|
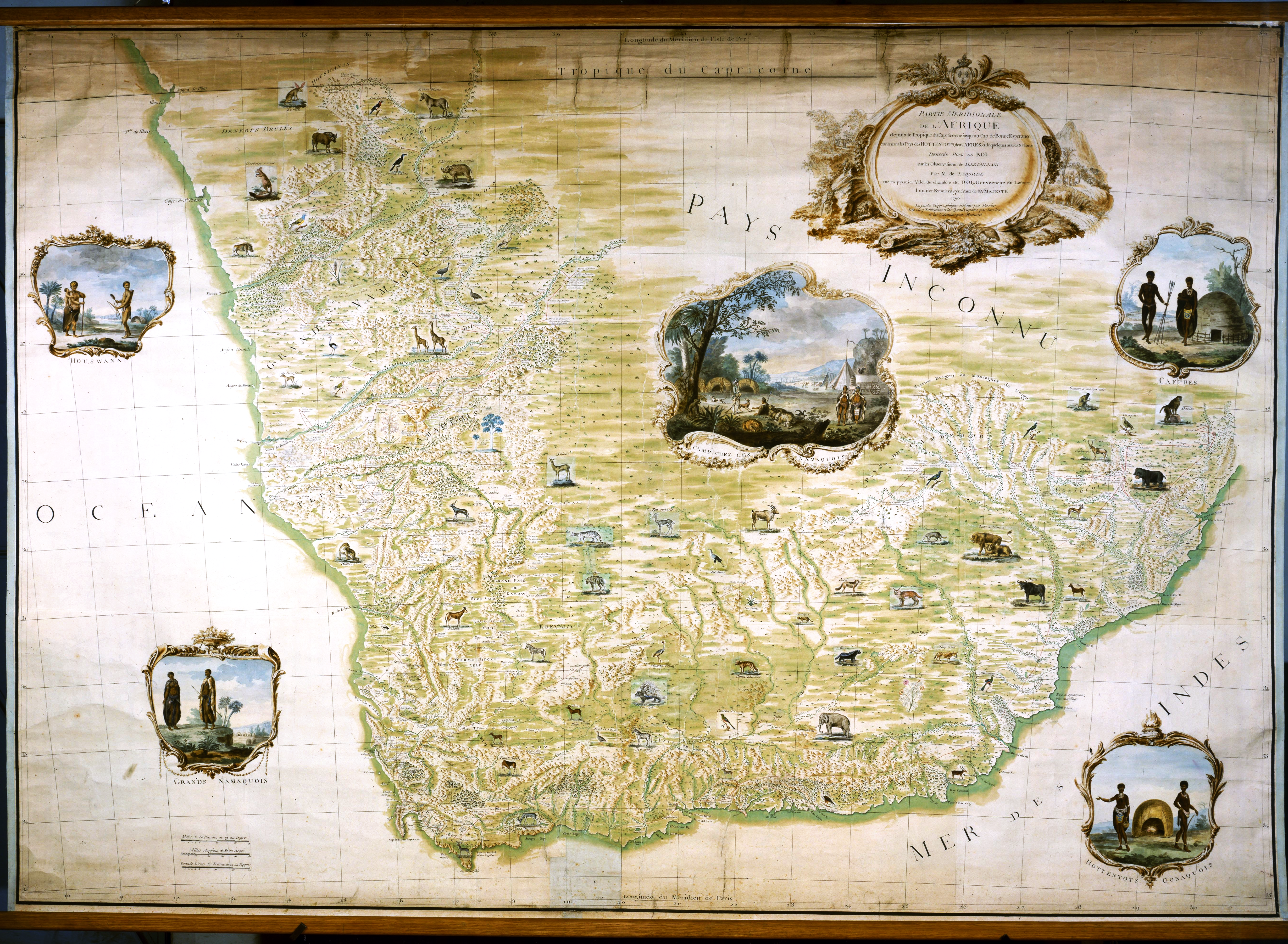
François Levaillant
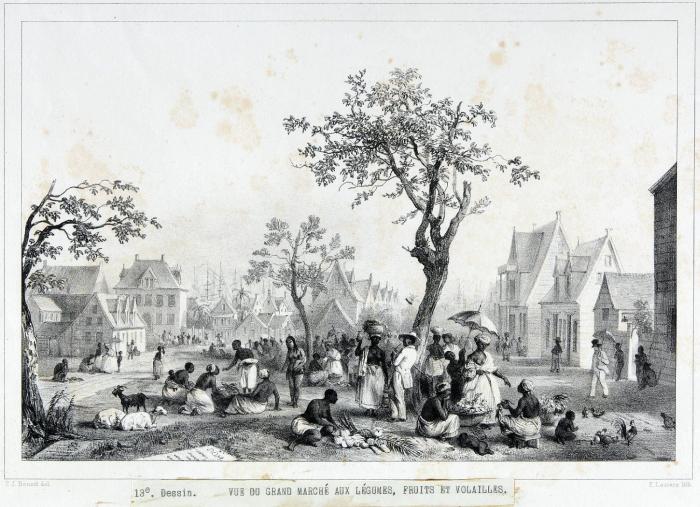
François Levaillant (born Vaillant, later in life as Le Vaillant, ''"The Valiant"'') (6 August 1753 – 22 November 1824) was a French author, explorer, naturalist, zoological collector, and noted ornithologist. He described many new species of birds based on birds he collected in Africa and several birds are named after him. He was among the first to use colour plates for illustrating birds and opposed the use of binomial nomenclature introduced by Carl Linnaeus, preferring instead to use descriptive French names such as the bateleur (meaning "tumbler or tight-rope walker") for the distinctive African eagle. Life François Vaillant was born in Paramaribo, the capital of Dutch Guiana ( Surinam), the son of Nicolas François, a French lawyer from Metz who had fled there after eloping with his mother Catherine Joséphine and then took up a position as the French Consul. Growing up amid forests, François took an interest in the local fauna, collecting birds and insects. His family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramaribo
Paramaribo (; ; nicknamed Par'bo) is the capital and largest city of Suriname, located on the banks of the Suriname River in the Paramaribo District. Paramaribo has a population of roughly 241,000 people (2012 census), almost half of Suriname's population. The historic inner city of Paramaribo has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2002. Name The city is named for the Paramaribo tribe living at the mouth of the Suriname River; the name is from Tupi–Guarani ''para'' "large river" + ''maribo'' "inhabitants". History The name Paramaribo is probably a corruption of the name of an Indian village, spelled Parmurbo in the earliest Dutch sources. This was the location of the first Dutch settlement, a trading post established by Nicolaes Baliestel and Dirck Claeszoon van Sanen in 1613. English and French traders also tried to establish settlements in Suriname, including a French post established in 1644 near present-day Paramaribo. All earlier settlements were abandone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
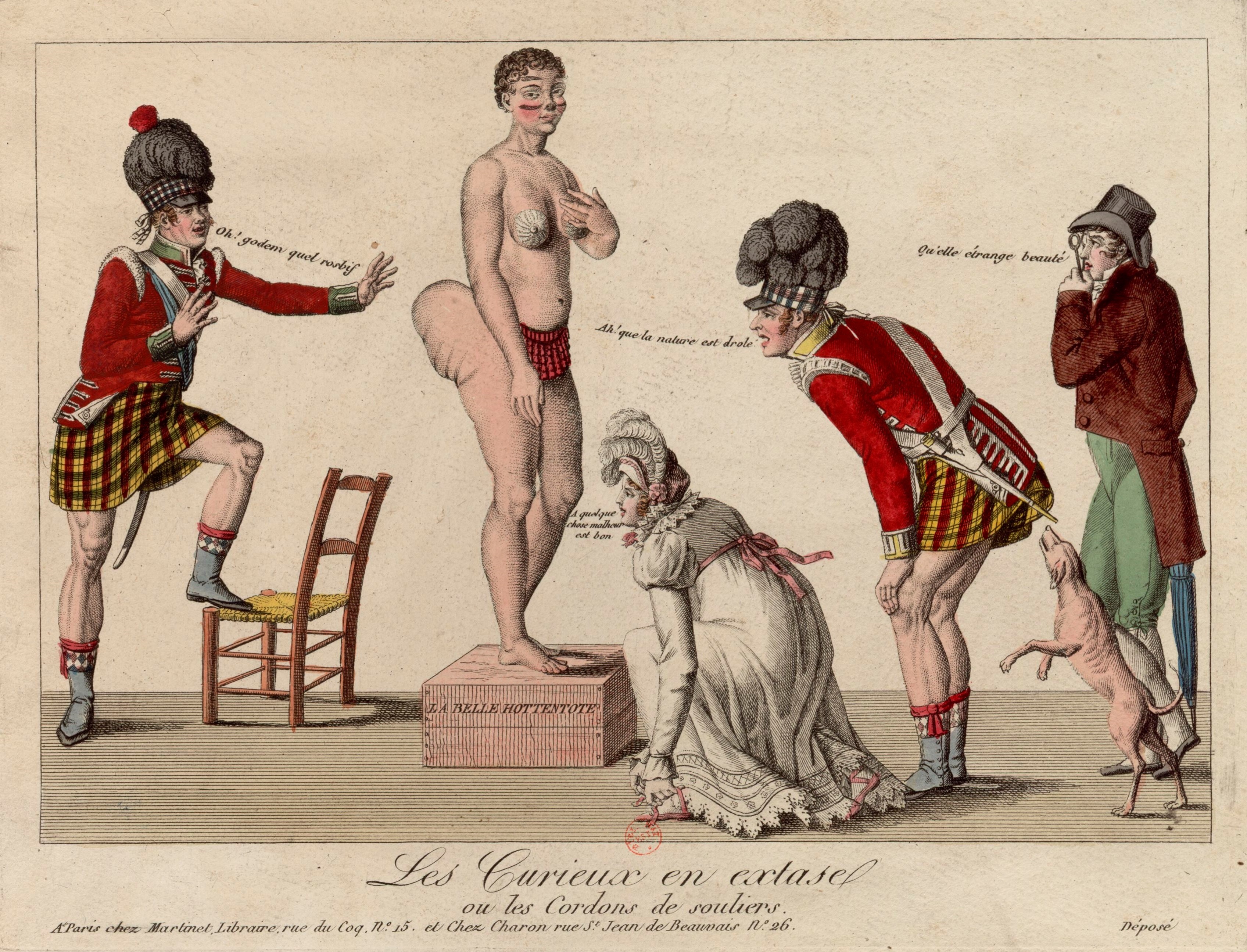
Saartjie Baartman
Sarah Baartman (; 1789– 29 December 1815), also spelt Sara, sometimes in the diminutive form Saartje (), or Saartjie, and Bartman, Bartmann, was a Khoikhoi woman who was exhibited as a freak show attraction in 19th-century Europe under the name Hottentot Venus, a name which was later attributed to at least one other woman similarly exhibited. The women were exhibited for their steatopygic body type uncommon in Western Europe which not only was perceived as a curiosity at that time, but became subject of scientific interest as well as of erotic projection. She is thought to have suffered from lipedema. "Venus" is sometimes used to designate representations of the female body in arts and cultural anthropology, referring to the Roman goddess of love and fertility. " Hottentot" was the colonial-era term for the indigenous Khoikhoi people of southwestern Africa, now usually considered an offensive term. The Sarah Baartman story is often regarded as the epitome of racist coloni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonaqua
The Gonaqua (or Gonaguas, meaning "borderers") were a Xhosa ethnic group, descendants of a very old union between the Khoikhoi and the Xhosa. This union predates the arrival of Europeans in South Africa. The Gonaqua have been regarded as outcasts by the Bantus. They were targets during the Second Frontier War, but received protection from the British British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, .... Sources "Gonaqua, n."''Dictionary of South African English''. Dictionary Unit for South African English, 2020. Accessed 1 March 2020. Ethnic groups in South Africa {{Africa-ethno-group-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chacma Baboon
The chacma baboon (''Papio ursinus''), also known as the Cape baboon, is, like all other baboons, from the Old World monkey family. It is one of the largest of all monkeys. Located primarily in southern Africa, the chacma baboon has a wide variety of social behaviours, including a dominance hierarchy, collective foraging, adoption of young by females, and friendship pairings. These behaviors form parts of a complex evolutionary ecology. In general, the species is not threatened, but human population pressure has increased contact between humans and baboons. Hunting, trapping, and accidents kill or remove many baboons from the wild, thereby reducing baboon numbers and disrupting their social structure. Taxonomy Due to hybridization between different baboon (''Papio'') populations across Africa, authors have occasionally grouped the entire radiation as a single species, the hamadryas baboon, ''Papio hamadryas''. Arbitrary boundaries were then used to separate the populations into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noble Savage
A noble savage is a literary stock character who embodies the concept of the Indigenous peoples, indigene, outsider, wild human, an "Other (philosophy), other" who has not been "corrupted" by civilization, and therefore symbolizes humanity's innate goodness. Besides appearing in many works of fiction and philosophy, the stereotype was also heavily employed in early Anthropology, anthropological works. In English, the phrase first appeared in the 17th century in John Dryden's heroic play ''The Conquest of Granada'' (1672), wherein it was used in reference to newly created man. "Savage" at that time could mean "wild beast" as well as "wild man". The phrase later became identified with the idealized picture of "nature's gentleman", which was an aspect of 18th-century Moral sense theory, sentimentalism. The noble savage achieved prominence as an oxymoronic rhetorical device after 1851, when used sarcastically as the title for a satirical essay by English novelist Charles Dickens, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturalis
Naturalis Biodiversity Center ( nl, Nederlands Centrum voor Biodiversiteit Naturalis) is a national museum of natural history and a research center on biodiversity in Leiden, Netherlands. It was named the European Museum of the Year 2021. Although its current name and organization are relatively recent, the history of Naturalis can be traced back to the early 1800s. Its collection includes approximately 42 million specimens, making it one of the largest natural history collections in the world. History The beginnings of Naturalis go back to the creation of the Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie (abbreviated RMNH, National Museum of Natural History) by Dutch King William I on August 9, 1820. In 1878, the geological and mineralogical collections of the museum were split off into a separate museum, remaining distinct until the merger of the Rijksmuseum van Natuurlijke Historie with the Rijksmuseum van Geologie en Mineralogie (abbreviated RGM) in 1984, to form the Nationaal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiden
Leiden (; in English and archaic Dutch also Leyden) is a city and municipality in the province of South Holland, Netherlands. The municipality of Leiden has a population of 119,713, but the city forms one densely connected agglomeration with its suburbs Oegstgeest, Leiderdorp, Voorschoten and Zoeterwoude with 206,647 inhabitants. The Netherlands Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) further includes Katwijk in the agglomeration which makes the total population of the Leiden urban agglomeration 270,879, and in the larger Leiden urban area also Teylingen, Noordwijk, and Noordwijkerhout are included with in total 348,868 inhabitants. Leiden is located on the Oude Rijn, at a distance of some from The Hague to its south and some from Amsterdam to its north. The recreational area of the Kaag Lakes ( Kagerplassen) lies just to the northeast of Leiden. A university city since 1575, Leiden has been one of Europe's most prominent scientific centres for more than four centuries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenraad Jacob Temminck
Coenraad Jacob Temminck (; 31 March 1778 – 30 January 1858) was a Dutch aristocrat, zoologist and museum director. Biography Coenraad Jacob Temminck was born on 31 March 1778 in Amsterdam in the Dutch Republic. From his father, Jacob Temminck, who was treasurer of the Dutch East India Company with links to numerous travellers and collectors, he inherited a large collection of bird specimens. His father was a good friend of Francois Levaillant who also guided Coenraad. Temminck's ''Manuel d'ornithologie, ou Tableau systématique des oiseaux qui se trouvent en Europe'' (1815) was the standard work on European birds for many years. He was also the author of ''Histoire naturelle générale des Pigeons et des Gallinacées'' (1813–1817), ''Nouveau Recueil de Planches coloriées d'Oiseaux'' (1820–1839), and contributed to the mammalian sections of Philipp Franz von Siebold's ''Fauna japonica'' (1844–1850). Temminck was the first director of the National Museum of Natural H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Baudelaire
Charles Pierre Baudelaire (, ; ; 9 April 1821 – 31 August 1867) was a French poet who also produced notable work as an essayist and art critic. His poems exhibit mastery in the handling of rhyme and rhythm, contain an exoticism inherited from Romantics, but are based on observations of real life. His most famous work, a book of lyric poetry titled ''Les Fleurs du mal'' (''The Flowers of Evil''), expresses the changing nature of beauty in the rapidly industrializing Paris during the mid-19th century. Baudelaire's highly original style of prose-poetry influenced a whole generation of poets including Paul Verlaine, Arthur Rimbaud and Stéphane Mallarmé, among many others. He is credited with coining the term modernity (''modernité'') to designate the fleeting, ephemeral experience of life in an urban metropolis, and the responsibility of artistic expression to capture that experience. Marshall Berman has credited Baudelaire as being the first Modernist. Early life Baude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sézanne
Sézanne () is a commune in the Marne department and Grand Est region in north-eastern France France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area .... Its inhabitants are called ''Sézannais''. Population Notable people * Leonie Aviat, Saint * Floresca Guépin (1813-1889), feminist, teacher, school founder * Raymond Marcellin, Politician See also * Communes of the Marne department References Communes of Marne (department) {{Marne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |