|
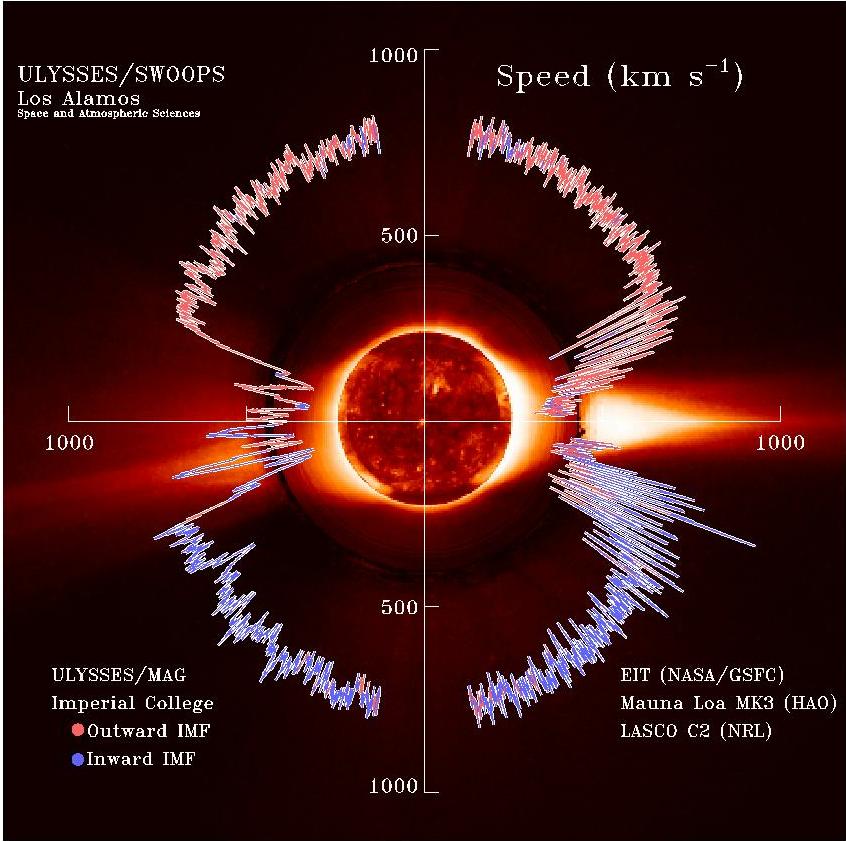
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of particle species found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of Chemical element, elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over Solar coordinate systems#Heliographic, solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Wind Speed Interplanetary Magnetic Field
Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the Earth on its revolution around the Sun ** Solar eclipse, an eclipse of a sun in which it is obstructed by the moon ** Solar System, the planetary system made up by the Sun and the objects orbiting it * Solar Maximum Mission, a satellite * SOLAR (ISS), an observatory on International Space Station Music * "Solar" (composition), attributed to Miles Davis * ''Solar'' (Red Garland album), 1962 * ''Solar'' (Taeyang album), 2010 * ''Solar'', a 2011 album by Rubik * "Solar", a song by Northlane from '' Mesmer'', 2017 * "Solar", a song by Sault from ''Air'', 2022 * ”Solar”, a song by Stam1na from '' Taival'', 2018 * SOLAR Records, a record label Geography * Solar (Spanish term), a type of urban site * Solar, Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
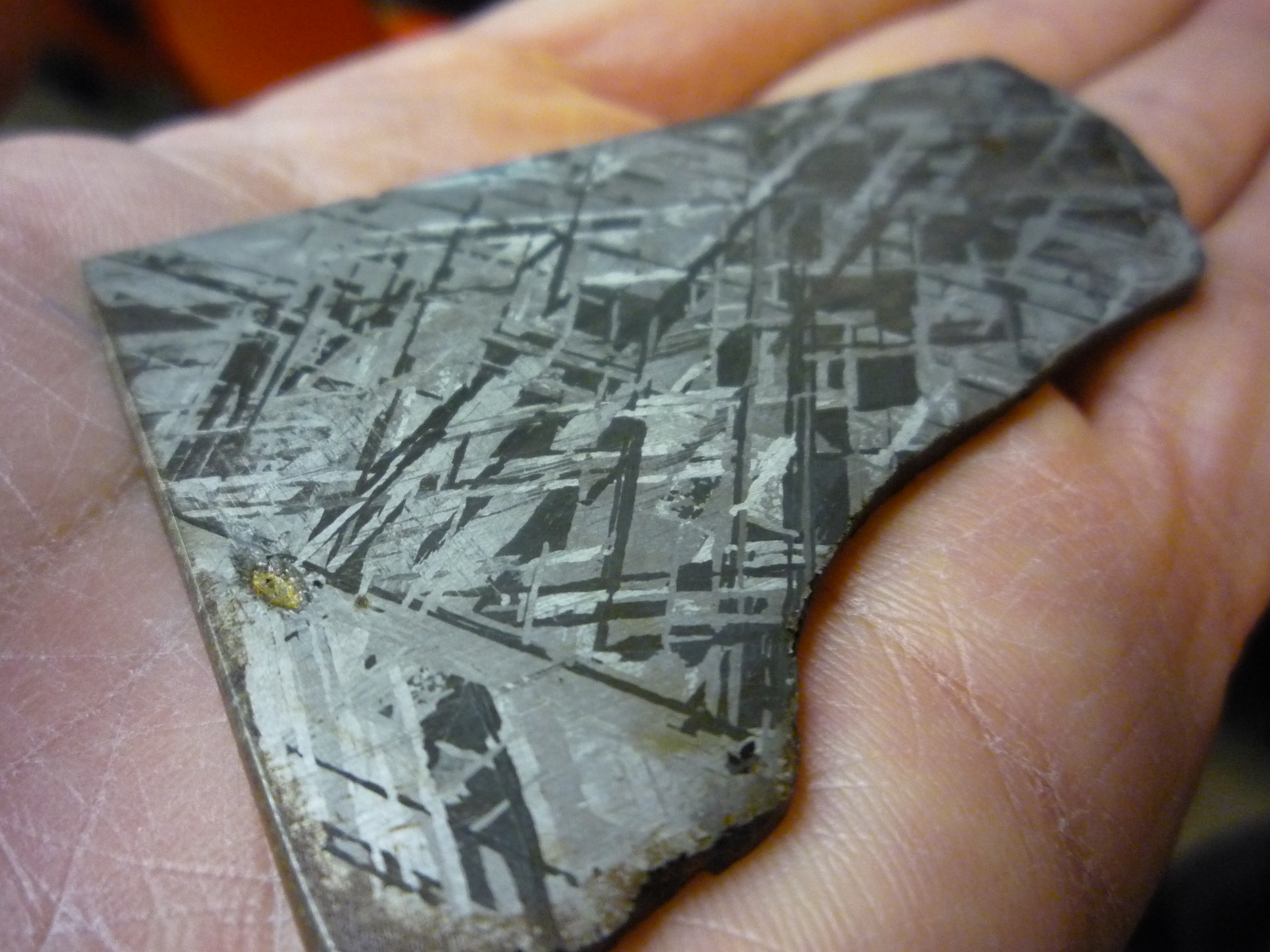
Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth's crust, being mainly deposited by meteorites in its metallic state. Extracting usable metal from iron ores requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching , about 500 °C (900 °F) higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BC and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys – in some regions, only around 1200 BC. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. In the modern world, iron alloys, such as steel, stainless steel, cast iron and special steels, are by far the most common industrial metals, due to their mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Radii
Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the Earth on its revolution around the Sun ** Solar eclipse, an eclipse of a sun in which it is obstructed by the moon ** Solar System, the planetary system made up by the Sun and the objects orbiting it * Solar Maximum Mission, a satellite * SOLAR (ISS), an observatory on International Space Station Music * "Solar" (composition), attributed to Miles Davis * ''Solar'' (Red Garland album), 1962 * ''Solar'' (Taeyang album), 2010 * ''Solar'', a 2011 album by Rubik * "Solar", a song by Northlane from '' Mesmer'', 2017 * "Solar", a song by Sault from '' Air'', 2022 * ”Solar”, a song by Stam1na from '' Taival'', 2018 * SOLAR Records, a record label Geography * Solar (Spanish term), a type of urban site * Sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfvén Surface
The Alfvén surface is the boundary separating a star's corona from the stellar wind defined as where the coronal plasma's Alfvén speed and the large-scale stellar wind speed are equal. It is named after Hannes Alfvén, and is also called Alfvén critical surface, Alfvén point, or Alfvén radius. In 2018, the Parker Solar Probe became the first spacecraft that crossed Alfvén surface of the Sun. Definition Stars do not have a solid surface. However, they have a superheated atmosphere, made of solar material bound to the star by gravity and magnetic forces. The stellar corona extends far beyond the solar surface, or photosphere, and is considered the outer boundary of the star. It marks the transition to the solar wind which moves through the planetary system. This limit is defined by the distance at which disturbances in the solar wind cannot propagate back to the solar surface. Those disturbances cannot propagate back towards a star if the outbound solar wind speed exceeds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force between objects and the Earth. This force is dominated by the combined gravitational interactions of particles but also includes effect of the Earth's rotation. Gravity gives weight to physical objects and is essential to understanding the mechanisms responsible for surface water waves and lunar tides. Gravity also has many important biological functions, helping to guide the growth of plants through the process of gravitropism and influencing the circulation of fluids in multicellular organisms. The gravitational attraction between primordial hydrogen and clumps of dark matter in the early universe caused the hydrogen gas to coalesce, eventually condensing and fusing to form stars. At larger scales this results in galaxies and clust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Coordinate Systems
In solar observation and imaging, coordinate systems are used to identify and communicate locations on and around the Sun. The Sun is made of Plasma (physics), plasma, so there are no permanent demarcated points that can be referenced. Background The Sun is a rotating sphere of Plasma (physics), plasma at the center of the Solar System. It lacks a solid or liquid surface, so the interface separating its interior and its exterior is usually defined as the boundary where plasma becomes opaque to visible light, the photosphere. Since plasma is gaseous in nature, this surface has no permanent demarcated points that can be used for reference. Furthermore, its rate of rotation varies with latitude, rotating faster at the equator than at the Poles of astronomical bodies, poles. Cardinal directions In observations of the solar disk, cardinal directions are typically defined so that the Sun's northern and southern hemispheres point toward Earth's northern and southern celestial poles, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed
In kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a non-negative scalar quantity. Introduction of the speed/velocity terminology by Prof. Tait, in 1882. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance travelled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as the duration of the time interval approaches zero. Speed is the magnitude of ''velocity'' (a vector), which indicates additionally the direction of motion. Speed has the dimensions of distance divided by time. The SI unit of speed is the metre per second (m/s), but the most common unit of speed in everyday usage is the kilometre per hour (km/h) or, in the US and the UK, miles per hour (mph). For air and marine travel, the knot is commonly used. The fastest possible speed at wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be used: \rho = \frac, where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance, the density is equal to its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium is the densest known element at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different systems of units, it is sometimes replaced by the dimensionless quantity "relative den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interplanetary Magnetic Field
The interplanetary magnetic field (IMF), also commonly referred to as the heliospheric magnetic field (HMF), is the component of the solar magnetic field that is dragged out from the solar corona by the solar wind flow to fill the Solar System. Coronal and solar wind plasma The coronal and solar wind plasmas are highly electrically conductive, meaning the magnetic field lines and the plasma flows are effectively "frozen" together and the magnetic field cannot diffuse through the plasma on time scales of interest. In the solar corona, the magnetic pressure greatly exceeds the plasma pressure and thus the plasma is primarily structured and confined by the magnetic field. However, with increasing altitude through the corona, the solar wind accelerates as it extracts energy from the magnetic field through the Lorentz force interaction, resulting in the flow momentum exceeding the restraining magnetic tension force and the coronal magnetic field is dragged out by the solar win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), but different nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have similar chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is derived from the Greek roots isos ( ἴσος "equal") and topos ( τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd in a 1913 suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy, who popularized the term. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called its atomic number and is equal to the number of el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere. Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores. Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |