|
Geology Of Mercury
The geology of Mercury is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mercury. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term ''geology'' is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. Historically, Mercury has been the least understood of all the terrestrial planets in the Solar System. This stems largely from its proximity to the Sun which makes reaching it with spacecraft technically challenging and Earth-based observations difficult. For decades, the principal source of geologic information about Mercury came from the 2,700 images taken by the Mariner 10 spacecraft during three flybys of the planet from 1974 to 1975. These images covered about 45% of the planet’s surface, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
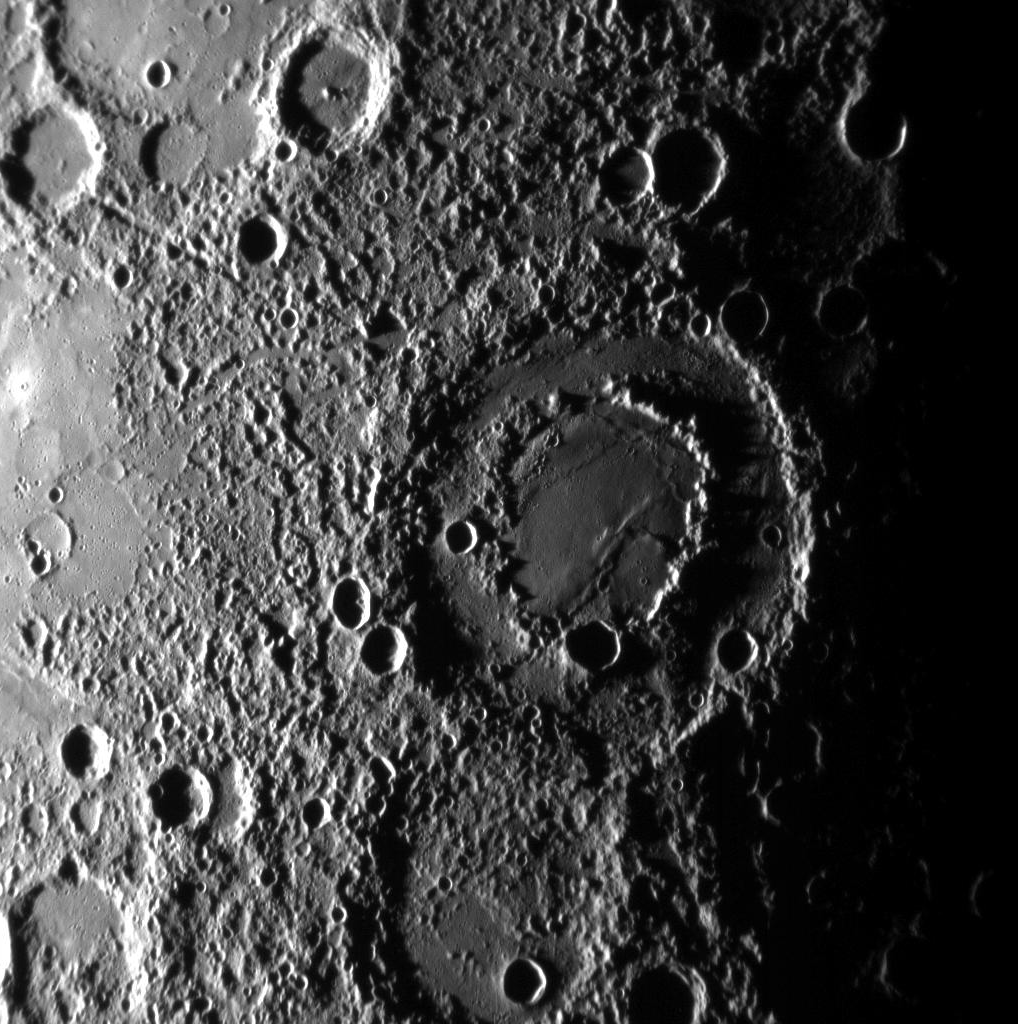
Mercury Double-Ring Impact Basin
Mercury commonly refers to: * Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun * Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg * Mercury (mythology), a Roman god Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to: Companies * Mercury (toy manufacturer), a brand of diecast toy cars manufactured in Italy * Mercury Communications, a British telecommunications firm set up in the 1980s * Mercury Drug, a Philippine pharmacy chain * Mercury Energy, an electricity generation and retail company in New Zealand * Mercury Filmworks, a Canadian independent animation studio * Mercury General, a multiple-line American insurance organization * Mercury Interactive, a software testing tools vendor * Mercury Marine, a manufacturer of marine engines, particularly outboard motors * Mercury Systems, a defense-related information technology company Computing * Mercury (programming language), a functional logic programming language * Mercury (metadata search system), a data search syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BepiColumbo
BepiColombo is a joint mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to the planet Mercury. The mission comprises two satellites launched together: the Mercury Planetary Orbiter (MPO) and ''Mio'' (Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter, MMO). The mission will perform a comprehensive study of Mercury, including characterization of its magnetic field, magnetosphere, and both interior and surface structure. It was launched on an Ariane 5 rocket on 20 October 2018 at 01:45 UTC, with an arrival at Mercury planned for on 5 December 2025, after a flyby of Earth, two flybys of Venus, and six flybys of Mercury. The mission was approved in November 2009, after years in proposal and planning as part of the European Space Agency's Horizon 2000+ programme; it is the last mission of the programme to be launched. Names ''BepiColombo'' is named after Giuseppe "Bepi" Colombo (1920–1984), a scientist, mathematician and engineer at the University of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong interaction, 1036 times weaker than the electromagnetic force and 1029 times weaker than the weak interaction. As a result, it has no significant influence at the level of subatomic particles. However, gravity is the most significant interaction between objects at the macroscopic scale, and it determines the motion of planets, stars, galaxies, and even light. On Earth, gravity gives weight to physical objects, and the Moon's gravity is responsible for sublunar tides in the oceans (the corresponding antipodal tide is caused by the inertia of the Earth and Moon orbiting one another). Gravity also has many important biological functions, helping to guide the growth of plants through the process of gravitropism and influencing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to spaceflight, fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather satellite, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, Planetary science, planetary exploration, and Space transport, transportation of Human spaceflight, humans and cargo spacecraft, cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters outer space, space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other Astronomical object, celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Time
Solar time is a calculation of the passage of time based on the position of the Sun in the sky. The fundamental unit of solar time is the day, based on the synodic rotation period. Two types of solar time are apparent solar time (sundial time) and mean solar time (clock time). Introduction A tall pole vertically fixed in the ground casts a shadow on any sunny day. At one moment during the day, the shadow will point exactly north or south (or disappear when and if the Sun moves directly overhead). That instant is local apparent noon, or 12:00 local apparent time. About 24 hours later the shadow will again point north–south, the Sun seeming to have covered a 360-degree arc around Earth's axis. When the Sun has covered exactly 15 degrees (1/24 of a circle, both angles being measured in a plane perpendicular to Earth's axis), local apparent time is 13:00 exactly; after 15 more degrees it will be 14:00 exactly. The problem is that in September the Sun takes less time (as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', "remote", and ''metron'', "measure". Systems that need external instructions and data to operate require the counterpart of telemetry, telecommand. Although the term commonly refers to wireless data transfer mechanisms (e.g., using radio, ultrasonic, or infrared systems), it also encompasses data transferred over other media such as a telephone or computer network, optical link or other wired communications like power line carriers. Many modern telemetry systems take advantage of the low cost and ubiquity of GSM networks by using SMS to receive and transmit telemetry data. A ''telemeter'' is a physical device used in telemetry. It consists of a sensor, a transmission path, and a display, recording, or control device. Electronic devices are widely used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere Of Mercury
Mercury, being the closest to the Sun, with a weak magnetic field and the smallest mass of the recognized terrestrial planets, has a very tenuous and highly variable atmosphere (surface-bound exosphere) containing hydrogen, helium, oxygen, sodium, calcium, potassium and water vapor, with a combined pressure level of about 10−14 bar (1 nPa). The exospheric species originate either from the Solar wind or from the planetary crust. Solar light pushes the atmospheric gases away from the Sun, creating a comet-like tail behind the planet. The existence of a Mercurian atmosphere was contentious until 1974, although by that time a consensus had formed that Mercury, like the Moon, lacked any substantial atmosphere. This conclusion was confirmed in 1974 when the unmanned ''Mariner 10'' spaceprobe discovered only a tenuous exosphere. Later, in 2008, improved measurements were obtained by the ''MESSENGER'' spacecraft, which discovered magnesium in the Mercurian exosphere. Composition Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
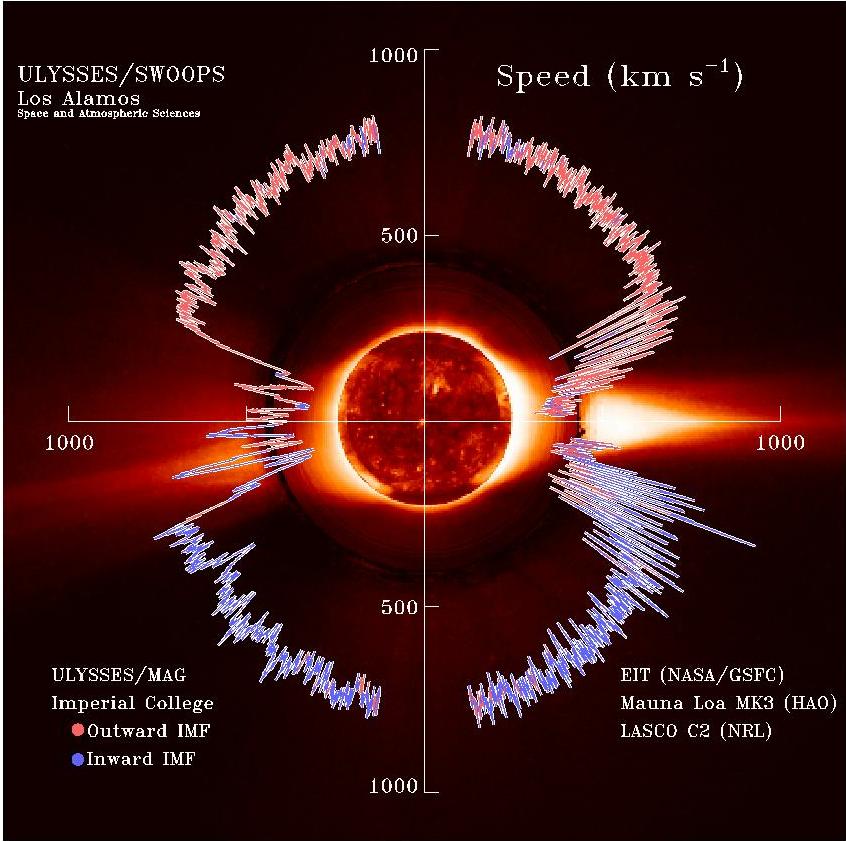
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei such as C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as P, Ti, Cr, 54Fe and 56Fe, and 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface. At a dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipole
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways: *An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system is a pair of charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign separated by some typically small distance. (A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.) *A magnetic dipole is the closed circulation of an electric current system. A simple example is a single loop of wire with constant current through it. A bar magnet is an example of a magnet with a permanent magnetic dipole moment. Dipoles, whether electric or magnetic, can be characterized by their dipole moment, a vector quantity. For the simple electric dipole, the electric dipole moment points from the negative charge towards the positive charge, and has a magnitude equal to the strength of each charge times the separation between the charges. (To be precise: for the definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault Scarp
A fault scarp is a small step or offset on the ground surface where one side of a fault has moved vertically with respect to the other. It is the topographic expression of faulting attributed to the displacement of the land surface by movement along faults. They are exhibited either by differential movement and subsequent erosion along an old ''inactive'' geologic fault (a sort of old rupture), or by a movement on a recent active fault. Characteristics Fault scarps often contain highly fractured rock of both hard and weak consistency. In many cases, bluffs form from the upthrown block and can be very steep. The height of the scarp formation is equal to the vertical displacement along the fault. Active scarps are usually formed by tectonic displacement, e.g. when an earthquake changes the elevation of the ground and can be caused by any type of fault, including strike-slip faults, whose motion is primarily horizontal. This movement is usually episodic, with the height of the bluf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Cone
Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and size of the fragments ejected during the eruption. Types of volcanic cones include stratocones, spatter cones, tuff cones, and cinder cones. Stratocone Stratocones are large cone-shaped volcanoes made up of lava flows, explosively erupted pyroclastic rocks, and igneous intrusives that are typically centered around a cylindrical vent. Unlike shield volcanoes, they are characterized by a steep profile and periodic, often alternating, explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions. Some have collapsed craters called calderas. The central core of a stratocone is commonly dominated by a central core of intrusive rocks that range from around to over several kilometers in diameter. This central core is surrounded by multiple generatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)