|
François-Joseph Servois
François-Joseph Servois (born 19 July 1767 in Mont-de-Laval, Doubs, France; died 17 April 1847 in Mont-de-Laval, Doubs, France) was a French priest, military officer and mathematician. His most notable contribution came in his publication of Essai sur un nouveau mode d’exposition des principes du calcul différentiel (Essay on a system of exposition of the principles of differential calculus) in 1814, where he first introduced the mathematical terms for commutative and distributive. Life Servois was born on 18 July 1767 in Mont-de-Laval, France to Jacques-Ignace Servois, a local merchant, and Jeanne-Marie Jolliet. Not much is known about his early life except that he had at least one sibling, a sister with which he would eventually move in with after his retirement. He attended several religious schools in both Mont-de-Laval and Besançon with the intention of becoming a priest. He was ordained at Besançon near the beginning of the French Revolution. His life as a priest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Forces. The current Chief of Staff of the French Army (CEMAT) is General , a direct subordinate of the Chief of the Defence Staff (CEMA). General Schill is also responsible to the Ministry of the Armed Forces for organization, preparation, use of forces, as well as planning and programming, equipment and Army future acquisitions. For active service, Army units are placed under the authority of the Chief of the Defence Staff (CEMA), who is responsible to the President of France for planning for, and use of forces. All French soldiers are considered professionals, following the suspension of French military conscription, voted in parliament in 1997 and made effective in 2001. , the French Army employed 118,600 personnel (including the Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph-Louis Lagrange
Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Luigi LagrangiaJoseph-Louis Lagrange, comte de l’Empire ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' or Giuseppe Ludovico De la Grange Tournier; 25 January 1736 – 10 April 1813), also reported as Giuseppe Luigi Lagrange or Lagrangia, was an and , later naturalized [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Diaz Gergonne
Joseph Diez Gergonne (19 June 1771 at Nancy, France – 4 May 1859 at Montpellier, France) was a French mathematician and logician. Life In 1791, Gergonne enlisted in the French army as a captain. That army was undergoing rapid expansion because the French government feared a foreign invasion intended to undo the French Revolution and restore Louis XVI to the throne of France. He saw action in the major battle of Valmy on 20 September 1792. He then returned to civilian life but soon was called up again and took part in the French invasion of Spain in 1794. In 1795, Gergonne and his regiment were sent to Nîmes. At this point, he made a definitive transition to civilian life by taking up the chair of "transcendental mathematics" at the new École centrale. He came under the influence of Gaspard Monge, the Director of the new École polytechnique in Paris. In 1810, in response to difficulties he encountered in trying to publish his work, Gergonne founded his own mathematics jour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annales De Mathématiques Pures Et Appliquées
The ''Annales de Mathématiques Pures et Appliquées'', commonly known as the ''Annales de Gergonne'', was a mathematical journal published in Nimes, France from 1810 to 1831 by Joseph Diez Gergonne. The annals were largely devoted to geometry, with additional articles on history, philosophy, and mathematics education showing interdisciplinarity. "In the ''Annales'', Gergonne established in form and content a set of exceptionally high standards for mathematical journalism. New symbols and new terms to enrich mathematical literature are found here for the first time. The journal, which met with instant approval, became a model for many another editor. Cauchy, Poncelet, Brianchon, Steiner, Plucker, Crelle, Poisson, Ampere, Chasles, and Liouville sent articles for publication." Operational calculus was developed in the journal in 1814 by Francois-Joseph Servois. Francois-Joseph Servois (1814Analise Transcendante. Essai sur unNouveu Mode d'Exposition des Principes der Calcul Diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Victor Poncelet
Jean-Victor Poncelet (; 1 July 1788 – 22 December 1867) was a French engineer and mathematician who served most notably as the Commanding General of the École Polytechnique. He is considered a reviver of projective geometry, and his work ''Traité des propriétés projectives des figures'' is considered the first definitive text on the subject since Gérard Desargues' work on it in the 17th century. He later wrote an introduction to it: ''Applications d'analyse et de géométrie''. As a mathematician, his most notable work was in projective geometry, although an early collaboration with Charles Julien Brianchon provided a significant contribution to Feuerbach's theorem. He also made discoveries about projective harmonic conjugates; relating these to the poles and polar lines associated with conic sections. He developed the concept of parallel lines meeting at a point at infinity and defined the circular points at infinity that are on every circle of the plane. These discoverie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Fère
La Fère () is a commune in the Aisne department in Hauts-de-France in France. Population See also * Communes of the Aisne department The following is a list of the 799 Communes of France, communes in the French Departments of France, department of Aisne. The communes cooperate in the following Communes of France#Intercommunality, intercommunalities (as of 2020): References Communes of Aisne Aisne communes articles needing translation from French Wikipedia {{Laon-geo-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metz
Metz ( , , lat, Divodurum Mediomatricorum, then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers. Metz is the prefecture of the Moselle department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand Est region. Located near the tripoint along the junction of France, Germany and Luxembourg,Says J.M. (2010) La Moselle, une rivière européenne. Eds. Serpenoise. the city forms a central place of the European Greater Region and the SaarLorLux euroregion. Metz has a rich 3,000-year history,Bour R. (2007) Histoire de Metz, nouvelle édition. Eds. Serpenoise. having variously been a Celtic ''oppidum'', an important Gallo-Roman city,Vigneron B. (1986) Metz antique: Divodurum Mediomatricorum. Eds. Maisonneuve. the Merovingian capital of Austrasia,Huguenin A. (2011) Histoire du royaume mérovingien d'Austrasie. Eds. des Paraiges. pp. 134,275 the birthplace of the Carolingian dynasty,Settipani C. (1989) Les ancêtres de Charlemagne. Ed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrien-Marie Legendre
Adrien-Marie Legendre (; ; 18 September 1752 – 9 January 1833) was a French mathematician who made numerous contributions to mathematics. Well-known and important concepts such as the Legendre polynomials and Legendre transformation are named after him. Life Adrien-Marie Legendre was born in Paris on 18 September 1752 to a wealthy family. He received his education at the Collège Mazarin in Paris, and defended his thesis in physics and mathematics in 1770. He taught at the École Militaire in Paris from 1775 to 1780 and at the École Normale Supérieure, École Normale from 1795. At the same time, he was associated with the Bureau des Longitudes. In 1782, the Prussian Academy of Sciences, Berlin Academy awarded Legendre a prize for his treatise on projectiles in resistant media. This treatise also brought him to the attention of Lagrange. The ''Académie des sciences'' made Legendre an adjoint member in 1783 and an associate in 1785. In 1789, he was elected a Fellow of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Paris (1814)
The Battle of Paris was fought on 30–31 March 1814 between the Sixth Coalition, consisting of Russia, Austria, and Prussia, against the French Empire. After a day of fighting in the suburbs of Paris, the French surrendered on March 31, ending the War of the Sixth Coalition and forcing Emperor Napoleon to abdicate and go into exile. Background Napoleon was retreating from his failed invasion of Russia in 1812. With the Russian armies following up victory, the Sixth Coalition was formed with Russia, Austria, Prussia, Portugal, Great Britain, Sweden, Spain and other nations hostile to the French Empire. Even though the French were victorious in the initial battles during their campaign in Germany, the Coalition armies eventually joined together and defeated them at the Battle of Leipzig in the autumn of 1813. After the battle, the Pro-French German Confederation of the Rhine collapsed, thereby loosening Napoleon's hold on Germany east of the Rhine. The Coalition forces i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




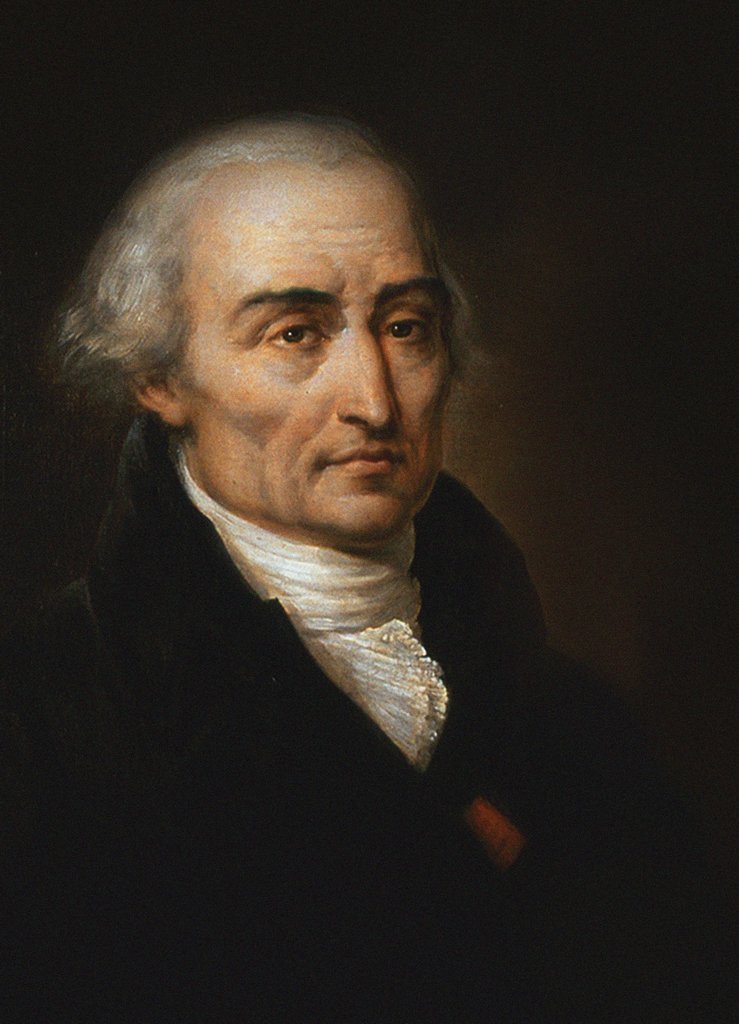

.jpg)