|
Solar Radii
Solar radius is a unit of distance used to express the size of stars in astronomy relative to the Sun. The solar radius is usually defined as the radius to the layer in the Sun's photosphere where the optical depth equals 2/3: :1\,R_ = 6.957\times 10^8 \hbox is approximately 10 times the average radius of Jupiter, about 109 times the radius of the Earth, and 1/215th of an astronomical unit, the distance of the Earth from the Sun. It varies slightly from pole to equator due to its rotation, which induces an oblateness in the order of 10 parts per million. Measurements The unmanned SOHO spacecraft was used to measure the radius of the Sun by timing transits of Mercury across the surface during 2003 and 2006. The result was a measured radius of . Haberreiter, Schmutz & Kosovichev (2008) determined the radius corresponding to the solar photosphere to be . This new value is consistent with helioseismic estimates; the same study showed that previous estimates using inflection po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre
The metre ( British spelling) or meter ( American spelling; see spelling differences) (from the French unit , from the Greek noun , "measure"), symbol m, is the primary unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), though its prefixed forms are also used relatively frequently. The metre was originally defined in 1793 as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a great circle, so the Earth's circumference is approximately km. In 1799, the metre was redefined in terms of a prototype metre bar (the actual bar used was changed in 1889). In 1960, the metre was redefined in terms of a certain number of wavelengths of a certain emission line of krypton-86. The current definition was adopted in 1983 and modified slightly in 2002 to clarify that the metre is a measure of proper length. From 1983 until 2019, the metre was formally defined as the length of the path travelled by light in a vacuum in of a second. After the 2019 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Rotation
Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface. The rotation of a star produces an equatorial bulge due to centrifugal force. As stars are not solid bodies, they can also undergo differential rotation. Thus the equator of the star can rotate at a different angular velocity than the higher latitudes. These differences in the rate of rotation within a star may have a significant role in the generation of a stellar magnetic field. The magnetic field of a star interacts with the stellar wind. As the wind moves away from the star its rate of angular velocity slows. The magnetic field of the star interacts with the wind, which applies a drag to the stellar rotation. As a result, angular momentum is transferred from the star to the wind, and over time this gradually slows the star's rate of rotation. Measurement Unless a star is being obse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Radius
Earth radius (denoted as ''R''🜨 or R_E) is the distance from the center of Earth to a point on or near its surface. Approximating the figure of Earth by an Earth spheroid, the radius ranges from a maximum of nearly (equatorial radius, denoted ''a'') to a minimum of nearly (polar radius, denoted ''b''). A ''nominal Earth radius'' is sometimes used as a unit of measurement in astronomy and geophysics, which is recommended by the International Astronomical Union to be the equatorial value. A globally-average value is usually considered to be with a 0.3% variability (±10 km) for the following reasons. The International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics (IUGG) provides three reference values: the ''mean radius'' (R) of three radii measured at two equator points and a pole; the ''authalic radius'', which is the radius of a sphere with the same surface area (R); and the ''volumetric radius'', which is the radius of a sphere having the same volume as the ellipsoid (R). All thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. This equates to about two nonillion ( short scale), two quintillion (long scale) kilograms or 2000 quettagrams: The solar mass is about times the mass of Earth (), or times the mass of Jupiter (). History of measurement The value of the gravitational constant was first derived from measurements that were made by Henry Cavendish in 1798 with a torsion balance. The value he obtained differs by only 1% from the modern value, but was not as precise. The diurnal parallax of the Sun was accurately measured during the transits of Venus in 1761 and 1769, yielding a value of (9 arcseconds, compared to the present value of ). From the value of the diurnal parallax, one can determine the distance to the Sun from the geome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Luminosity
The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux ( power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun. One nominal solar luminosity is defined by the International Astronomical Union to be . This does not include the solar neutrino luminosity, which would add , or , i.e. a total of (the mean energy of the solar photons is 26 MeV and that of the solar neutrinos 0.59 MeV, i.e. 2.27%; the Sun emits photons and as many neutrinos each second, of which per m2 reach the Earth each second). The Sun is a weakly variable star, and its actual luminosity therefore fluctuates. The major fluctuation is the eleven-year solar cycle (sunspot cycle) that causes a quasi-periodic variation of about ±0.1%. Other variations over the last 200–300 years are thought to be much smaller than this. Determination Solar luminosity is related to solar irradiance (the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
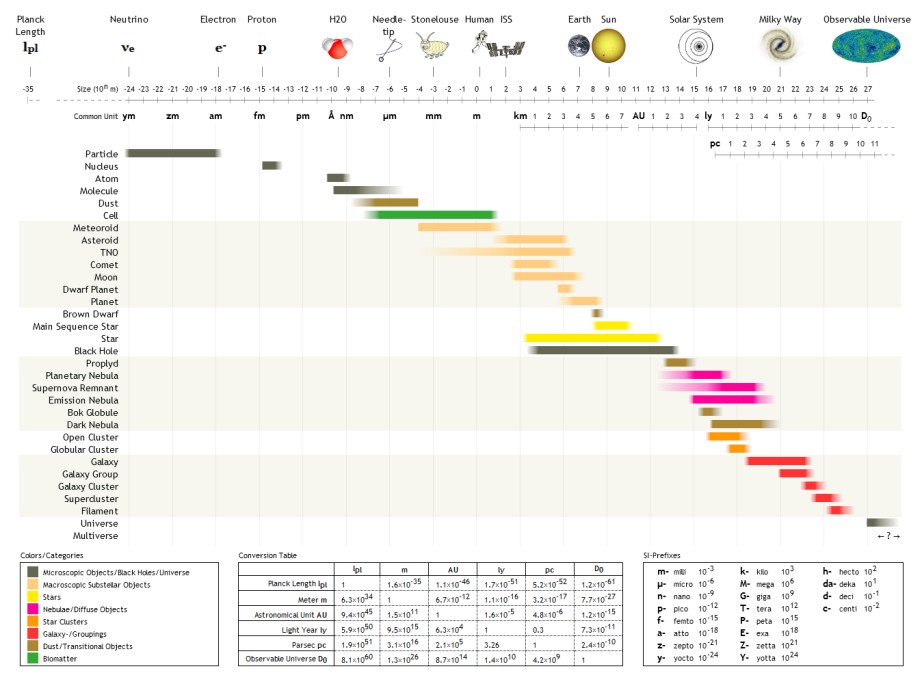
Orders Of Magnitude (length)
The following are examples of orders of magnitude for different lengths. __TOC__ Overview Detailed list To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following list describes various lengths between 1.6 \times 10^ metres and 10^metres. Subatomic scale Atomic to cellular scale Cellular to human scale Human to astronomical scale Astronomical scale Less than 1 zeptometre The ' ( SI symbol: ') is a unit of length in the metric system equal to . To help compare different orders of magnitude, this section lists lengths shorter than 10−21 m (1 zm). *1.6 × 10−5 quectometres (1.6 × 10−35 metres) – the Planck length (Measures of distance shorter than this do not make physical sense, according to current theories of physics.) *1 qm – 1 quectometre, the smallest named subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one nonillionth of a metre *1 rm – 1 rontometre, a subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one octillio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Largest Known Stars
Below are lists of the largest stars currently known, ordered by radius and separated into categories by galaxy. The unit of measurement used is the radius of the Sun (approximately ). The angular diameters of stars can be measured directly using stellar interferometry. Other methods can use lunar occultations or from eclipsing binaries, which can be used to test indirect methods of finding stellar radii. Only a few useful supergiant stars can be occulted by the Moon, including Antares A (Alpha Scorpii A). Examples of eclipsing binaries are Epsilon Aurigae (Almaaz), VV Cephei, and V766 Centauri (HR 5171). Angular diameter measurements can be inconsistent because the boundary of the very tenuous atmosphere (opacity) differs depending on the wavelength of light in which the star is observed. Uncertainties remain with the membership and order of the lists, especially when deriving various parameters used in calculations, such as stellar luminosity and effective temperatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits the Sun, from a maximum ( aphelion) to a minimum ( perihelion) and back again once each year. The astronomical unit was originally conceived as the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion; however, since 2012 it has been defined as exactly (see below for several conversions). The astronomical unit is used primarily for measuring distances within the Solar System or around other stars. It is also a fundamental component in the definition of another unit of astronomical length, the parsec. History of symbol usage A variety of unit symbols and abbreviations have been in use for the astronomical unit. In a 1976 resolution, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) had used the symbol ''A'' to denote a length equal to the ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parker Solar Probe
The Parker Solar Probe (PSP; previously Solar Probe, Solar Probe Plus or Solar Probe+) is a NASA space probe launched in 2018 with the mission of making observations of the outer corona of the Sun. It will approach to within 9.86 solar radii (6.9 million km or 4.3 million miles) from the center of the Sun, and by 2025 will travel, at closest approach, as fast as , or 0.064% the speed of light. It is the fastest object ever built. The project was announced in the fiscal 2009 budget year. The cost of the project is US$1.5 billion. Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory designed and built the spacecraft, which was launched on 12 August 2018. It became the first NASA spacecraft named after a living person, honoring nonagenarian physicist Eugene Newman Parker, professor emeritus at the University of Chicago. A memory card containing the names of over 1.1 million people was mounted on a plaque and installed below the spacecraft's high-gain antenna on 18 May 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Orbiter
The Solar Orbiter (SolO) is a Sun-observing satellite developed by the European Space Agency (ESA). SolO, designed to obtain detailed measurements of the inner heliosphere and the nascent solar wind, will also perform close observations of the polar regions of the Sun which is difficult to do from Earth. These observations are important in investigating how the Sun creates and controls its heliosphere. SolO makes observations of the Sun from an eccentric orbit moving as close as ≈60 solar radii (RS), or 0.284 astronomical units (au), placing it inside Mercury's perihelion of 0.3075 au. During the mission the orbital inclination will be raised to about 24°. The total mission cost is US$1.5 billion, counting both ESA and NASA contributions. SolO was launched on 10 February 2020. The mission is planned to last seven years. Spacecraft The Solar Orbiter spacecraft is a Sun-pointed, three-axis stabilised platform with a dedicated heat shield to provide protection from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded in 1919 and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. As of 2018, the Union had over 13,700 individual members, spanning 90 countries, and 82 national members. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar And Heliospheric Observatory
The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) is a European Space Agency (ESA) spacecraft built by a European industrial consortium led by Matra Marconi Space (now Airbus Defence and Space) that was launched on a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIAS launch vehicle on 2 December 1995, to study the Sun. It has also discovered over 4,000 comets.(2,703 discoveries as of 21 April 2014) It began normal operations in May 1996. It is a joint project between the (ESA) and . SOHO was part of the In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
