|
Fusarium Dry Rot
''Fusarium'' dry rot is one of the most common potato diseases. It is caused by fungi in the genus ''Fusarium''. This fungi causes a variety of colored rots in potatoes. This pathogen, while having both a sexual and asexual form, stays in an asexual cycle due to the way it spreads. Preferring warmer climates, it is not uncommon to find this pathogen in the northern United States where it has been reported to affect yield as much as 60%. Hosts and symptoms ''Fusarium'' dry rot of potato is a devastating post-harvest losses (vegetables) disease affecting both seed potatoes and potatoes for human consumption.Rowe, R.C., Miller, S.A, & Riedel R.M. ''Fusarium'' Dry Rot and Seed Piece Decay of Potato. Retrieved from http://www.oardc.ohio-state.edu/sallymiller/extension/factsheets/fuspotato.pdf Dry rot causes the skin of the tuber to wrinkle. The rotted areas of the potato may be brown, grey, or black and the rot creates depressions in the surface of the tuber. Seed pieces may rot complet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae. Wild potato species can be found from the southern United States to southern Chile. The potato was originally believed to have been domesticated by Native Americans independently in multiple locations,University of Wisconsin-Madison, ''Finding rewrites the evolutionary history of the origin of potatoes'' (2005/ref> but later genetic studies traced a single origin, in the area of present-day southern Peru and extreme northwestern Bolivia. Potatoes were domesticated there approximately 7,000–10,000 years ago, from a species in the ''Solanum brevicaule'' complex. Lay summary: In the Andes region of South America, where the species is indigenous, some close relatives of the potato are cultivated. Potatoes were introduced to Europe from the Americas by the Spanish in the second half of the 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizoctonia
''Rhizoctonia'' is a genus of fungi in the order Cantharellales. Species form thin, effused, corticioid basidiocarps (fruit bodies), but are most frequently found in their sterile, anamorphic state. ''Rhizoctonia'' species are saprotrophic, but some are also facultative plant pathogens, causing commercially important crop diseases. Some are also endomycorrhizal associates of orchids. The genus name was formerly used to accommodate many superficially similar, but unrelated fungi. Taxonomy History Anamorphs ''Rhizoctonia'' was introduced in 1815 by French mycologist Augustin Pyramus de Candolle for anamorphic plant pathogenic fungi that produce both hyphae and sclerotia. The name is derived from Ancient Greek, ῥίζα (''rhiza'', "root") + κτόνος (''ktonos'', "murder"), and de Candolle's original species, ''Rhizoctonia crocorum'' (teleomorph ''Helicobasidium purpureum''), is the causal agent of violet root rot of carrots and other root vegetables. Subsequent authors added ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
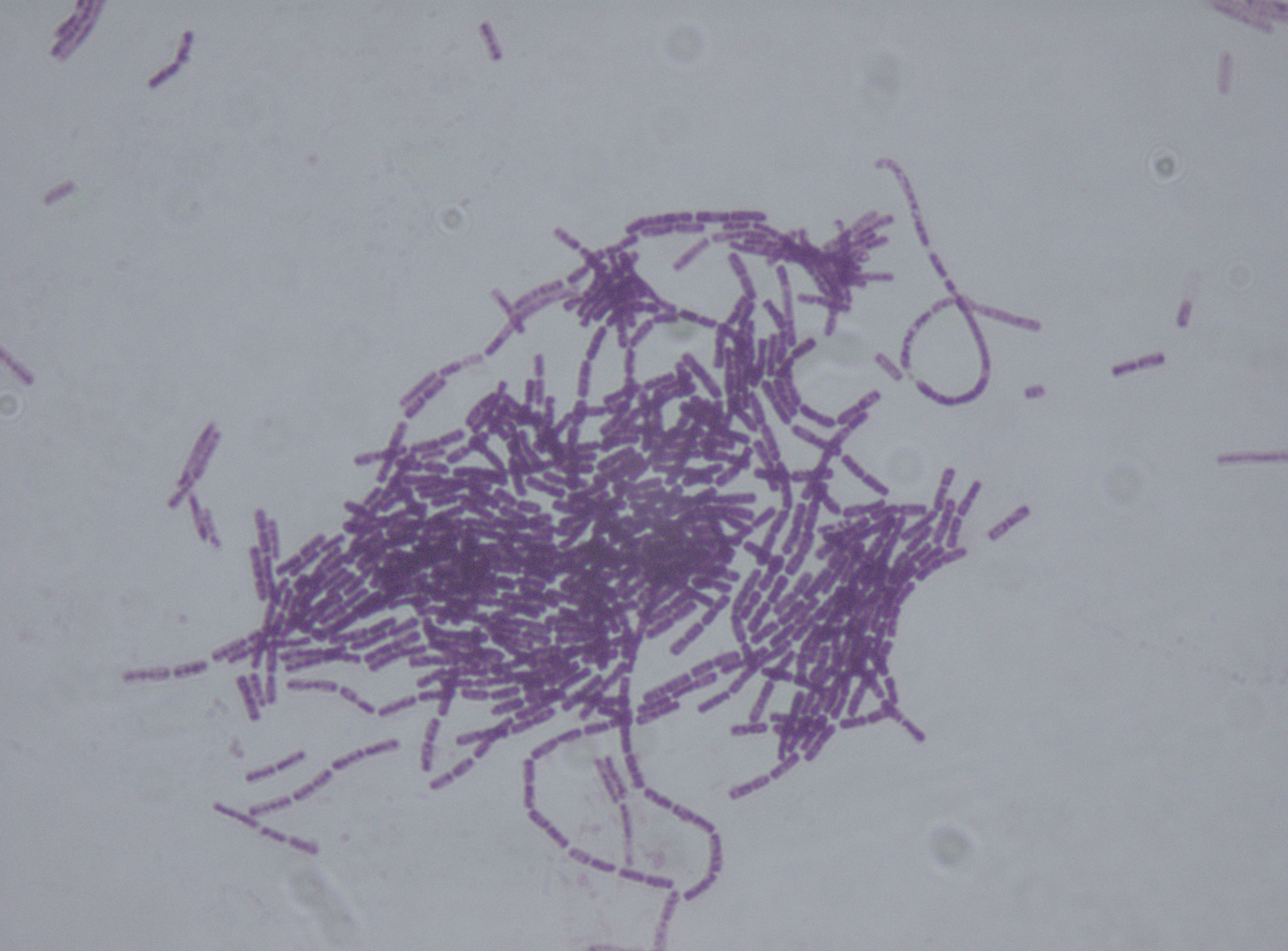
Bacillus Thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflies, as well on leaf surfaces, aquatic environments, animal feces, insect-rich environments, and flour mills and grain-storage facilities. It has also been observed to parasitize other moths such as ''Cadra calidella''—in laboratory experiments working with ''C. calidella'', many of the moths were diseased due to this parasite. During sporulation, many Bt strains produce crystal proteins (proteinaceous inclusions), called delta endotoxins, that have insecticidal action. This has led to their use as insecticides, and more recently to genetically modified crops using Bt genes, such as Bt corn. Many crystal-producing Bt strains, though, do not have insecticidal properties. The subspecies ''israelensis'' is commonly used for control of mosq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunisia
) , image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg , map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa , image_map2 = , capital = Tunis , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , official_languages = Arabic Translation by the University of Bern: "Tunisia is a free State, independent and sovereign; its religion is the Islam, its language is Arabic, and its form is the Republic." , religion = , languages_type = Spoken languages , languages = Minority Dialects : Jerba Berber (Chelha) Matmata Berber Judeo-Tunisian Arabic (UNESCO CR) , languages2_type = Foreign languages , languages2 = , ethnic_groups = * 98% Arab * 2% Other , demonym = Tunisian , government_type = Unitary presidential republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Kais Saied , leader_ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus
''Bacillus'' (Latin "stick") is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum ''Bacillota'', with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural ''Bacilli'' is the name of the class of bacteria to which this genus belongs. ''Bacillus'' species can be either obligate aerobes which are dependent on oxygen, or facultative anaerobes which can survive in the absence of oxygen. Cultured ''Bacillus'' species test positive for the enzyme catalase if oxygen has been used or is present. ''Bacillus'' can reduce themselves to oval endospores and can remain in this dormant state for years. The endospore of one species from Morocco is reported to have survived being heated to 420 °C. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients: the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. They are not true spores (i.e., not an offspring). Endospore formation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichoderma Harzianum
''Trichoderma harzianum'' is a fungus that is also used as a fungicide. It is used for foliar application, seed treatment and soil treatment for suppression of fungal pathogens causing various fungal plant diseases. Commercial biotechnological products such as 3Tac have been useful for treatment of '' Botrytis'', ''Fusarium'' and ''Penicillium'' sp. It is also used for manufacturing enzymes. Taxonomy and genetics Most ''Trichoderma'' strains have no sexual stage but instead produce only asexual spores. However, for a few strains the sexual stage is known, but not among strains that have usually been considered for biocontrol purposes. The sexual stage, when found, is within the Ascomycetes in the genus ''Hypocrea''. Traditional taxonomy was based upon differences in morphology, primarily of the asexual sporulation apparatus, but more molecular approaches are now being used. Consequently, the taxa recently have gone from nine to at least thirty-three species. Genetics Most stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Pumilis
''Bacillus pumilus'' is a Gram-positive, aerobic, spore-forming bacillus commonly found in soil. ''Bacillus pumilus'' spores—with the exception of mutant strain ATCC 7061—generally show high resistance to environmental stresses, including UV light exposure, desiccation, and the presence of oxidizers such as hydrogen peroxide. Strains of ''B. pumilus'' found at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory were found to be particularly resistant to hydrogen peroxide. A strain of ''B. pumilus'' isolated from black tiger shrimp (''Penaeus monodon'') was found to have high salt tolerance and to inhibit the growth of marine pathogens, including ''Vibrio alginolyticus'', when cultured together. Genome and cell structure ''Bacillus pumilus'' contains one circular chromosome including about 4000 genes and 3600-3900 proteins with varying length in the range of 3.7 to 3.8 Mbp. 41% of the DNA base pairs in ''B. pumilus'' are G-C. The cellular structure of ''B. pumilus'' is similar to other ''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'', known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacillus'', ''B. subtilis'' is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. ''B. subtilis'' has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. ''B. subtilis'' is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies. Description ''Bacillus subtilis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, rod-shaped and catalase-positive. It was originally named ''Vibrio subtilis'' by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, and renamed ''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colletotrichum Coccodes
''Colletotrichum coccodes'' is a plant pathogen, which causes anthracnose on tomato and black dot disease of potato The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae. Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit .... Fungi survive on crop debris and disease emergence is favored by warm temperatures and wet weather. Hosts and symptoms ''Colletotrichum coccodes'' can infect potato, onion, tomato and has a large host range. The disease also infects hosts from the Cucurbitaceae, Fabaceae and Solanaceae families). ''Colletotrichum coccodes'' can cause lesions, twisted leaves, and a bleached color on onion. On tomato, can see that there are sunken in dark spots. As the disease continues to develop can begin to see spots that are rotting. The pathogen can infect both green and ripe fruit; spots are not evident on green right away, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Scurf
''Silver scurf'' is a plant disease that is caused by the plant pathogen ''Helminthosporium solani.'' Silver scurf is a blemish disease, meaning the effect it has on tubers is mostly cosmetic and affects "fresh market, processing and seed tuber potatoes." There are some reports of it affecting development, meaning growth and tuber yield. This is caused by light brown lesions, which in turn change the permeability of tuber skin and then it causes tuber shrinkage and water loss, which finally causes weight loss. The disease has become economically important because silver scurf affected potatoes for processing and direct consumption have been rejected by the industry. The disease cycle can be divided into two stages: field and storage. It is mainly a seed borne disease and the primary source of inoculum is mainly infected potato seed tubers. Symptoms develop and worsen in storage because the conditions are conducive to sporulation. The ideal conditions for the spread of this disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mertect
Tiabendazole (INN, BAN), also known as thiabendazole (AAN, USAN) or TBZ and the trade names Mintezol, Tresaderm, and Arbotect, is a preservative, an antifungal agent, and an antiparasitic agent. Uses Preservative Tiabendazole is used primarily to control mold, blight, and other fungal diseases in fruits (e.g. oranges) and vegetables; it is also used as a prophylactic treatment for Dutch elm disease. Tiabendazole is also used as a food additive, a preservative with E number E233 ( INS number 233). For example, it is applied to bananas to ensure freshness, and is a common ingredient in the waxes applied to the skins of citrus fruits. It is not approved as a food additive in the EU, Australia and New Zealand. Use in treatment of aspergillosis has been reported. It is also used in anti-fungal wallboards as a mixture with azoxystrobin. Parasiticide As an antiparasitic, tiabendazole is able to control roundworms (such as those causing strongyloidiasis), hookworms, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |