|
Garudimimus
''Garudimimus'' (meaning "Garuda mimic") is a genus of ornithomimosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous. The genus is known from a single specimen found in 1981 by a Soviet-Mongolian paleontological expedition in the Bayan Shireh Formation and formally described in the same year by Rinchen Barsbold; the only species is ''Garudimimus brevipes''. Several interpretations about the anatomical traits of ''Garudimimus'' were made in posterior examinations of the specimen, but most of them were criticized during its comprehensive redescription in 2005. Extensive undescribed ornithomimosaur remains at the type locality of ''Garudimimus'' may represent additional specimens of the genus. The only known specimen of ''Garudimimus'' was a medium-sized animal measuring nearly in length and weighing about . It was an ornithomimosaur with a mix of basal and derived features; unlike primitive ornithomimosaurs, both upper and lower jaws were toothless, a trait that is often reporte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinocheiridae
Deinocheiridae is a family of ornithomimosaurian dinosaurs, living in Asia and the Americas from the Albian until the Maastrichtian. The family was originally named by Halszka Osmólska and Roniewicz in 1970, including only the type genus ''Deinocheirus''. In a 2014 study by Yuong-Nam Lee and colleagues and published in the journal ''Nature'', it was found that Deinocheiridae was a valid family. Lee ''et al.'' found that based on a new phylogenetic analysis including the recently discovered complete skeletons of ''Deinocheirus'', the type genus, as well as ''Garudimimus'' and ''Beishanlong'', could be placed as a successive group, with ''Beishanlong'' as the most primitive and ''Deinocheirus'' as most derived. The family Garudimimidae, named in 1981 by Rinchen Barsbold, is now a junior synonym of Deinocheiridae as the latter family includes the type genus of the former. The group existed from 115 to 69 million years ago, with ''Beishanlong'' living from 115 to 100 mya, ''Garudimi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1981 In Paleontology
Plants Angiosperms Arthropoda Insects Archosauromorpha Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Remarks on newly named birds * ''Palaeopteryx thomsoni'' Jensen, 1981. is most probably not a bird but perhaps a small dinosaur, it is best treated as a taxon non avium. * ''Plegadis pharangites'' Olson, 1981. is a new name for ''Plegadis gracilis'' Miller et Bowman, 1956, preoccupied by ''Plegadis gracilis'' (Lydekker, 1891), described as ''Milnea gracilis'' Lydekker, 1891 and transferred to the genus ''Plegadis'' Kaup, 1829 by Cheneval, 1984. Newly named birds Plesiosaurs * Carroll, R. C., 1981, Plesiosaur ancestors from the Upper Permian of Madagascar: Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B, v. 293, p. 315- 383. Pterosaurs New taxa Synapsids Non-mammalian References {{portal, Paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinocheirus
''Deinocheirus'' ( ) is a genus of large ornithomimosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous around 70 million years ago. In 1965, a pair of large arms, shoulder girdles, and a few other bones of a new dinosaur were first discovered in the Nemegt Formation of Mongolia. In 1970, this specimen became the holotype of the only species within the genus, ''Deinocheirus mirificus''; the genus name is Greek for "horrible hand". No further remains were discovered for almost fifty years, and its nature remained a mystery. Two more complete specimens were described in 2014, which shed light on many aspects of the animal. Parts of these new specimens had been looted from Mongolia some years before, but were repatriated in 2014. ''Deinocheirus'' was an unusual ornithomimosaur, the largest of the clade at long, and weighing . Though it was a bulky animal, it had many hollow bones which saved weight. The arms were among the largest of any bipedal dinosaur at long, with large, blunt claws o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayan Shireh Formation
The Bayan Shireh Formation (also known as Baynshiree/Baynshire, Baynshirenskaya Svita or Baysheen Shireh) is a geological formation in Mongolia, that dates to the Cretaceous period. It was first described and established by Vasiliev et al. 1959. Description The Bayan Shireh Formation is primarily composed by varicoloured claystones and sandstones with calcareous concretions and characterized by grey mudstones and yellowish-brown medium grained sandstones. Up to thick, the most complete sections are found in the eastern Gobi Desert, consisting of fine-grained, often cross-stratified gray sandstone interbedded with claystone and concretionary, intraformational conglomerates with relatively thick units of red to brown mudstone in the upper part. The Baynshire and Burkhant localities are mainly composed by mudstone, siltstone, sandstone, and conglomerates, with most of their sedimentation being fluvial. The environments that were present on the Bayan Shireh Formation consisted ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rinchen Barsbold
, Rinchyengiin Barsbold, born December 21, 1935 in Ulaanbaatar) is a Mongolian paleontologist and geologist. He works with the Institute of Geology, at Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. He is an expert in vertebrate paleontology and Mesozoic stratigraphy. Barsbold has been instrumental in the discovery and recovery of one of the largest dinosaur collections in the world. His work has helped to form a more modern understanding of the later stages of dinosaur evolution in Eurasia. Barsbold has had considerable influence on dinosaur paleontology in the Communist world. His scientific work has made him a leading authority on theropods of the Gobi Desert, starting with his doctoral dissertation on these dinosaurs. As early as 1983, he noted that in different lineages of theropods, many features previously only known from birds had evolved in various combinations (Barsbold 1983). He postulated that as a result of this "ornithization", one or several lineages of theropods that happened to acquire th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, ( gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and engineering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessarily "typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
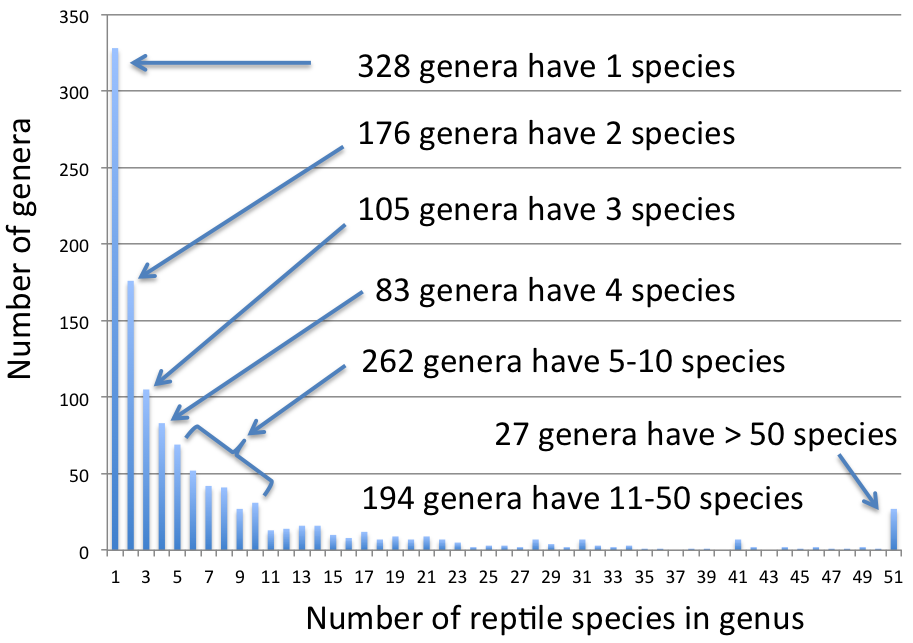
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Mythology
The Buddhist traditions have created and maintained a vast body of mythological literature. The central myth of Buddhism is the life of the Buddha. This is told in relatively realistic terms in the earliest texts, and was soon elaborated into a complex literary mythology. The chief motif of this story, and the most distinctive feature of Buddhist myth, is the Buddha's renunciation: leaving his home and family for a spiritual quest. Alongside this central myth, the traditions contain large numbers of smaller stories, which are usually supposed to convey an ethical or Buddhist teaching. These include the popular Jātakas, folk tales or legends believed to be past lives of Gautama Buddha. Since these are regarded as episodes in the life of the Buddha, they are treated here as “myth”, rather than distinguishing between myth, legend, and folk-tale. Buddhist mythology is maintained in texts, but these have always existed alongside oral traditions of storytelling, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |