|
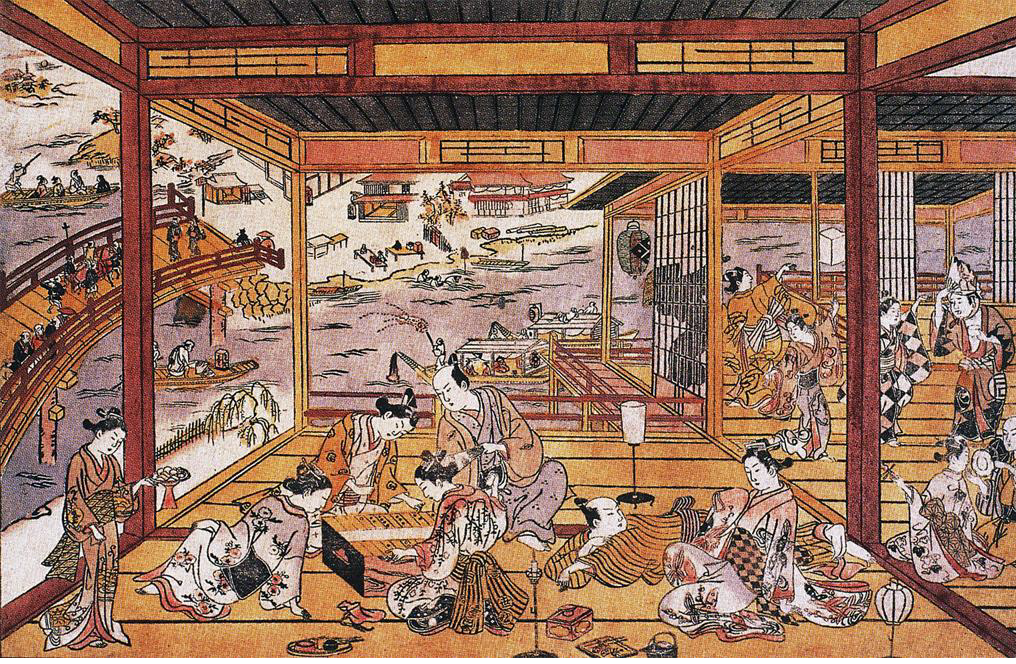
Furuyama Moromasa
__NOTOC__ Furuyama Moromasa (Japanese: 古山師政, act. ca. 1695-1748) was a Japanese ukiyo-e painter and print artist, active during the 18th century. Life and works Few details of his life have survived. He was born in Edo (Tokyo), the son of the artist Furuyama Moroshige, who in turn was the son of the master artist Hishikawa Moronobu but established his own lineage, the Furuyama School. Moromasa designed woodblock prints with genre scenes of ordinary life, sporting contests, activities in the Yoshiwara district and similar subjects. He was one of the first Japanese artists to use linear perspective, a technique first used to show interiors, such as tea houses, in a genre known as uki-e. This was likely done under the influence of megane-e (''vedute'') from Europe and China. He also produced paintings in the popular category of 'beautiful women' (''bijin-ga''). Moromasa's most famous work is a pair of handscroll paintings depicting the theater district (''Azuma yarō''; own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukiyo-e
Ukiyo-e is a genre of Japanese art which flourished from the 17th through 19th centuries. Its artists produced woodblock prints and paintings Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and ai ... of such subjects as female beauties; kabuki actors and sumo wrestlers; scenes from history and folk tales; travel scenes and landscapes; Flora of Japan, flora and Wildlife of Japan#Fauna, fauna; and Shunga, erotica. The term translates as "picture[s] of the floating world". In 1603, the city of Edo (Tokyo) became the seat of the ruling Tokugawa shogunate. The ''chōnin'' class (merchants, craftsmen and workers), positioned at the bottom of Four occupations, the social order, benefited the most from the city's rapid economic growth, and began to indulge in and patronise the entertainment o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hishikawa Moronobu
Hishikawa Moronobu ( ja, 菱川 師宣; 1618 – 25 July 1694) was a Japanese artist known for popularizing the ukiyo-e genre of woodblock prints and paintings in the late 17th century. He consolidated the works of scattered Japanese art styles and forged the early development of ukiyo-e. Early life Born in Hoda at the distant end of Edo Bay, Moronobu was the son of a well-respected embroiderer of rich tapestries who produced it for the use of temples and wealthy patrons. After moving to Edo in the 1660s, Moronobu, who had likely learned skills from his father's craft, and studied both Tosa and Kanō-style painting. He thus had a solid grounding in both decorative crafts and academic painting, which served him well when he then turned to ukiyo-e, which he studied with his mentor, the Kanbun Master. Work The earliest known illustration of Moronobu that can be dated comes from his work titled ''One Hundred Warrior Poets'' from 1672, although earlier works are yet possibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genre Art
Genre art is the pictorial representation in any of various media of scenes or events from everyday life, such as markets, domestic settings, interiors, parties, inn scenes, work, and street scenes. Such representations (also called genre works, genre scenes, or genre views) may be realistic, imagined, or romanticized by the artist. Some variations of the term ''genre art'' specify the medium or type of visual work, as in ''genre painting'', ''genre prints'', ''genre photographs'', and so on. The following concentrates on painting, but genre motifs were also extremely popular in many forms of the decorative arts, especially from the Rococo of the early 18th century onwards. Single figures or small groups decorated a huge variety of objects such as porcelain, furniture, wallpaper, and textiles. Genre painting ''Genre painting'', also called ''genre scene'' or ''petit genre'', depicts aspects of everyday life by portraying ordinary people engaged in common activities. One comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoshiwara
was a famous (red-light district) in Edo, present-day Tokyo, Japan. Established in 1617, Yoshiwara was one of three licensed and well-known red-light districts created during the early 17th century by the Tokugawa shogunate, alongside Shimabara in Kyoto in 1640Avery, Anne Louise. ''Flowers of the Floating World: Geisha and Courtesans in Japanese Prints and Photographs, 1772–1926'' xhibition Catalogue(Sanders of Oxford & Mayfield Press: Oxford, 2006) and Shinmachi in Osaka. Created by the shogunate to curtail the tastes of and sequester the nouveau riche (merchant) classes, the entertainment offered in Yoshiwara, alongside other licensed districts, would eventually give rise to the creation of geisha, who would become known as the fashionable companions of the classes and simultaneously cause the demise of , the upper-class courtesans of the red-light districts. History 17th and 18th century The licensed district of Yoshiwara was created in the city of Edo, near to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
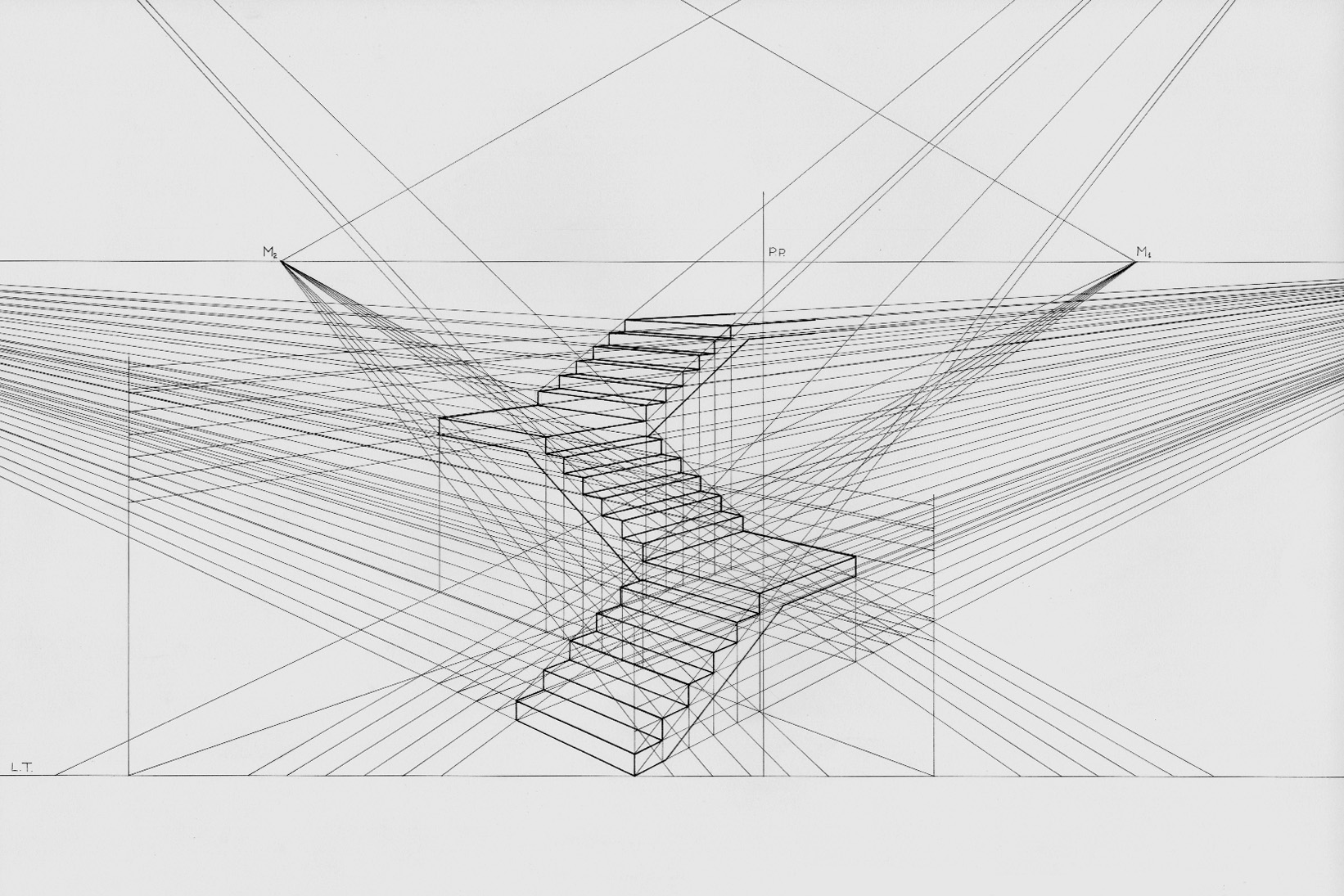
Linear Perspective
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of 3D projection, graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uki-e
refers to a genre of ukiyo-e pictures that employs western conventions of linear perspective. Although they never constituted more than a minor genre, pictures in perspective were drawn and printed by Japanese artists from their introduction in the late 1730s through to the mid-nineteenth century.Hockley, p. 79 Around 1739, Okumura Masanobu studied European engravings to learn the rules of perspective. His engravings found their way to Japan either through Dejima or China. Masanobu was the first to apply the term Uki-e to perspective images, and Utagawa Toyoharu fully developed the form in the late 1750s when he produced colored woodblock copies of engravings after Canaletto and Guardi. Toyoharu was also the first to adapt these techniques to Japanese subjects. The interior of Kabuki theaters was a common subject in Uki-e prints. Interior scenes tend to be favored as it is easier to accurately apply one point perspective to architecture than to landscape. See also *Ranga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megane-e
In Japanese art, a ' (, 'optique picture') is a print designed using graphical perspective techniques and viewed through a convex lens to produce a three-dimensional effect. The term derives from the French '. The device used to view them was called an ' (, 'Dutch glasses') or ' (, 'peeping glasses'), and the pictures were also known as ' (, 'tricky picture'). Perspective boxes first appeared in Renaissance Europe and were popular until superseded by the stereoscope in the mid-19th century. The Dutch brought the first such device to Japan in the 1640s as a gift to the ''shōgun''. The devices became popular in Japan only after the Chinese popularized them in Japan about 1758, after which they began to influence Japanese artists. The artist Maruyama Ōkyo (1733–95) made serious study of imported perspective techniques and applied them to his painting. He gained an interest in making ukiyo-e prints through the artist Utagawa Toyoharu Utagawa Toyoharu (歌川 豊春, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bijin-ga
is a generic term for pictures of beautiful women () in Japanese art, especially in woodblock printing of the ukiyo-e genre. Definition defines as a picture that simply "emphasizes the beauty of women", and the ''Shincho Encyclopedia of World Art'' defines it as depiction of "the beauty of a woman's appearance". On the other hand, defines as pictures that explore "the inner beauty of women". For this reason, the essence of cannot always be expressed only through the depiction of a , a woman aligning with the beauty image. In fact, in ukiyo-e , it was not considered important that the picture resemble the facial features of the model, and the depiction of women in ukiyo-e is stylized rather than an attempt to create a realistic image; For example, throughout the Edo period (1603-1867), married women had a custom of shaving their eyebrows (), but in , there was a rule to draw the eyebrows for married women. History Ukiyo-e itself is a genre of woodblock prints and pain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Library, Edinburgh
Central Library in Edinburgh, Scotland, opened in 1890, was the first public library building in the city. Edinburgh Central library comprises six libraries: Lending, Reference, Music, Art and Design, Edinburgh and Scottish and the Children's Library. History Today there are 28 public libraries in Edinburgh but, as the first to open in the Scottish capital, the creation of Central Library was funded with £50,000 by philanthropist Andrew Carnegie.Central Library City of Edinburgh CouncilEdinburgh Public Libraries 1890–1950, p. 2Armstrong & White, p. 3 At the opening ceremony a telegram from Carnegie was read out stating: "We trust that this Library is to grow in usefullness year after year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stibbert Museum
The Stibbert Museum ( it, Museo Stibbert) is located on via Frederick Stibbert on the hill of Montughi in Florence, Italy. The museum contains over 36,000 artifacts, including a vast collection of armour from Eastern and Western civilizations. History of the family and museum The museum was founded by Frederick Stibbert (1838–1906). His father was English and his mother Italian; he received his education in England. The Stibbert family's extreme wealth came from Frederick's grandfather, Giles Stibbert, who was the commander in chief for the British East India Company in Bengal at the end of the 18th century and ruled as governor for many years. Frederick Stibbert inherited the entire estate from his grandfather and did not work for the rest of his life. Instead, he dedicated his life to collecting objects, antiques, and artifacts and turned his villa into a museum. When the size of the collections outgrew the villa, Stibbert hired architect Giuseppe Poggi, painter Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schools Of Ukiyo-e Artists
Ukiyo-e artists may be organized into schools, which consist of a founding artist and those artists who were taught by or strongly influenced by him. Artists of the Osaka school are united both stylistically and geographically.Assignment of artists into schools is derived from ''Hotei Encyclopedia of Japanese Woodblock Prints,'' 2005 Not all of these artists designed woodblock prints, and some ukiyo-e artists had more than one teacher, and others are not known to be associated with any particular school. Asayama school (in Osaka) :Asayama Ashikuni (founder) :Ashisato :Ashifune :Ashihiro :Ashikiyo :Asayama Ashitaka :Asayama Ashitomo : Gigadō Ashiyuki (Nagakuni) :Jukōdō Yoshilkuni Eishi school (also known as Hosoda school) :Chōbunsai Eishi (founder) :Ichirakute Eisui :Chōkōsai Eishō :Chōkyōsai Eiri :Gessai Gabimaru :Chōensai Eishin :Rekisentei Eiri :Harukawa Eizan Furuyama school : Furuyama Moroshige (founder) :Furuyama Moromasa :Furuyama Morotane :Furuyama Morotsug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_Three_Beauties_of_the_Present_Time%2C_MFAB_21.6382.jpg)
