Atmosphere Of Mercury on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mercury, being the closest to the Sun, with a weak magnetic field and the smallest mass of the recognized terrestrial planets, has a very tenuous and highly variable
 The fourth species detected in Mercury's exosphere was
The fourth species detected in Mercury's exosphere was

 Because of Mercury's proximity to the Sun, the pressure of solar light is much stronger than near Earth. Solar radiation pushes neutral atoms away from Mercury, creating a comet-like tail behind it. McClintock 2009, p. 610–611 The main component in the tail is sodium, which has been detected beyond 24 million km (1000 RM) from the planet.
Because of Mercury's proximity to the Sun, the pressure of solar light is much stronger than near Earth. Solar radiation pushes neutral atoms away from Mercury, creating a comet-like tail behind it. McClintock 2009, p. 610–611 The main component in the tail is sodium, which has been detected beyond 24 million km (1000 RM) from the planet.
atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
(surface-bound exosphere
The exosphere ( grc, ἔξω "outside, external, beyond", grc, σφαῖρα "sphere") is a thin, atmosphere-like volume surrounding a planet or natural satellite where molecules are gravitationally bound to that body, but where the densit ...
) containing hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
, helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
, sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable iso ...
, calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
, potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosphe ...
and water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous pha ...
, with a combined pressure level of about 10−14 bar
Bar or BAR may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages
* Candy bar
* Chocolate bar
Science and technology
* Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment
* Bar (tropical cyclone), a layer of cloud
* Bar (u ...
(1 nPa). The exospheric species originate either from the Solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sol ...
or from the planetary crust. Solar light pushes the atmospheric gases away from the Sun, creating a comet-like tail behind the planet.
The existence of a Mercurian atmosphere was contentious until 1974, although by that time a consensus had formed that Mercury, like the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, lacked any substantial atmosphere. This conclusion was confirmed in 1974 when the unmanned '' Mariner 10'' spaceprobe discovered only a tenuous exosphere. Later, in 2008, improved measurements were obtained by the ''MESSENGER
''MESSENGER'' was a NASA robotic space probe that orbited the planet Mercury between 2011 and 2015, studying Mercury's chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field. The name is a backronym for "Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geoche ...
'' spacecraft, which discovered magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
in the Mercurian exosphere.
Composition
The Mercurian exosphere consists of a variety of species originating either from theSolar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sol ...
or from the planetary crust. Killen, 2007, pp. 433–434 The first constituents discovered were atomic hydrogen
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constit ...
(H), helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
(He) and atomic oxygen
There are several known allotropes of oxygen. The most familiar is molecular oxygen (O2), present at significant levels in Earth's atmosphere and also known as dioxygen or triplet oxygen. Another is the highly reactive ozone (O3). Others are:
*A ...
(O), which were observed by the ultraviolet radiation photometer
A photometer is an instrument that measures the strength of electromagnetic radiation in the range from ultraviolet to infrared and including the visible spectrum. Most photometers convert light into an electric current using a photoresistor, ...
of the '' Mariner 10'' spaceprobe in 1974. The near-surface concentrations of these elements were estimated to vary from 230 cm−3 for hydrogen to 44,000 cm−3 for oxygen, with an intermediate concentration of helium. In 2008 the ''MESSENGER
''MESSENGER'' was a NASA robotic space probe that orbited the planet Mercury between 2011 and 2015, studying Mercury's chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field. The name is a backronym for "Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geoche ...
'' probe confirmed the presence of atomic hydrogen, although its concentration appeared higher than the 1974 estimate. McClintock 2008, p. 93 Mercury's exospheric hydrogen and helium are believed to come from the Solar wind, while the oxygen is likely to be of crustal origin.
 The fourth species detected in Mercury's exosphere was
The fourth species detected in Mercury's exosphere was sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable iso ...
(Na). It was discovered in 1985 by Drew Potter and Tom Morgan, who observed its Fraunhofer emission lines at 589 and 589.6 nm. Killen, 2007, pp. 434–436 The average column density of this element is about 1 cm−2. Sodium is observed to concentrate near the poles, forming bright spots. Killen, 2007, pp. 438–442 Its abundance is also enhanced near the dawn terminator as compared to the dusk terminator. Killen, 2007, pp. 442–444 Some research has claimed a correlation of the sodium abundance with certain surface features such as Caloris or radio bright spots; however these results remain controversial. A year after the sodium discovery, Potter and Morgan reported that potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosphe ...
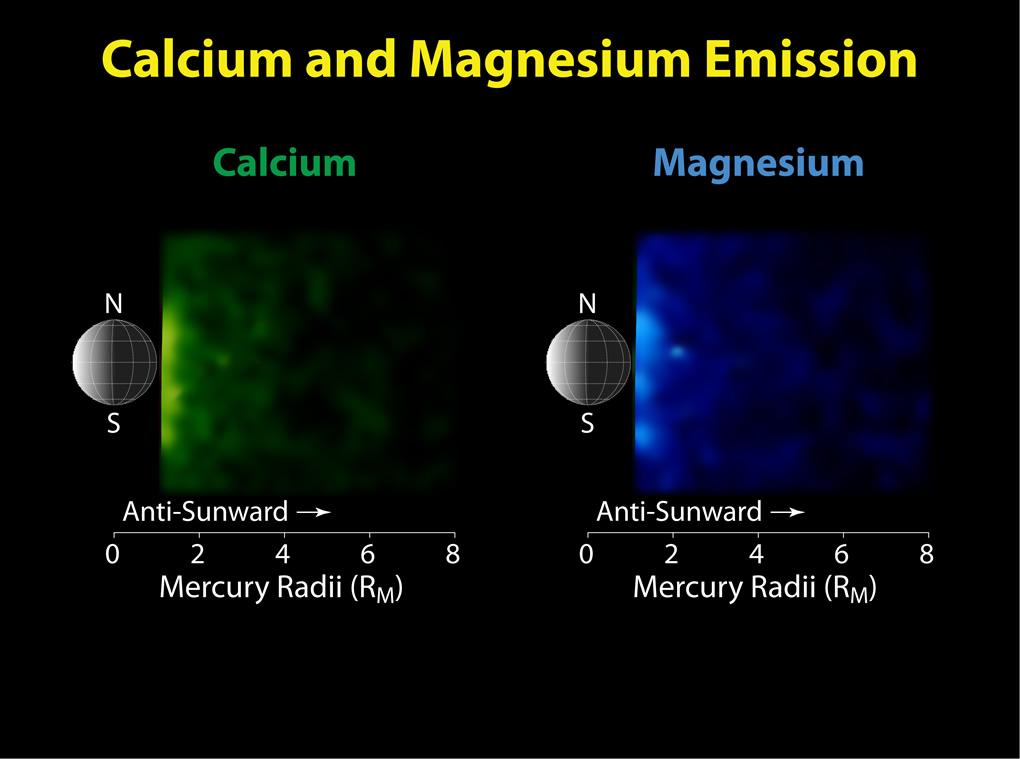
(K) is also present in the exosphere of Mercury, though with a column density two orders of magnitude lower than that of sodium. The properties and spatial distribution of these two elements are otherwise very similar. Killen, 2007, pp. 449–452 In 1998 another element, calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
(Ca), was detected with column density three orders of magnitude below that of sodium. Killen, 2007, pp. 452–453 Observations by the ''MESSENGER'' probe in 2009 showed that calcium is concentrated mainly near the equator—opposite to what is observed for sodium and potassium. McClintock 2009, p. 612–613 Further observations by Messenger reported in 2014 note the atmosphere is supplemented by materials vaporized off the surface by meteors both sporadic and in a meteor shower
A meteor shower is a celestial event in which a number of meteors are observed to radiate, or originate, from one point in the night sky. These meteors are caused by streams of cosmic debris called meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at extre ...
associated with Comet Encke
Comet Encke , or Encke's Comet (official designation: 2P/Encke), is a periodic comet that completes an orbit of the Sun once every 3.3 years. (This is the shortest period of a reasonably bright comet; the faint main-belt comet 311P/PanSTARRS ha ...
.
In 2008 the ''MESSENGER
''MESSENGER'' was a NASA robotic space probe that orbited the planet Mercury between 2011 and 2015, studying Mercury's chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field. The name is a backronym for "Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geoche ...
'' probe's Fast Imaging Plasma Spectrometer (FIPS) discovered several molecular and different ions in the vicinity of Mercury, including H2O+ (ionized water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous pha ...
) and H2S+ (ionized hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The unde ...
). Their abundances relative to sodium are about 0.2 and 0.7, respectively. Other ions such as H3O+ (hydronium
In chemistry, hydronium (hydroxonium in traditional British English) is the common name for the aqueous cation , the type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. It is often viewed as the positive ion present when an Arrhenius acid is d ...
), OH (hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
), O2+ and Si+ are present as well. Zurbuchen 2008, p. 91, Table 1 During its 2009 flyby, the Ultraviolet and Visible Spectrometer (UVVS) channel of the Mercury Atmospheric and Surface Composition Spectrometer (MASCS) on board the ''MESSENGER'' spacecraft first revealed the presence of magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
in the Mercurian exosphere. The near-surface abundance of this newly detected constituent is roughly comparable to that of sodium.
Properties
''Mariner 10''ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than ...
observations have established an upper bound on the exospheric surface density at about 105 particles per cubic centimeter. This corresponds to a surface pressure of less than 10−14 bar
Bar or BAR may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages
* Candy bar
* Chocolate bar
Science and technology
* Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment
* Bar (tropical cyclone), a layer of cloud
* Bar (u ...
(1 nPa). Domingue, 2007, pp. 162–163
The temperature of Mercury's exosphere depends on species as well as geographical location. For exospheric atomic hydrogen, the temperature appears to be about 420 K, a value obtained by both ''Mariner 10'' and ''MESSENGER''. The temperature for sodium is much higher, reaching 750–1,500 K on the equator and 1,500–3,500 K at the poles. Killen, 2007, pp. 436–438 Some observations show that Mercury is surrounded by a hot corona of calcium atoms with temperature between 12,000 and 20,000 K. In the early 2000s, a simulation of Mercury's Na exosphere and its temporal variation was conducted to identify the source process that supplied crustal species to the exosphere. Processes like; evaporation, diffusion from the interior, sputtering by photons and energetic ions, chemical sputtering by photons, and meteoritic vaporization were tested. However, evaporation provides the strongest match when comparing the changes in the sodium exosphere with solar distance and time of day to the 2001 observations of Mercury's sodium tail.
Tails

 Because of Mercury's proximity to the Sun, the pressure of solar light is much stronger than near Earth. Solar radiation pushes neutral atoms away from Mercury, creating a comet-like tail behind it. McClintock 2009, p. 610–611 The main component in the tail is sodium, which has been detected beyond 24 million km (1000 RM) from the planet.
Because of Mercury's proximity to the Sun, the pressure of solar light is much stronger than near Earth. Solar radiation pushes neutral atoms away from Mercury, creating a comet-like tail behind it. McClintock 2009, p. 610–611 The main component in the tail is sodium, which has been detected beyond 24 million km (1000 RM) from the planet.Schmidt
Schmidt may refer to:
* Schmidt (surname), including list of people with the surname
* Schmidt (singer) (born 1990), German pop and jazz singer
* Schmidt (lunar crater), a small lunar impact crater
* Schmidt (Martian crater), a List of craters on ...
2010, p. 9–16 This sodium tail expands rapidly to a diameter of about 20,000 km at a distance of 17,500 km. Killen, 2007, p. 448 In 2009, ''MESSENGER'' also detected calcium and magnesium in the tail, although these elements were only observed at distances less than 8 RM.
Observation difficulties
Mercury is the least explored planet of theinner Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
due to the many difficulties of observation. The position of Mercury as seen from Earth is always very close to the Sun, which causes challenges when trying to observe it. The Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versa ...
and other Earth-based space imaging systems have highly sensitive sensors so they can observe deep space objects. They must not be directed toward the Sun, lest its powerful radiation destroy the sensors.
Instead, flyby and orbital missions to Mercury can study the planet and receive accurate data. Even though Mercury is closer to Earth than Pluto is, the transfer orbit
{{Astrodynamics
Orbits
Astrodynamics
In orbital mechanics, a transfer orbit is an intermediate elliptical orbit that is used to move a spacecraft in an orbital maneuver from one circular, or largely circular, orbit to another.
There are several ...
from Earth to Mercury requires more energy. Mercury being so close to the Sun, space probes going there are accelerating as they approach, due to the Sun's gravitational pull. This requires the use of retrorocket
A retrorocket (short for ''retrograde rocket'') is a rocket engine providing thrust opposing the motion of a vehicle, thereby causing it to decelerate. They have mostly been used in spacecraft, with more limited use in short-runway aircraft land ...
s, which use fuel that the probe must carry instead of better instruments.
See also
*Orders of magnitude (pressure)
This is a tabulated listing of the orders of magnitude in relation to pressure expressed in pascals.
References
{{Orders of magnitude
Units of pressure
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to ...
*Magnetosphere of Mercury
Mercury's magnetic field is approximately a magnetic dipole (meaning the field has only two magnetic poles) apparently global, on planet Mercury. Data from ''Mariner 10'' led to its discovery in 1974; the spacecraft measured the field's strengt ...
References
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * {{Authority control Mercury Mercury (planet)