|
Gaj's Alphabet
Gaj's Latin alphabet ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, Gajeva latinica, separator=" / ", Гајева латиница}, ), also known as ( sh-Cyrl, абецеда, ) or ( sh-Cyrl, гајица, link=no, ), is the form of the Latin script used for writing Serbo-Croatian and all of its standard varieties: Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin, and Serbian. The alphabet was initially devised by Croatian linguist Ljudevit Gaj in 1835 during the Illyrian movement in ethnically Croatian parts of Austrian Empire. It was largely based on Jan Hus's Czech alphabet and was meant to serve as a unified orthography for three Croat-populated kingdoms within the Austrian Empire at the time, namely Croatia, Dalmatia and Slavonia, and their three dialect groups, Kajkavian, Chakavian and Shtokavian, which historically utilized different spelling rules. A slightly modified version of it was later adopted as the formal Latin writing system for the unified Serbo-Croatian standard language per the Vienna Literary A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllable, and logographic systems use characters to represent words, morphemes, or other semantic units. The first fully phonemic script, the Proto-Sinaitic script, later known as the Phoenician alphabet, is considered to be the first alphabet and is the ancestor of most modern alphabets, including Arabic, Cyrillic, Greek, Hebrew, Latin, and possibly Brahmic. It was created by Semitic-speaking workers and slaves in the Sinai Peninsula (as the Proto-Sinaitic script), by selecting a small number of hieroglyphs commonly seen in their Egyptian surroundings to describe the sounds, as opposed to the semantic values of the Canaanite languages. However, Peter T. Daniels distinguishes an abugida, a set of graphemes that represent consonantal base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
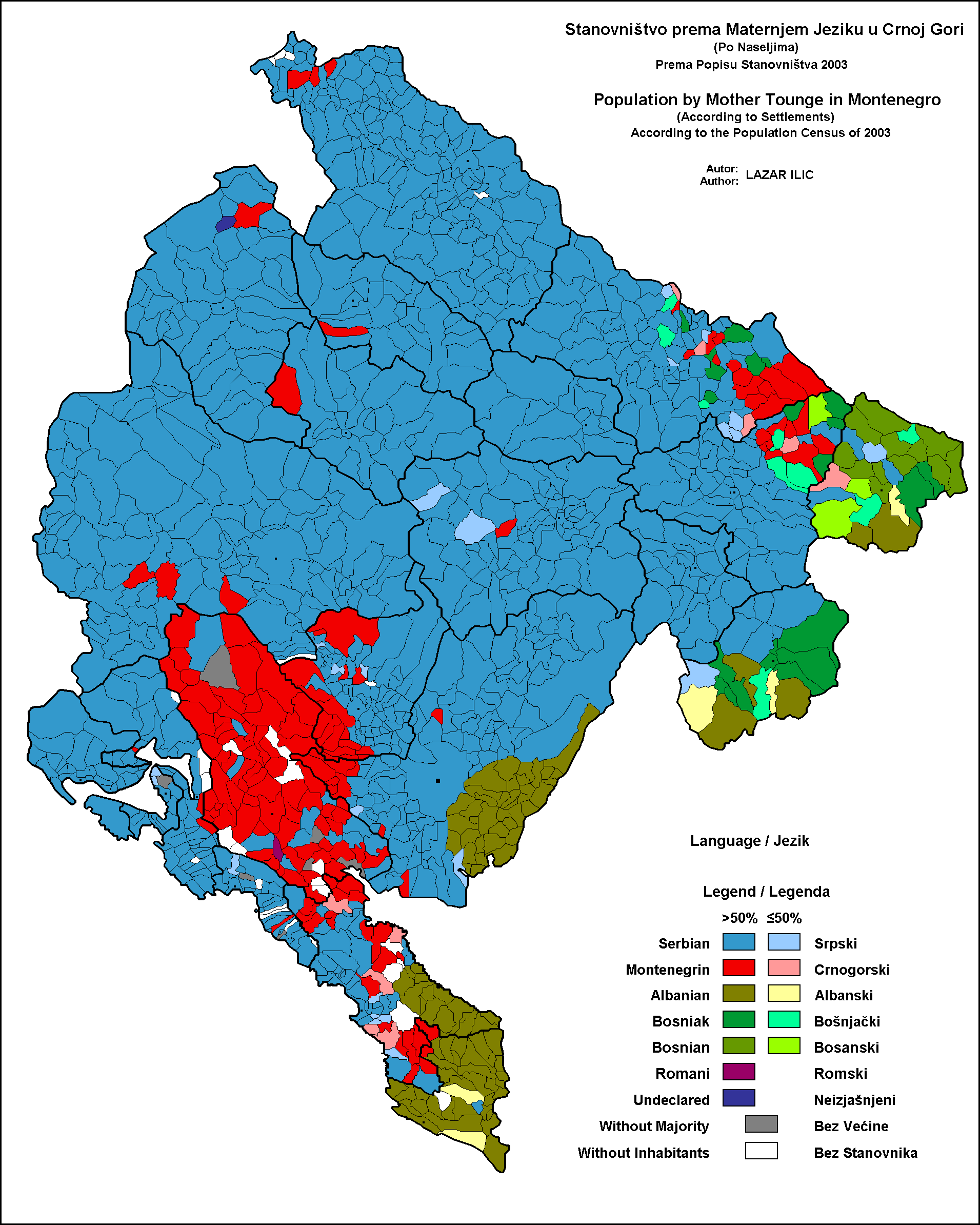
Montenegrin Language
Montenegrin ( ; cnr, label=none, / ) is a normative variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Montenegrins and is the official language of Montenegro. Montenegrin is based on the most widespread dialect of Serbo-Croatian, Shtokavian, more specifically on Eastern Herzegovinian, which is also the basis of Standard Croatian, Serbian, and Bosnian. Montenegro's language has historically and traditionally been called either Serbian or Montenegrin. The idea of a standardized Montenegrin standard language separate from Serbian appeared in the 1990s during the breakup of Yugoslavia, through proponents of Montenegrin independence from the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro. Montenegrin became the official language of Montenegro with the ratification of a new constitution on 22 October 2007. Language standardization In January 2008, the government of Montenegro formed the Board (Council) for Standardization of the Montenegrin Language, which aims to standardize the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shtokavian
Shtokavian or Štokavian (; sh-Latn, štokavski / sh-Cyrl, italics=no, штокавски, ) is the prestige dialect of the pluricentric Serbo-Croatian language and the basis of its Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian and Montenegrin standards. It is a part of the South Slavic dialect continuum. Its name comes from the form for the interrogatory pronoun for "what" in Western Shtokavian, (it is in Eastern Shtokavian). This is in contrast to Kajkavian and Chakavian ( and also meaning "what"). Shtokavian is spoken in Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, much of Croatia, as well as the southern part of Austria's Burgenland. The primary subdivisions of Shtokavian are based on two principles: one is whether the subdialect is Old-Shtokavian or Neo-Shtokavian, and different accents according to the way the old Slavic phoneme ''jat'' has changed. Modern dialectology generally recognises seven Shtokavian subdialects. Early history of Shtokavian The Proto-Shtokavian idiom app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chakavian
Chakavian or Čakavian (, , , sh-Latn, čakavski proper name: or own name: ''čokovski, čakavski, čekavski'') is a South Slavic regiolect or language spoken primarily by Croats along the Adriatic coast, in the historical regions of Dalmatia, Istria, Croatian Littoral and parts of coastal and southern Central Croatia (now collectively referred to as Adriatic Croatia). Chakavian, like Kajkavian, is not spoken in Serbo-Croatian-speaking regions beyond Croatia. Chakavian was the basis for early literary standards in Croatia. Today, it is spoken almost entirely within Croatia's borders, apart from the Burgenland Croatian in Austria and Hungary and a few villages in southern Slovenia. History Chakavian is one of the oldest written South Slavic varieties that had made a visible appearance in legal documents—as early as 1275 ( Istrian land survey) and 1288 (Vinodol codex), the predominantly vernacular Chakavian is recorded, mixed with elements of Church Slavic. Many of these a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kajkavian
Kajkavian (Kajkavian noun: ''kajkavščina''; Shtokavian adjective: ''kajkavski'' , noun: ''kajkavica'' or ''kajkavština'' ) is a South Slavic regiolect or language spoken primarily by Croats in much of Central Croatia, Gorski Kotar and northern Istria.The Kajkavian speech of northern Istria is conventionally called Kajkavian but the features that differentiate it from neighboring Chakavian are not strictly or distinctly Kajkavian nor are those speech forms located in continuum with any other Kajkavian speech in Croatia. Conversely, the same applies to the northeastern Slovene dialects under classification as Slovene that transition into or bundle with Kajkavian Croatian and dialects of both Slovenia and Croatia further south. They have features common to both Slovene across the border as well as Kajkavian elsewhere. There are differing opinions over whether Kajkavian is best considered a dialect of Serbo-Croatian or a fully-fledged language of its own, as it is only partiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Slavonia
The Kingdom of Slavonia ( hr, Kraljevina Slavonija, la, Regnum Sclavoniae, hu, Szlavón Királyság, german: Königreich Slawonien, sr-Cyrl, Краљевина Славонија) was a kingdom of the Habsburg monarchy and the Austrian Empire that existed from 1699 to 1868. The kingdom included northern parts of present-day regions of Slavonia (today in Croatia) and Syrmia (today in Serbia and Croatia). The southern parts of these regions were part of the Slavonian Military Frontier, which was a component of the Military Frontier separating the Habsburg monarchy from the Ottoman Empire. Geography The Kingdom of Slavonia was bounded by the Kingdom of Croatia to the west, the Kingdom of Hungary to the north and the east, and the Ottoman Empire to the south. Together with the Slavonian Military Frontier, Slavonia was about 6,600 miles squared in area. It was divided into the three counties of Požega, Virovitica and Syrmia. Besides a chain of mountains in the middle of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Dalmatia
The Kingdom of Dalmatia ( hr, Kraljevina Dalmacija; german: Königreich Dalmatien; it, Regno di Dalmazia) was a crown land of the Austrian Empire (1815–1867) and the Cisleithanian half of Austria-Hungary (1867–1918). It encompassed the entirety of the region of Dalmatia, with its capital at Zadar. History The Habsburg monarchy had annexed the lands of Dalmatia after the Napoleonic War of the First Coalition: when Napoleon Bonaparte launched his Italian Campaign into the Habsburg duchies of Milan and Mantua in 1796, culminating in the Siege of Mantua, he compelled Emperor Francis II to make peace. In 1797 the Treaty of Campo Formio was signed, whereby the Habsburg emperor renounced possession of the Austrian Netherlands and officially recognized the independence of the Italian Cisalpine Republic. In turn, Napoleon ceded to him the possessions of the Republic of Venice, including the Dalmatian coast (Venetian Dalmatia) and the Bay of Kotor (Venetian Albania). ''La Sereniss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Croatia (Habsburg)
The Kingdom of Croatia ( hr, Kraljevina Hrvatska; la, Regnum Croatiae; hu, Horvát Királyság, german: Königreich Kroatien) was part of the lands of the Habsburg monarchy from 1527, following the Election in Cetin, and the Austrian Empire from 1804 to 1867. It was also a part of the Lands of the Hungarian Crown, but was subject to direct Imperial Austrian rule for significant periods of time, including its final years. Its capital was Zagreb. The Kingdom of Croatia had large territorial losses in wars with the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century. Until the 18th century, the kingdom included only a small north-western part of present-day Croatia around Zagreb, and a small strip of coastland around Rijeka, that were not part of the Ottoman Empire or part of the Military Frontier. Between 1744 and 1868, the Kingdom of Croatia included a subordinate autonomous kingdom, the Kingdom of Slavonia. The territory of the Slavonian kingdom was recovered from the Ottoman Empire, and was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triune Kingdom
The Triune Kingdom ( hr, Trojedna kraljevina) or Triune Kingdom of Croatia, Slavonia and Dalmatia ( hr, Trojedna Kraljevina Hrvatske, Slavonije i Dalmacije) was the concept—advocated by the leaders of the 19th-century Croatian national revival—of a united kingdom between Croatia, Slavonia and Dalmatia, which were already within the Austrian Empire under one king, who was also the Emperor of Austria, but were politically and administratively separate entities. This concept had roots in the high medieval period, as a successor to the historical Kingdom of Croatia which was made up of those regions. After 1867, Croatia and Slavonia were within the Hungarian half of Austria-Hungary and were united in 1868 as the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia, where the name ''Triune Kingdom of Croatia, Slavonia and Dalmatia'' became official. However, Dalmatia, being located in the Austrian half, still remained de facto separate. Until the end of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, several Croatian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Hus
Jan Hus (; ; 1370 – 6 July 1415), sometimes anglicized as John Hus or John Huss, and referred to in historical texts as ''Iohannes Hus'' or ''Johannes Huss'', was a Czech theologian and philosopher who became a Church reformer and the inspiration of Hussitism, a key predecessor to Protestantism, and a seminal figure in the Bohemian Reformation. Hus is considered by some to be the first Church reformer, even though some designate the theorist John Wycliffe. His teachings had a strong influence, most immediately in the approval of a reformed Bohemian religious denomination and, over a century later, on Martin Luther. Hus was a master, dean and rector at the Charles University in Prague between 1409 and 1410. Jan Hus was born in Husinec, Bohemia, to poor parents. In order to escape poverty, Hus trained for the priesthood. At an early age he traveled to Prague, where he supported himself by singing and serving in churches. His conduct was positive and, reportedly, his commitment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, it was the third most populous monarchy in Europe after the Russian Empire and the United Kingdom. Along with Prussia, it was one of the two major powers of the German Confederation. Geographically, it was the third-largest empire in Europe after the Russian Empire and the First French Empire (). The empire was proclaimed by Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis II in 1804 in response to Napoleon's declaration of the First French Empire, unifying all Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg possessions under one central government. It remained part of the Holy Roman Empire until the latter's dissolution in 1806. It continued fighting against Napoleon throughout the Napoleonic Wars, except for a period between 1809 and 1813, when Austria was first all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Montenegro, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia and Slovenia. Due to political, social and economic reasons, many Croats migrated to North and South America as well as New Zealand and later Australia, establishing a diaspora in the aftermath of World War II, with grassroots assistance from earlier communities and the Roman Catholic Church. In Croatia (the nation state), 3.9 million people identify themselves as Croats, and constitute about 90.4% of the population. Another 553,000 live in Bosnia and Herzegovina, where they are one of the three constituent ethnic groups, predominantly living in Western Herzegovina, Central Bosnia and Bosnian Posavina. The minority in Serbia number about 70,000, mostly in Vojvodina. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.png)