|
GLIPR1
Glioma pathogenesis-related protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GLIPR1'' gene. Function This gene encodes a protein with similarity to both the pathogenesis-related protein (PR) superfamily and the cysteine-rich secretory protein (CRISP) family. Discovery The previous finding of RTVP1 (GLIPR1) as a p53 target gene with tumor suppressor functions prompted the researches to initiate a genome-wide sequence homology search for RTVP1/GLIPR1-like (GLIPR1L) genes. p53, the tumor suppressor gene is the most commonly mutated gene in human cancer. Mutation in p53 gene can lead to cellular malfunctions such as malignant growth and metsastatis. Human GLIPR1, was initially identified in human glioblastoma and was called as GLIPR1 (glioma pathogenesis-related protein 1) or RTVP1 (related to testes-specific, vespid, and pathogenesis protein 1). Furthermore, it was identified as a marker of myelomocytic differentiation in macrophage. RTVP-1 cluster proteins share si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
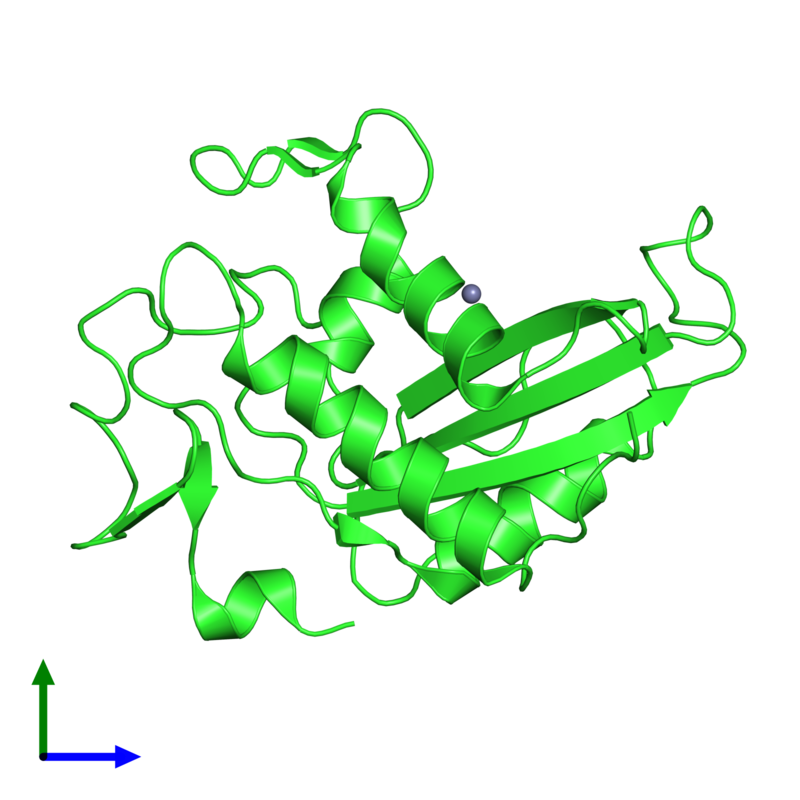
Structure Of GlIPR1
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as organism, biological organisms, minerals and chemical substance, chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a Complex network, network featuring many-to-many Link (geometry), links, or a lattice (order), lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, Ant colony, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of Structural load, load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and nonbuilding structure, non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimeric proteins. Background The concept of the domain was first proposed in 1973 by Wetlaufer aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNP Position Vs Freq
SNP may refer to: Computing * SNP (complexity), in theoretical computer science * SNP file format, for Microsoft Access reports * Scalable Networking Pack, to extend Microsoft Windows Server 2003 * Secure Network Programming, a prototype Internet protocol and API * SnP file or Touchstone file, an electrical circuit simulation data format Entertainment * '' The Sunday Night Project'', a British television show * "SNP (Shining Nature Purity)", a 2020 song by W24 Places * Six Nations Polytechnic, post-secondary institution in Ontario, Canada * State Nature Preserves of the Kentucky State Nature Preserves Commission * SNP Stadium, Banská Bystrica, Slovakia Political parties * Scottish National Party The Scottish National Party (SNP; sco, Scots National Pairty, gd, Pàrtaidh Nàiseanta na h-Alba ) is a Scottish nationalist and social democratic political party in Scotland. The SNP supports and campaigns for Scottish independence from ..., Scotland * Seychelles Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthotopic
Orthotopic procedures (from Greek ''orthos'', straight + ''topos'', place) are those occurring at the normal place. Examples include: * Orthotopic liver transplantation, in which the previous liver is removed and the transplant is placed at that location in the body * Orthotopic heart transplantation * Orthotopic kidney transplantation. When organs are transplanted to a different anatomical location the procedure is said to be heterotopic (e.g. heterotopic heart transplantation A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure or severe coronary artery disease when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. , the most common proce ...). References {{DEFAULTSORT:Orthotopic procedures Medical lists Organ transplantation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunocompetent
In immunology, immunocompetence is the ability of the body to produce a normal immune response following exposure to an antigen. Immunocompetence is the opposite of immunodeficiency (also known as ''immuno-incompetence'' or being ''immuno-compromised''). Examples include: * a newborn who does not yet have a fully functioning immune system but may have maternally transmitted antibodies – immunodeficient; * a late stage AIDS patient with a failed or failing immune system – immuno-incompetent; or * a transplant recipient taking medication so their body will not reject the donated organ – immunocompromised. There may be cases of overlap but these terms all describe immune system not fully functioning. The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that household and other close contacts of persons with altered immunocompetence receive the MMR, varicella, and rotavirus vaccines according to the standard schedule of vaccines, as well as receiving an annual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignancies
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse. Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues. A benign tumor has none of those properties. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis. Malignant tumors are also characterized by genome instability, so that cancers, as assessed by whole genome sequencing, frequently have between 10,000 and 100,000 mutations in their entire genomes. Cancers usually show tumour heterogeneity, containing multiple subclones. They also frequently have reduced expression of DNA repair enzymes due to epigenetic methylation of DNA repair genes or altered microRNAs that control DNA repair gene expression. Tumours can be detected through the visuali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in addition to" the traditional genetic basis for inheritance. Epigenetics most often involves changes that affect the regulation of gene expression, but the term can also be used to describe any heritable phenotypic change. Such effects on cellular and physiological phenotypic traits may result from external or environmental factors, or be part of normal development. The term also refers to the mechanism of changes: functionally relevant alterations to the genome that do not involve mutation of the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification, each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Gene expression can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are the histones. These proteins, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division (where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form). Before this happens, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and both copies are joined by a centromere, resulting either in an X-shaped structure (pictured above), if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-arm structure, if the centromere is located distally. The joined copies are now called si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystine
Cystine is the oxidized derivative of the amino acid cysteine and has the formula (SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H)2. It is a white solid that is poorly soluble in water. As a residue in proteins, cystine serves two functions: a site of redox reactions and a mechanical linkage that allows proteins to retain their three-dimensional structure. Formation and reactions Structure Cystine is the disulfide derived from the amino acid cysteine. The conversion can be viewed as an oxidation: : Cystine contains a disulfide bond, two amine groups, and two carboxylic acid groups. As for other amino acids, the amine and carboxylic acid groups exist is rapid equilibrium with the ammonium-carboxylate tautomer. The great majority of the literature concerns the ''l,l-''cystine, derived from ''l''-cysteine. Other isomers include ''d,d''-cystine and the meso isomer d,l-cystine, neither of which is biologically significant. Occurrence Cystine is common in many foods such as eggs, meat, dairy products, and whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is one of the most aggressive types of cancer that begin within the brain. Initially, signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality changes, nausea, and symptoms similar to those of a stroke. Symptoms often worsen rapidly and may progress to unconsciousness. The cause of most cases of glioblastoma is not known. Uncommon risk factors include genetic disorders, such as neurofibromatosis and Li–Fraumeni syndrome, and previous radiation therapy. Glioblastomas represent 15% of all brain tumors. They can either start from normal brain cells or develop from an existing low-grade astrocytoma. The diagnosis typically is made by a combination of a CT scan, MRI scan, and tissue biopsy. There is no known method of preventing the cancer. Treatment usually involves surgery, after which chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used. The medication temozolomide is frequently used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |