|
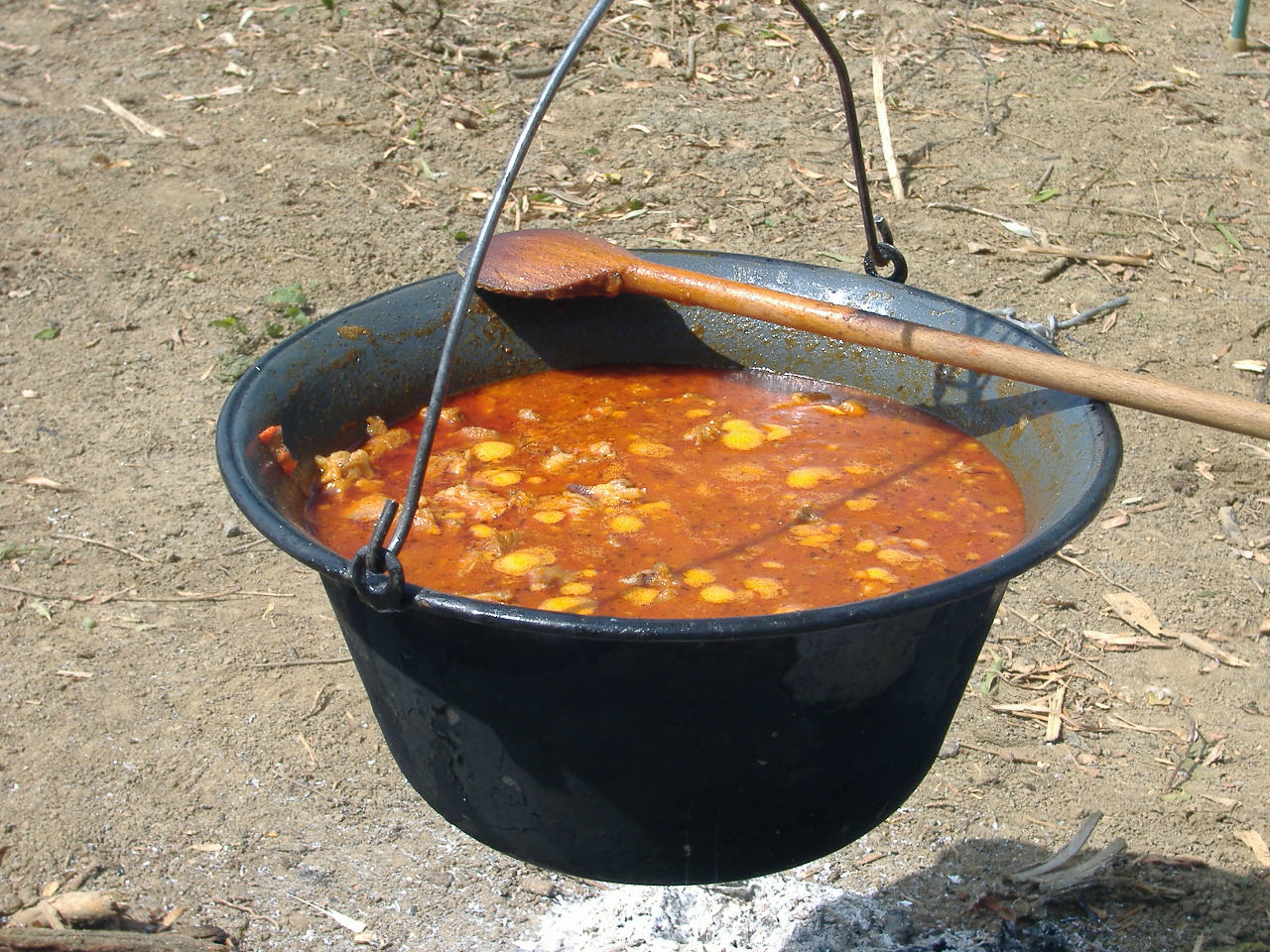
Gamasot
''Gamasot'' (), or simply ''sot'' (), is a big, heavy pot or cauldron used for Korean cooking. Origin The origins of the ‘sot’ originate in the "Chung" which is made of bronze. Researchers have speculated that copper would be easier to handle because it has a lower melting point than steel. Bronze ‘sot’ are frequently unearthed as remains of the Three Kingdoms period, because the meaning of 'Chung' was symbolic of the nation, the throne, and the industry. However, the history of iron ‘sot’ goes up to the Bronze Age much earlier than the Three Kingdoms period . The copper ‘sot’ on the Korean Peninsula were first discovered in the remains of Gojoson, which belongs to the late Bronze Age Korean copper sword culture period. A large amount of ‘sot’ is excavated from the ruins of the 'Hansa-gun' which was installed as the Gojoseon was destroyed by Han in 108 BC. In particular, the remains of ‘Nakrang-gun’ are famous for the largest number of pots among the fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamasot
''Gamasot'' (), or simply ''sot'' (), is a big, heavy pot or cauldron used for Korean cooking. Origin The origins of the ‘sot’ originate in the "Chung" which is made of bronze. Researchers have speculated that copper would be easier to handle because it has a lower melting point than steel. Bronze ‘sot’ are frequently unearthed as remains of the Three Kingdoms period, because the meaning of 'Chung' was symbolic of the nation, the throne, and the industry. However, the history of iron ‘sot’ goes up to the Bronze Age much earlier than the Three Kingdoms period . The copper ‘sot’ on the Korean Peninsula were first discovered in the remains of Gojoson, which belongs to the late Bronze Age Korean copper sword culture period. A large amount of ‘sot’ is excavated from the ruins of the 'Hansa-gun' which was installed as the Gojoseon was destroyed by Han in 108 BC. In particular, the remains of ‘Nakrang-gun’ are famous for the largest number of pots among the fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamasot Miryang
''Gamasot'' (), or simply ''sot'' (), is a big, heavy pot or cauldron used for Korean cuisine, Korean cooking. Origin The origins of the ‘sot’ originate in the "Chung" which is made of bronze. Researchers have speculated that copper would be easier to handle because it has a lower melting point than steel. Bronze ‘sot’ are frequently unearthed as remains of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, Three Kingdoms period, because the meaning of 'Chung' was symbolic of the nation, the throne, and the industry. However, the history of iron ‘sot’ goes up to the Bronze Age much earlier than the Three Kingdoms of Korea, Three Kingdoms period . The copper ‘sot’ on the Korean Peninsula were first discovered in the remains of Gojoseon, Gojoson, which belongs to the late Bronze Age Korean copper sword culture period. A large amount of ‘sot’ is excavated from the ruins of the 'Hansa-gun' which was installed as the Gojoseon was destroyed by Han in 108 BC. In particular, the remains o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauldron
A cauldron (or caldron) is a large pot (kettle) for cooking or boiling over an open fire, with a lid and frequently with an arc-shaped hanger and/or integral handles or feet. There is a rich history of cauldron lore in religion, mythology, and folklore. Etymology The word cauldron is first recorded in Middle English as ''caudroun'' (13th century). It was borrowed from Norman ''caudron''T. F. Hoad, ''English Etymology'', Oxford University Press, 1993 (). p. 67. ( Picard ''caudron'', french: chaudron). It represents the phonetical evolution of Vulgar Latin ''*caldario'' for Classical Latin ''caldārium'' "hot bath", that derives from ''cal(i)dus'' "hot". The Norman-French word replaces the Old English ''ċetel'' (German ''(Koch)Kessel'' "cauldron", Dutch ''(kook)ketel'' "cauldron"), Middle English ''chetel''. The word "kettle" is a borrowing of the Old Norse variant ''ketill'' "cauldron". History Cauldrons can be found from the late Bronze Age period - vast cauldrons with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauldrons
A cauldron (or caldron) is a large pot (kettle) for cooking or boiling over an open fire, with a lid and frequently with an arc-shaped hanger and/or integral handles or feet. There is a rich history of cauldron lore in religion, mythology, and folklore. Etymology The word cauldron is first recorded in Middle English as ''caudroun'' (13th century). It was borrowed from Norman ''caudron''T. F. Hoad, ''English Etymology'', Oxford University Press, 1993 (). p. 67. ( Picard ''caudron'', french: chaudron). It represents the phonetical evolution of Vulgar Latin ''*caldario'' for Classical Latin ''caldārium'' "hot bath", that derives from ''cal(i)dus'' "hot". The Norman-French word replaces the Old English ''ċetel'' (German ''(Koch)Kessel'' "cauldron", Dutch ''(kook)ketel'' "cauldron"), Middle English ''chetel''. The word "kettle" is a borrowing of the Old Norse variant ''ketill'' "cauldron". History Cauldrons can be found from the late Bronze Age period - vast cauldrons with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cooking Vessels
This is a list of cooking vessels. A cooking vessel is a type of cookware or bakeware designed for cooking, baking, roasting, boiling or steaming. Cooking vessels are manufactured using materials such as steel, cast iron, aluminum, clay and various other ceramics. Some cooking vessels, such as ceramic ones, absorb and retain heat after cooking has finished. Cooking vessels * Bain-marie or double boiler – in cooking applications, usually consists of a pan of water in which another container or containers of food to be cooked is placed within the pan of water. * Beanpot – a deep, wide-bellied, short-necked vessel used to cook bean-based dishes. Beanpots are typically made of ceramic, though pots made of other materials, like cast iron, can also be found. * Billycan – a lightweight cooking pot in the form of a metal bucketFarrell, Michael. "Death Watch: Reading the Common Object of the Billycan in ‘Waltzing Matilda’." Journal of the Association for the Study of Austr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolsot
A ''dolsot'' () or ''gopdolsot'' () is a small-sized piece of cookware or serveware made of agalmatolite, suitable for one to two servings of ''bap'' (cooked rice). In Korean cuisine, various hot rice dishes such as bibimbap or '' gulbap'' (oyster rice) as well as plain white rice can be prepared and served in ''dolsot''. As a ''dolsot'' does not cool off as soon as removed from the stove, rice continues to cook and arrives at the table still sizzling. On the bottom of a ''dolsot'', there forms a thin crust of scorched rice, to be scraped off and eaten in the case of bibimbap, or made into ''sungnyung'' (숭늉, infusion) in the case of unseasoned rice dishes. In the former case ''dolsot'' can be brushed with sesame oil beforehand to facilitate scraping. To make ''sungnyung'', the unscorched part of rice is scooped and transferred into another serving bowl right after served, and hot water or tea (usually mild grain teas such as barley tea or corn tea) is poured into the ''dols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bap (food)
''Bap'' ( ko, 밥) is a Korean name for cooked rice prepared by boiling rice or other grains, such as black rice, barley, sorghum, various millets, and beans, until the water has cooked away. Special ingredients such as vegetables, seafood, and meat can also be added to create different kinds of ''bap''. In the past, except for the socially wealthy class, people used to eat mixed grain rice together with beans and barley rather than only rice. In Korea, grain food centered on rice has been the most commonly used since ancient times and has established itself as a staple food in everyday diets. In Korean, the honorific terms for ''bap'' (meal) include ''jinji'' () for an elderly person, ''sura'' () for a monarch, and ''me'' () for the deceased (in the ancestral rites). Preparation Traditionally, ''bap'' was made using ''gamasot'' (a cast iron cauldron) for a large family; however, in modern times, an electronic rice cooker is usually used to cook rice. A regular heavy-bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950) , place = Korean Peninsula, Yellow Sea, Sea of Japan, Korea Strait, China–North Korea border , territory = Korean Demilitarized Zone established * North Korea gains the city of Kaesong, but loses a net total of {{Convert, 1506, sqmi, km2, abbr=on, order=flip, including the city of Sokcho, to South Korea. , result = Inconclusive , combatant1 = {{Flag, First Republic of Korea, name=South Korea, 1949, size=23px , combatant1a = {{Plainlist , * {{Flagicon, United Nations, size=23px United Nations Command, United Nations{{Refn , name = nbUNforces , group = lower-alpha , On 9 July 1951 troop constituents were: US: 70.4%, ROK: 23.3% other UNC: 6.3%{{Cite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
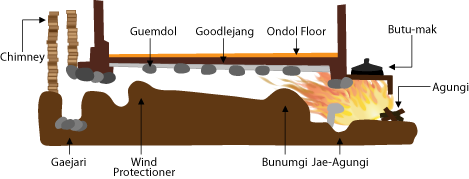
Agungi
An ''agungi'' ( ko, 아궁이) is a firebox found in traditional Korean kitchens which is used to burn firewood or other fuel for cooking. It is also a part of the traditional floor heating system, or ondol. The flat cooktop counter or hearth installed over the ''agungi'' is called a ''buttumak'' (). History Early ''buttumak'' have been dated to the 10th‒4th century BCE. Iron and ceramic ''buttumaks'', similar to their later forms, were excavated from Goguryeo 1st century BCE historical sites, such as Anak Tomb No. 3. Many Korean agrarian kitchens had ''buttumak'' with charcoal-fueled ''agungi'' until the early 1970s. File:Goguryeo buttumak 1.jpg, Iron ''buttumak'' from Goguryeo (37 BCE ‒ 668 CE) File:Agungi door 1.jpg, ''Agungi'' door from agrarian South Korea in the mid-20th century Structure ''Buttumaks'' in agrarian Korean kitchens were commonly made from brick or stone and then smoothed with clay. Above each ''agungi'' is an upward opening where ''gamasot'' (bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeongseon County
Jeongseon (''Jeongseon-gun'') is a county in the province of Gangwon-do, South Korea. It is famous as the hometown of "Jeongseon Arirang," a traditional Korean folksong. It is also the hometown of actor Won Bin and footballer Seol Ki-hyeon. History It was ruled by the Goguryeo Dynasty during the Three Kingdoms period, called Ingpyae-hyeon (잉패현). After the Silla Dynasty unified the Korean peninsula, it was renamed Jeongseon-hyeon in 757. After the Goryeo Dynasy was founded, it was promoted from a ''hyeon'' to a county (''gun'') in 1012 or 1018. After the Joseon Dynasty was founded and the territory was divided into 8 Provinces, the region was involved in the province of Gangwon. After the territory was divided into 23 districts in 1895 with the 8-provincial system abolished, it was included in the district of Chugju. When a 13-provincial system was enacted in 1896, it returned to Gangwon Province. Administrative divisions Towns (eup) * Gohan-eup * Jeongseon-eup * Sabuk- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andong
Andong () is a city in South Korea, and the capital of North Gyeongsang Province. It is the largest city in the northern part of the province with a population of 167,821 as of October 2010. The Nakdong River flows through the city. Andong is a market centre for the surrounding agricultural areas. Since the 1970s Andong has developed rapidly, although the population has fallen by nearly seventy thousand as people have moved away to Seoul, Busan, Daegu and other urban centres. In the late 1990s and early 2000s it became a tourism and cultural center. Andong is known as a centre of culture and folk traditions. The surrounding area maintains many types of traditions and the Andong Folk Festival is held in mid October every year. One of the most famous aspects of these cultural festivities are the Andong masks. Andong National University, specialising in education and Korean folklore, has grown rapidly since the 1970s. Other tertiary institutions include Andong Science College and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dosan Seowon
Dosan Seowon (alternatively, ''Tosansowon'') was established in 1574 in what is present day Andong, South Korea, in memory of and four years after the death of Korean Confucian scholar Yi Hwang by some of his disciples and other Korean Confucian authorities. Yi Hwang had retired to the location in 1549 and begun construction on the facility, a private Korean Confucian academy offering instruction in the classics and honouring the sages with regular memorial rites. Like other Korean Confucian academies, Dosan Seowon serves two purposes: education and commemoration. The site was well known in Korea as one of the leading academies and was home to the Toegye School of Thought for over 400 years. Although the educational function of the facility has long since ceased, the commemorative ceremonies have been and are still held twice a year. The ancient academy was royally chartered in 1575 by King Seonjo and was featured on the reverse of the South Korean 1,000 won bill from 1975 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |