|
GDP-Man
Guanosine diphosphate mannose or GDP-mannose is a nucleotide sugar that is a substrate for glycosyltransferase reactions in metabolism. This compound is a substrate for enzymes called mannosyltransferases. Known as donor of activated mannose in all glycolytic reactions, GDP-mannose is essential in eukaryotes. Biosynthesis GDP-mannose is produced from GTP and mannose-6-phosphate by the enzyme mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase. One of the enzymes from the family of nucleootidyl-transferases, GDP-Mannose Pyrophosphorylase (GDP-MP) is an pervasive enzyme found in bacteria, fungi, plants, and animals. References See also * Nucleoside * Nucleotide * Guanosine * Guanosine diphosphate Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of a pyrophosphate group, a pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine. GDP is the product ... Nucleotides Coenzymes {{bioch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide Sugar
Nucleotide sugars are the activated forms of monosaccharides. Nucleotide sugars act as glycosyl donors in glycosylation reactions. Those reactions are catalyzed by a group of enzymes called glycosyltransferases. History The anabolism of oligosaccharides - and, hence, the role of nucleotide sugars - was not clear until the 1950s when Leloir and his coworkers found that the key enzymes in this process are the glycosyltransferases. These enzymes transfer a glycosyl group from a sugar nucleotide to an acceptor. Biological importance and energetics To act as glycosyl donors, those monosaccharides should exist in a highly energetic form. This occurs as a result of a reaction between nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) and glycosyl monophosphate (phosphate at anomeric carbon). The recent discovery of the reversibility of many glycosyltransferase-catalyzed reactions calls into question the designation of sugar nucleotides as 'activated' donors. Types There are nine sugar nucleotides in hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosyltransferase
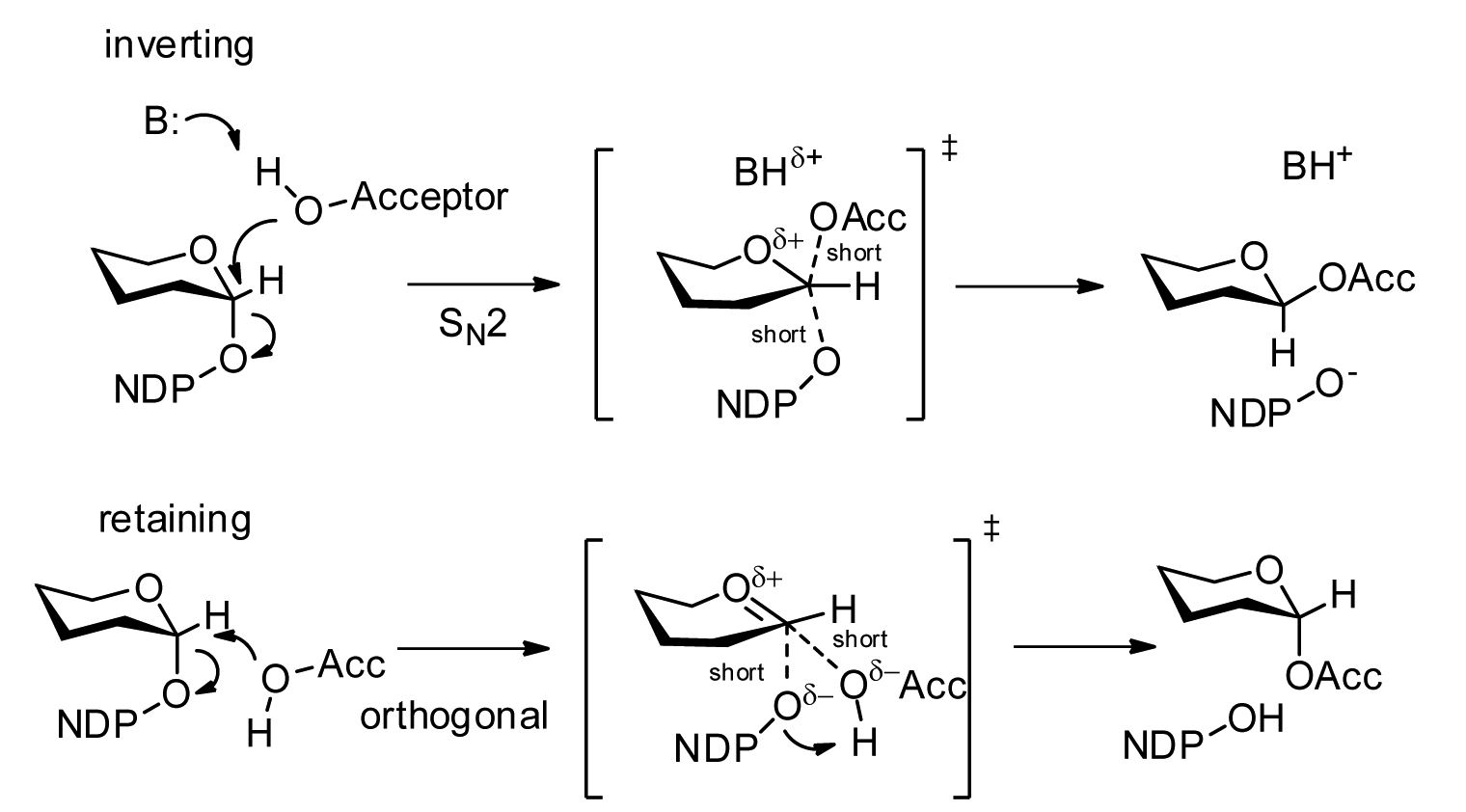
Glycosyltransferases (GTFs, Gtfs) are enzymes ( EC 2.4) that establish natural glycosidic linkages. They catalyze the transfer of saccharide moieties from an activated nucleotide sugar (also known as the "glycosyl donor") to a nucleophilic glycosyl acceptor molecule, the nucleophile of which can be oxygen- carbon-, nitrogen-, or sulfur-based. The result of glycosyl transfer can be a carbohydrate, glycoside, oligosaccharide, or a polysaccharide. Some glycosyltransferases catalyse transfer to inorganic phosphate or water. Glycosyl transfer can also occur to protein residues, usually to tyrosine, serine, or threonine to give O-linked glycoproteins, or to asparagine to give N-linked glycoproteins. Mannosyl groups may be transferred to tryptophan to generate C-mannosyl tryptophan, which is relatively abundant in eukaryotes. Transferases may also use lipids as an acceptor, forming glycolipids, and even use lipid-linked sugar phosphate donors, such as dolichol phosphates in eukaryotic o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic'' – the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannosyltransferase
A mannosyltransferase is a type of glycosyltransferase that acts upon mannose Mannose is a sugar monomer of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. It is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins. Several congenital disorders of glycosylation .... An example is heteroglycan alpha-mannosyltransferase. References EC 2.4.1 {{2.4-enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine Triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It is one of the building blocks needed for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. Its structure is similar to that of the guanosine nucleoside, the only difference being that nucleotides like GTP have phosphates on their ribose sugar. GTP has the guanine nucleobase attached to the 1' carbon of the ribose and it has the triphosphate moiety attached to ribose's 5' carbon. It also has the role of a source of energy or an activator of substrates in metabolic reactions, like that of ATP, but more specific. It is used as a source of energy for protein synthesis and gluconeogenesis. GTP is essential to signal transduction, in particular with G-proteins, in second-messenger mechanisms where it is converted to guanosine diphosphate (GDP) through the action of GTPases. Uses Energy transfer GTP is involved in energy transfer within the cell. For instance, a GTP molecule is generated by one of the enz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannose-6-phosphate
Mannose-6-phosphate (M6P) is a molecule bound by lectin in the immune system. M6P is converted to fructose 6-phosphate by mannose phosphate isomerase. M6P is a key targeting signal for acid hydrolase precursor proteins that are destined for transport to lysosomes. The M6P tag is added to such proteins in the ''cis''-Golgi apparatus. Specifically, in a reaction involving uridine diphosphate (UDP) and ''N''-acetylglucosamine, the enzyme N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase catalyzes the ''N''-linked glycosylation of asparagine residues with M6P. Once appropriately marked with the M6P targeting signal, these proteins are moved to the ''trans''-Golgi network. There, the M6P moiety is recognized and bound by mannose 6-phosphate receptor (MPR) proteins at pH 6.5–6.7. The M6P-tagged lysosomal enzymes are shipped to the late endosomes via vesicular transport. Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) for several lysosomal storage diseases relies on this pathway to efficiently direct syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannose-1-phosphate Guanylyltransferase
In enzymology, a mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :GTP + alpha-D-mannose 1-phosphate \rightleftharpoons diphosphate + GDP-mannose Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are GTP and alpha-D-mannose 1-phosphate, whereas its two products are diphosphate and GDP-mannose. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring phosphorus-containing nucleotide groups (nucleotidyltransferases). The systematic name of this enzyme class is GTP:alpha-D-mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase. Other names in common use include GTP-mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase, PIM-GMP (phosphomannose isomerase-guanosine 5'-diphospho-D-mannose, pyrophosphorylase), GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase, guanosine 5'-diphospho-D-mannose pyrophosphorylase, guanosine diphosphomannose pyrophosphorylase, guanosine triphosphate-mannose 1-phosphate guanylyltransferase, and mannose 1-phosphate guanylyltransferase (guanosine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleoside
Nucleosides are glycosylamines that can be thought of as nucleotides without a phosphate group. A nucleoside consists simply of a nucleobase (also termed a nitrogenous base) and a five-carbon sugar (ribose or 2'-deoxyribose) whereas a nucleotide is composed of a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. In a nucleoside, the anomeric carbon is linked through a glycosidic bond to the N9 of a purine or the N1 of a pyrimidine. Nucleotides are the molecular building-blocks of DNA and RNA. List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases The reason for 2 symbols, shorter and longer, is that the shorter ones are better for contexts where explicit disambiguation is superfluous (because context disambiguates) and the longer ones are for contexts where explicit disambiguation is judged to be needed or wise. For example, when discussing long nucleobase sequences in genomes, the CATG symbol system is much preferable to the Cyt-Ade-Thy-Gua symbol system (see '' N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide
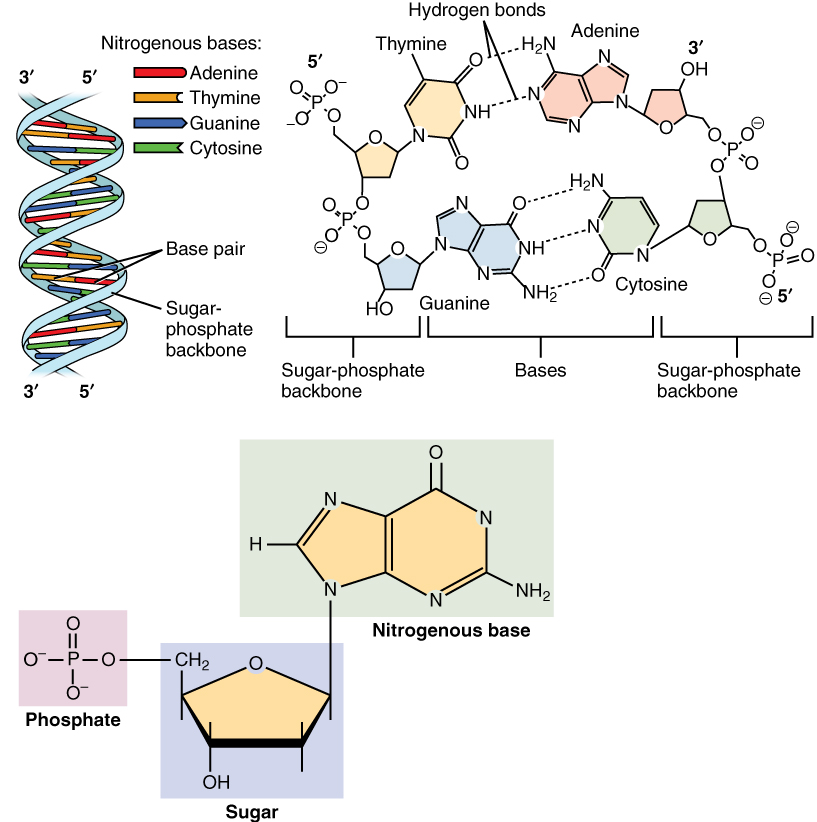
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP) and uridine triphosphate (UTP)—throughout the cell for the many cellular func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine
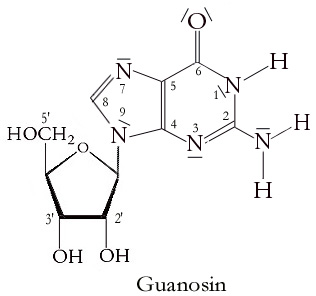
Guanosine (symbol G or Guo) is a purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose (ribofuranose) ring via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Guanosine can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP), and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction, and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). When guanine is attached by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of a deoxyribose ring it is known as deoxyguanosine. Physical and chemical properties Guanosine is a white, crystalline powder with no odor and mild saline taste. It is very soluble in acetic acid, slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene and chloroform. Functions Guanosine is required for an RNA splicing reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron removes itself from the mRNA messag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine Diphosphate
Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of a pyrophosphate group, a pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine. GDP is the product of GTP dephosphorylation by GTPases, e.g., the G-proteins that are involved in signal transduction. GDP is converted into GTP with the help of pyruvate kinase and phosphoenolpyruvate. See also * DNA *Guanosine triphosphate *Nucleoside *Nucleotide *Oligonucleotide *RNA Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Guanosine phosphate2 Nucleotides Phosphate esters Purines Pyrophosphates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotides
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP) and uridine triphosphate (UTP)—throughout the cell for the many cellular fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |