|
Fu Song'e
Fu Song'e (苻娀娥, died September 404) was a consort of Murong Xi (Emperor Zhaowen), emperor of the Xianbei-led Chinese Later Yan dynasty. She was posthumously honored as Empress Min (愍皇后). She was the older sister of Murong Xi's empress Fu Xunying. Early life Fu Song'e was the oldest daughter of Fu Mo (苻謨), the mayor of Later Yan's capital Zhongshan (中山, in modern Baoding, Hebei) in the 390s. Shortly after the Later Yan emperor Murong Bao (Emperor Huimin) abandoned Zhongshan in face of Northern Wei military attacks, Fu Mo was killed by Murong Xiang (慕容詳) the Duke of Kaifeng, who wanted to be emperor himself. His family was also slaughtered. Somehow, however, Fu Song'e and her younger sister Fu Xunying were not killed—perhaps they escaped the slaughter, or perhaps they were not in Zhongshan at that point. As Murong Xi's consort After Murong Xi became emperor in 401, he took Fu Song'e and Fu Xunying as imperial consorts in late 401 and greatly favored the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murong Xi
Murong Xi (; 385–407; r. 401–407), courtesy name Daowen (道文), formally Emperor Zhaowen of (Later) Yan ((後)燕昭文帝), was an emperor of the Xianbei-led Later Yan dynasty of China. He was one of the youngest sons of Murong Chui (Emperor Wucheng), and after the death of his nephew Murong Sheng (Emperor Zhaowu) became emperor due to his affair with Murong Sheng's mother, Empress Dowager Ding. He was regarded as a cruel and capricious ruler, who acted at the whims of himself and his wife, Empress Fu Xunying, greatly damaging the Later Yan state. After Empress Fu died in 407, he left the capital Longcheng (龍城, in modern Jinzhou, Liaoning) to bury her, and the soldiers in Longcheng took this chance to rebel and replace him with Murong Bao's adopted son Murong Yun (Emperor Huiyi), and Murong Xi himself was captured and killed. (Because Murong Yun was an adopted son who later changed his name back to Gao Yun, some historians treat Murong Xi as the last emperor of Late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the Wuhuan and Xianbei when they were defeated by the Xiongnu at the end of the third century BC. The Xianbei were largely subordinate to larger nomadic powers and the Han dynasty until they gained prominence in 87 AD by killing the Xiongnu chanyu Youliu. However unlike the Xiongnu, the Xianbei state, Xianbei political structure lacked the organization to pose a concerted challenge to the Chinese for most of their time as a nomadic people. After suffering several defeats by the end of the Three Kingdoms, Three Kingdoms period, the Xianbei migrated south and settled in close proximity to Han society and submitted as vassals, being granted the titles of dukes. As the Xianbei Murong, Tuoba, and Duan tribes were one of the Five Barbarians who were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
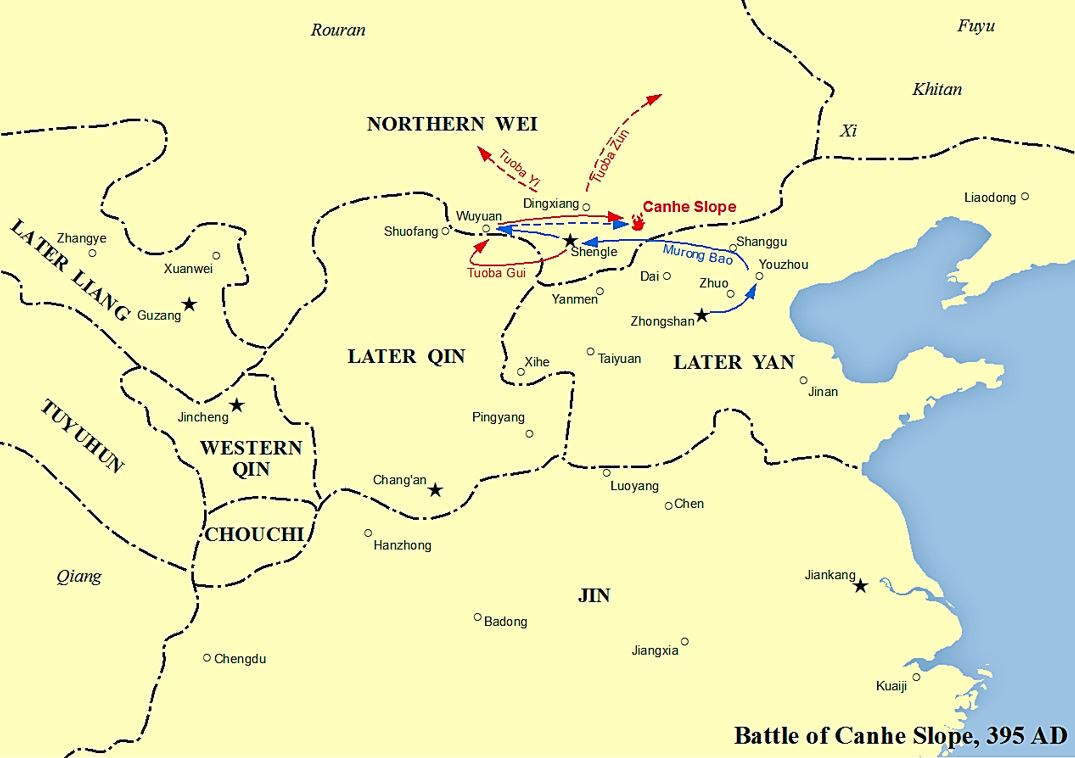
Later Yan
Yan, known in historiography as the Later Yan (; 384 – 407 or 409) was a dynastic state of China ruled by the Xianbei people, located in modern-day northeast China, during the era of Sixteen Kingdoms. All rulers of the Later Yan declared themselves "emperors". Rulers of the Later Yan See also *Battle of Canhebei * Wu Hu *List of past Chinese ethnic groups *Xianbei The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Yan History of Mongolia 384 establishments 409 disestablishments Dynasties in Chinese history Former countries in Chinese history 4th-century establishments in China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fu Xunying
Fu Xunying (苻訓英) (died 407) was an empress of the Xianbei-led Chinese Later Yan dynasty. Her husband was Murong Xi (Emperor Zhaowen). Life Fu Xunying was a daughter of Fu Mo (苻謨), a member of Former Qin's imperial house before he surrendered to Later Yan under military pressure. As of 397, he was the mayor of Later Yan's capital Zhongshan (中山, in modern Baoding, Hebei) when the Later Yan emperor Murong Bao (Emperor Huimin) abandoned Zhongshan in face of Northern Wei military attacks, and he was subsequently killed by Murong Bao's nephew Murong Xiang (慕容詳) the Duke of Kaifeng, who wanted to be emperor himself. His family was slaughtered. Somehow, however, Fu Xunying and her older sister Fu Song'e were not killed—perhaps they escaped the slaughter, or perhaps they were no longer in Zhongshan at that point. After Murong Xi became emperor in 401 after succeeding his nephew Murong Sheng (Emperor Zhaowu), he took Fu Song'e and Fu Xunying as imperial consorts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baoding
Baoding (), formerly known as Baozhou and Qingyuan, is a prefecture-level city in central Hebei province, approximately southwest of Beijing. As of the 2010 census, Baoding City had 11,194,382 inhabitants out of which 2,176,857 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made of 4 out of 5 urban districts: Lianchi, Jingxiu, Qingyuan and Mancheng largely being conurbated, on . Baoding is among 13 Chinese cities with a population of over 10 million, ranking seventh. One can also note that Zhuozhou City in the northern part has now grown into part of the Beijing built-up (or metro) area. History Baoding is a city with a history dating back to the Western Han Dynasty. It was destroyed by the Mongols in the 13th century, but after the Mongols established the Yuan Dynasty, it was rebuilt. It acquired the name "Baoding" during the Yuan dynasty — the name is roughly interpreted as "protecting the capital", referring to the city's proximity to Beijing. Baoding served for many years as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and 0.3% Mongol. Three Mandarin dialects are spoken: Jilu Mandarin, Beijing Mandarin and Jin. Hebei borders the provinces of Shanxi to the west, Henan to the south, Shandong to the southeast, Liaoning to the northeast, and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region to the north. Its economy is based on agriculture and manufacturing. The province is China's premier steel producer, although the steel industry creates serious air pollution. Five UNESCO World Heritage Sites can be found in the province, the: Great Wall of China, Chengde Mountain Resort, Grand Canal, Eastern Qing tombs, and Western Qing tombs. It is also home to five National Famous Historical and Cultural Cities: Handan, Baoding, Chengde, Zhengding and Shanhaiguan. Historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murong Bao
Murong Bao (; 355–398), courtesy name Daoyou (道佑), Xianbei name Kugou (庫勾), formally Emperor Huimin of (Later) Yan ((後)燕惠愍帝), temple name Liezong (烈宗) or Liezu (烈祖), was an emperor of the Xianbei-led Chinese Later Yan dynasty. He inherited from his father Murong Chui (Emperor Wucheng) a sizable empire but lost most of it within a span of a year, and would be dead in less than three, a victim of a rebellion by his granduncle Lan Han. Historians largely attributed this to his irresolution and inability to judge military and political decisions. While Later Yan would last for one more decade after his death, it would never regain the power it had under Murong Chui. Prior to Later Yan's establishment Murong Bao was Murong Chui's fourth son, by his first wife Princess Duan while he was the Prince of Wu under his brother Murong Jun (Emperor Jingzhao of Former Yan). He was initially not his father's heir apparent—his older brother Murong Ling (慕容令) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei (), Tuoba Wei (), Yuan Wei () and Later Wei (), was founded by the Tuoba (Tabgach) clan of the Xianbei. The first of the Northern and Southern dynasties#Northern dynasties, Northern dynasties, it ruled northern China from 386 to 535 during the period of the Northern and Southern dynasties. Described as "part of an era of political turbulence and intense social and cultural change", the Northern Wei dynasty is particularly noted for unifying northern China in 439, bringing to an end the chaotic Sixteen Kingdoms period, and strengthening imperial control over the rural landscape via reforms in 485. This was also a period of introduced foreign ideas, such as Buddhism, which became firmly established. The Northern Wei were referred to as "Plaited Barbarians" (索虜 ''suolu'') by writers of the Southern dynasties, who considered themselves the true upholders of Chinese culture. During the Taihe period (477–499), Empress Dowager ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaoyang, Liaoning
Chaoyang () is a prefecture-level city in western Liaoning province, People's Republic of China. With a vast land area of almost , it is by area the largest prefecture-level city in Liaoning, and borders on Hebei province and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region to the west. The area under Chaoyang's jurisdictional control is split up into two counties (Jianping, Chaoyang), two urban districts (Longcheng, Shuangta), two county-level cities (Beipiao, Lingyuan), and the Harqin Left Wing Mongolian Autonomous County. The total regional population is 3 million, while the urban centre where the government office is located has a population of 430,000 and forms the core of Chaoyang. Known as China's 'fossil city', many important paleontological discoveries have been made in Chaoyang, and the Harqin region is the oldest currently known prehistoric site in northern China. Two of the most remarkable Early Cretaceous birds known to date were recovered in the vicinity of the Jiufotang Form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liaoning
Liaoning () is a coastal province in Northeast China that is the smallest, southernmost, and most populous province in the region. With its capital at Shenyang, it is located on the northern shore of the Yellow Sea, and is the northernmost coastal province of the People's Republic of China. Historically a gateway between China proper and Manchuria, the modern Liaoning province was established in 1907 as Fengtian or Fengtien province and was renamed Liaoning in 1929. It was also known at that time as Mukden Province for the Manchu name of ''Shengjing'', the former name of Shenyang. Under the Japanese-puppet Manchukuo regime, the province reverted to its 1907 name, but the name Liaoning was restored for a brief time in 1945 and then again in 1954. Liaoning borders the Yellow Sea ( Korea Bay) and Bohai Sea in the south, North Korea's North Pyongan and Chagang provinces in the southeast, Jilin to the northeast, Hebei to the southwest, and Inner Mongolia to the northwest. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dismember
Dismemberment is the act of cutting, ripping, tearing, pulling, wrenching or otherwise disconnecting the limbs from a living or dead being. It has been practiced upon human beings as a form of capital punishment, especially in connection with regicide, but can occur as a result of a traumatic accident, or in connection with murder, suicide, or cannibalism. As opposed to surgical amputation of the limbs, dismemberment is often fatal. In criminology, a distinction is made between offensive dismemberment, in which dismemberment is the primary objective of the dismemberer, and defensive dismemberment, in which the motivation is to destroy evidence. In 2019, Michael H. Stone, Gary Brucato and Ann Burgess proposed formal criteria by which "dismemberment" might be systematically distinguished from the act of "mutilation", as these terms are commonly used interchangeably. They suggested that dismemberment involves "the entire removal, by any means, of a large section of the body of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Annals Of The Sixteen Kingdoms
The ''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Sixteen Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese title ''Shiliuguo Chunqiu'' () is a Chinese biographical historical work of the Sixteen Kingdoms compiled by the Northern Wei official Cui Hong between 501 and 522. It became one of the chief sources for the compilation of the ''Book of Wei'' and ''Book of Jin''. Parts of the book went missing from the early Tang dynasty and did not survive intact. It originally contained 100 volumes, a preface and a chronological table. By the time of the early Song dynasty, many of them were lost and only about 20 volumes remained, which were quoted extensively by Sima Guang. There are two extant versions dating from the late Ming dynasty, the edition by Tu Qiaosun containing 100 volumes, and the one by He Tang containing 16 volumes, reprinted in the ''Hanwei Congshu'', a compilation of histories. Tu's edition was published for the third time in 1781. Also there is a 100 volumes edition together with a chronologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |