|
Gazella Bennettii
The chinkara (''Gazella bennettii''), also known as the Indian gazelle, is a gazelle species native to Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India. Taxonomy The following six subspecies are considered valid: * Deccan chinkara (''G. b. bennettii'') (Sykes 1831) – ranges from South India, from the Ganges Valley (east to the borders of West Bengal) south at least to Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, Deccan Plateau; * Gujarat chinkara ''(G. b. christii)'' (Blyth, 1842) – ranges from the desert lowlands of Pakistan, western India, Rann of Kutch, Kathiawar, Saurastra region and as far east of Ahmedabad district in Gujarat; * Kennion gazelle, eastern jebeer gazelle or Baluchistan gazelle (''G. b. fuscifrons'') ( Blanford, 1873) – occurs in eastern Iran, (southeast and along the Makran coast, Sistan and Baluchistan) southern Afghanistan, Pakistan, Balochistan Province to Sindh and northwestern India, Rajasthan, also the darkest subspecies; * Bushehr gazelle (''G. b. karamii'') ( Groves, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's 20th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-largest hot subtropical desert. About 85% of the Thar Desert is in India, and about 15% is in Pakistan. The Thar Desert is about 4.56% of the total geographical area of India. More than 60% of the desert lies in the Indian state of Rajasthan; the portion in India also extends into Gujarat, Punjab, and Haryana. The portion in Pakistan extends into the provinces of Sindh and Punjab (the portion in the latter province is referred to as the Cholistan Desert). History of desertification Ice-age desertification During the Last Glacial Maximum 20,000 before present, an approximately ice sheet covered the Tibetan Plateau, See chapter entitled: "Reconstruction of an approximately complete Quaternary Tibetan Inland Glaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Blyth
Edward Blyth (23 December 1810 – 27 December 1873) was an English zoologist who worked for most of his life in India as a curator of zoology at the museum of the Asiatic Society of India in Calcutta. Blyth was born in London in 1810. In 1841 he travelled to India to become the curator of the museum of the Asiatic Society, Royal Asiatic Society of Bengal. He set about updating the museum's catalogues, publishing a ''Catalogue of the Birds of the Asiatic Society'' in 1849. He was prevented from doing much fieldwork himself, but received and described bird specimens from Allan Octavian Hume, A.O. Hume, Samuel Tickell, Robert Swinhoe and others. He remained as curator until 1862, when ill-health forced his return to England. His ''Natural History of the Cranes'' was published posthumously in 1881. Avian species bearing his name include Blyth's hornbill, Blyth's leaf warbler, Blyth's hawk-eagle, Blyth's olive bulbul, Blyth's parakeet, Blyth's frogmouth, Blyth's reed warbler, Blyth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colin Groves
Colin Peter Groves (24 June 1942 – 30 November 2017) was a British-Australian biologist and anthropologist. Groves was Professor of Biological Anthropology at the Australian National University in Canberra, Australia. Education Born in England, Groves completed a Bachelor of Science at University College London in 1963, and a Doctor of Philosophy at the Royal Free Hospital School of Medicine in 1966. From 1966 to 1973, he was a Postdoctoral Researcher and Teaching Fellow at the University of California, Berkeley, Queen Elizabeth College and the University of Cambridge. Career Groves emigrated to Australia in 1973 and joined the Australian National University, where he was promoted to full Professor in 2000 and remained Emeritus Professor until his death. Along with the Czech biologist Professor Vratislav Mazák, Groves was the describer of ''Homo ergaster''. Groves also wrote ''Primate Taxonomy'' published by the Smithsonian Institution Press in 2001, and Ungulate Taxonom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bushehr Gazelle
Bushehr, Booshehr or Bushire ( fa, بوشهر ; also romanised as ''Būshehr'', ''Bouchehr'', ''Buschir'' and ''Busehr''), also known as Bandar Bushehr ( fa, ; also romanised as ''Bandar Būshehr'' and ''Bandar-e Būshehr''), previously Antiochia in Persis ( grc, Ἀντιόχεια τῆς Περσίδος, Antiócheia tês Persídos) and Bukht Ardashir, is the capital city of Bushehr Province, Iran and a port city in south of Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 161,674, in 40,771 families. Bushehr lies in a vast plain running along the coastal region on the Persian Gulf coast of south-western Iran. It is built near the ancient port city of Rishahr (Sassanian, Riv Ardasher). It was the chief seaport of the country and is the administrative center of its province. Its location is about south of Tehran. Bushehr has a desert climate. Bushehr was the main trade center of Iran in the past centuries. The city structures are traditional in style, modest in proportion an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province by population after Punjab. It shares land borders with the Pakistani provinces of Balochistan to the west and north-west and Punjab to the north. It shares International border with the Indian states of Gujarat and Rajasthan to the east; it is also bounded by the Arabian Sea to the south. Sindh's landscape consists mostly of alluvial plains flanking the Indus River, the Thar Desert in the eastern portion of the province along the international border with India, and the Kirthar Mountains in the western portion of the province. The economy of Sindh is the second-largest in Pakistan after the province of Punjab; its provincial capital of Karachi is the most populous city in the country as well as its main financial hub. Sindh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balochistan, Pakistan
Balochistan (; bal, بلۏچستان; ) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southwestern region of the country, Balochistan is the largest province of Pakistan by land area but is the least populated one. It shares land borders with the Pakistani provinces of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Punjab to the north-east and Sindh to the south-east. It shares International borders with Iran to the west and Afghanistan to the north; It is also bound by the Arabian Sea to the south. Balochistan is an extensive plateau of rough terrain divided into basins by ranges of sufficient heights and ruggedness. It has the world's largest deep sea port, The Port of Gwadar lying in the Arabian Sea. Balochistan shares borders with Punjab and the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa to the northeast, Sindh to the east and southeast, the Arabian Sea to the south, Iran ( Sistan and Baluchestan) to the west and Afghanistan ( Helmand, Nimruz, Kandahar, Paktika and Zabul Provinces) to the north and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makran
Makran ( fa, مكران), mentioned in some sources as Mecran and Mokrān, is the coastal region of Baluchistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in Balochistan, in Pakistan and Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. It extends westwards, from the Sonmiani Bay to the northwest of Karachi in the east, to the fringes of the region of Bashkardia/Bāšgerd in the southern part of the Sistān and Balučestān province of modern Iran. Makrān is thus bisected by the modern political boundary between Pakistan and Iran. Etymology The southern part of Balochistan is called ''Kech Makran'' on Pakistani side and Makran on the Iranian side which is also the name of a former Iranian province. The location corresponds to that of the Maka satrapy in Achaemenid times. The Sumerian trading partners of Magan are identified with Makran. In Varahamihira's Brihat Samhita, there is a mention of a tribe called ''Makara'' inhabiting the lands west of India. Arrian used the term ''Ichthyophagi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Thomas Blanford
William Thomas Blanford (7 October 183223 June 1905) was an English geologist and naturalist. He is best remembered as the editor of a major series on ''The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma''. Biography Blanford was born in London to William Blanford and Elizabeth Simpson. His father owned a factory next to their house on Bouverie street, Whitefriars. He was educated in private schools in Brighton (until 1846) and Paris (1848). He joined his family business in carving and gilding and studied at the School of Design in Somerset House. Suffering from ill health, he spent two years in a business house at Civitavecchia owned by a friend of his father. His initial aim was to enter a mercantile career. On returning to England in 1851 he was induced to enter the newly established Royal School of Mines (now part of Imperial College London), which his younger brother Henry F. Blanford (1834–1893), afterwards head of the Indian Meteorological Department, had alr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
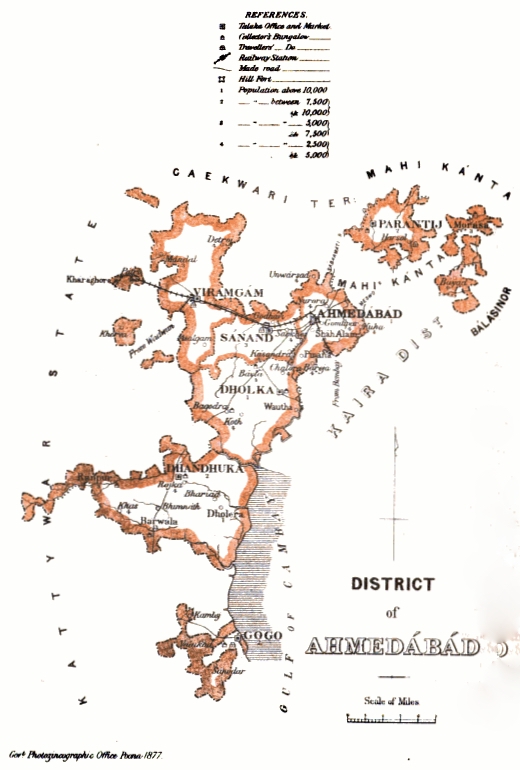
Ahmedabad District
{{Infobox settlement , name = Ahmedabad District , native_name = , native_name_lang = , settlement_type = District of Gujarat , image_skyline = Delhi Darwaja 1.jpg , imagesize = , HDI {{nobold, (2018) , blank_info_sec2 = {{increase 0.783{{cite web , title=Sub-national HDI – Area Database = 778(high) , image_alt = , image_caption = Delhi Darwaza, one of the gates to the old city , image_flag = , flag_alt = , image_seal = , seal_alt = , image_shield = , shield_alt = , nickname = Ahm , motto = save water drink beer , image_map = Ahmedabad in Gujarat (India).svg , map_alt = , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)