's gravi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)



