|
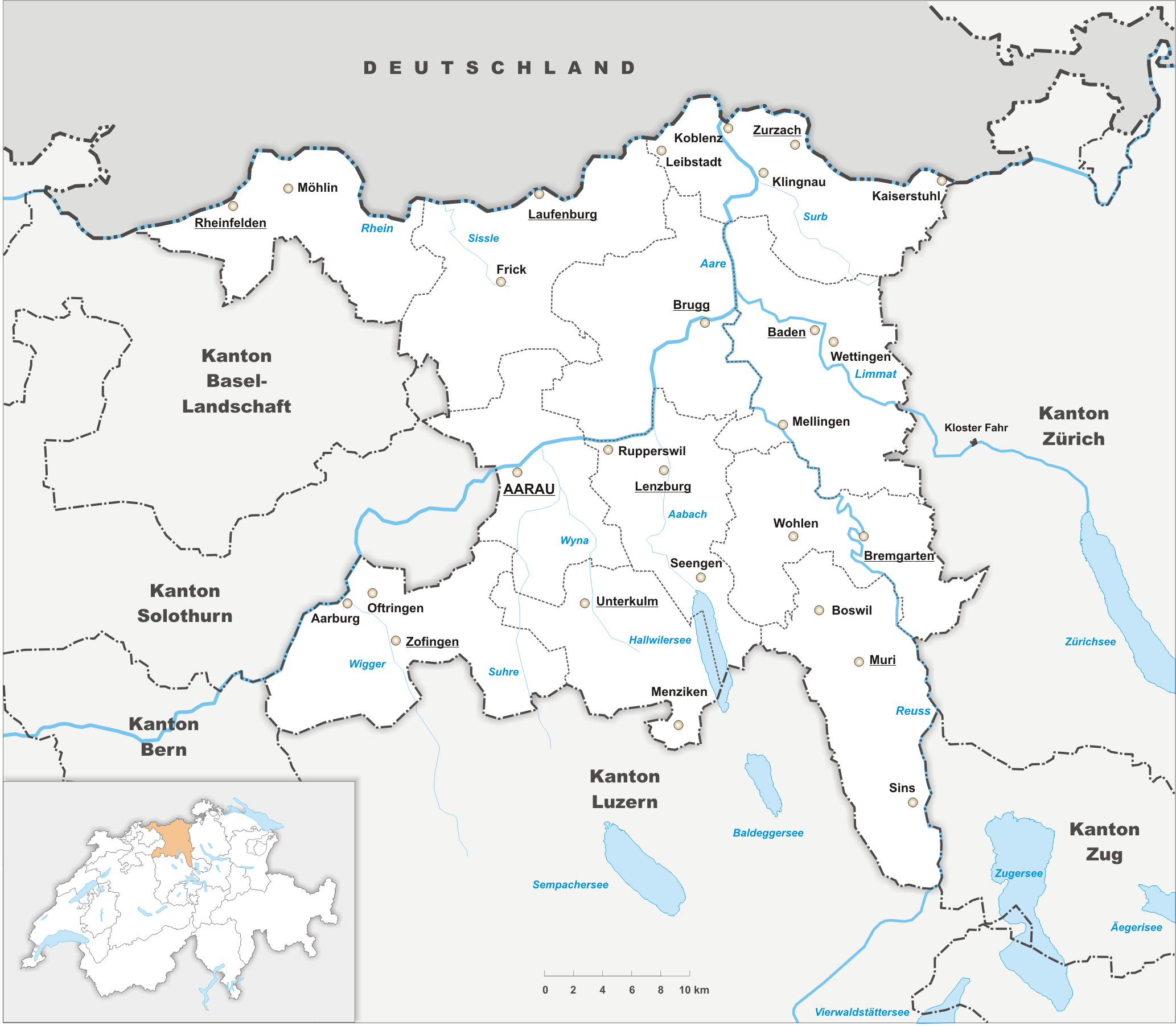
Fricktal
The Fricktal ("Frick Valley") is a region on Northwestern Switzerland, comprising the Laufenburg and Rheinfelden districts of the Swiss canton of Aargau. The region was known as ''Frickgau'' in the medieval period, ultimately from a Late Latin , in reference to the iron mine located here in the Roman era, also transferred to the village of Frick as the main settlement. Frickgau was part of Breisgau within Further Austria in the early modern period. It was joined to Switzerland only during the Napoleonic period. It now forms a northwestern extension to the canton of Aargau to the east of Basel, between the High Rhine forming the border with Germany in the north and the Jura Mountains in the south. History In the Early Middle Ages, Fricktal formed part of the Alemannic '' Augstgau'' between the Rhine and Aar rivers, from the 10th century onwards of the smaller ''Frickgau'' region within Upper Burgundy, owned by the Counts of Homberg-Thierstein in the 11th and 12th centuries. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aargau
Aargau, more formally the Canton of Aargau (german: Kanton Aargau; rm, Chantun Argovia; french: Canton d'Argovie; it, Canton Argovia), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capital is Aarau. Aargau is one of the most northerly cantons of Switzerland. It is situated by the lower course of the Aare River, which is why the canton is called ''Aar- gau'' (meaning "Aare province"). It is one of the most densely populated regions of Switzerland. History Early history The area of Aargau and the surrounding areas were controlled by the Helvetians, a member of the Celts, as far back as 200 BC. It was eventually occupied by the Romans and then by the 6th century, the Franks. The Romans built a major settlement called Vindonissa, near the present location of Brugg. Medieval Aargau The reconstructed Old High German name of Aargau is ''Argowe'', first unambiguously attested (in the spelling ''Argue'') in 795. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheinfelden (Aargau)
Rheinfelden ( gsw, Rhyfälde, ) is a municipality in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland, seat of the district of Rheinfelden. It is located 15 kilometres east of Basel. The name means the fields of the Rhine, as the town is located on the High Rhine. It is home to Feldschlösschen, the most popular beer in Switzerland. The city is across the river from Rheinfelden in Baden-Württemberg; the two cities were joined until Napoleon Bonaparte fixed the Germany–Switzerland border on the Rhine in 1802 and are still socially and economically tied. Geography The old town of Rheinfelden lies on the left bank of the Rhine, where the river is divided into two arms by the "Inseli", a roughly long island. Downstream of the Inseli and the ''Rheinbrücke'', the river bottoms drops to about deep, creating a huge and deadly vortex, known as the ''St-Anna-Loch. Nearly east is the '' Magdenerbach''. The wooded, gently-rising foothills of the '' Tafeljura'' lie south of the town. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frick, Switzerland
Frick is a municipality in the district of Laufenburg in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. History At the nearby ''Wittnauer Horn'', a prehistorical fortification was discovered, with object finds dated to the Late Bronze Age. A Roman villa was located at the site of the later village in the 2nd century, and a small Roman fort was built in the early 4th century to protect the military road from Vindonissa to Augusta Raurica (extended in AD 370). A Roman settlement developed in the vicinity of the fort, replaced by an Alemannic settlement during the 6th to 9th centuries. The Alemannic settlement had a fortified church, the foundations are still visible near the current village church. The name of the village was taken from that of the encompassing region of Frickgau (mentioned as ''Frichgowe'' in 926), from a Vulgar Latin , in reference to the iron mine located here in the Roman era (a formation based on Latin ''ferrāria'' "iron mine" with the ''-icius'' suffix), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
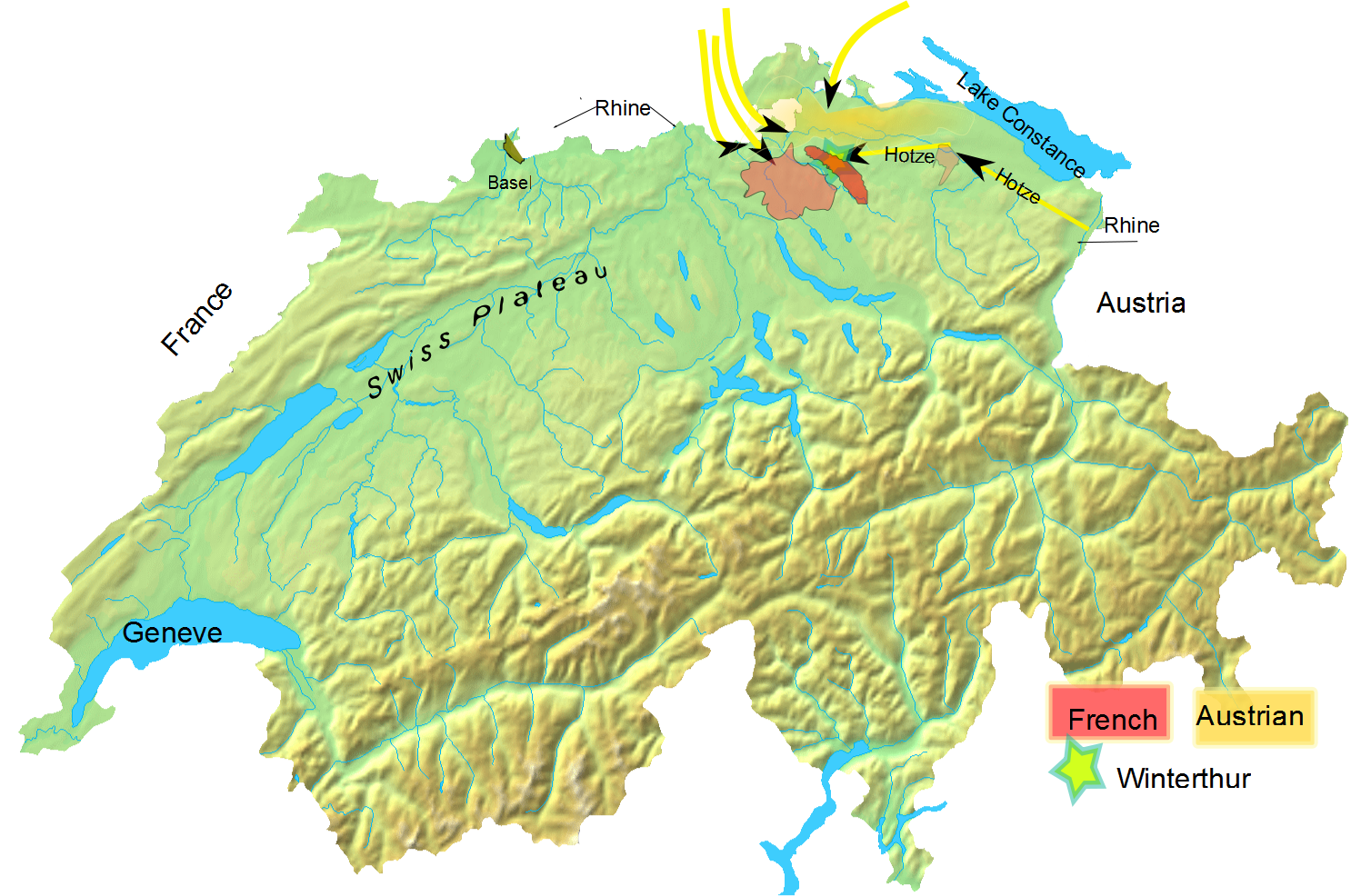
Further Austria
Further Austria, Outer Austria or Anterior Austria (german: Vorderösterreich, formerly ''die Vorlande'' (pl.)) was the collective name for the early (and later) possessions of the House of Habsburg in the former Swabian stem duchy of south-western Germany, including territories in the Alsace region west of the Rhine and in Vorarlberg. While the territories of Further Austria west of the Rhine and south of Lake Constance (except Konstanz itself) were gradually lost to France and the Swiss Confederacy, those in Swabia and Vorarlberg remained under Habsburg control until the Napoleonic Era. Geography Further Austria mainly comprised the Alsatian County of Ferrette in the Sundgau, including the town of Belfort, and the adjacent Breisgau region east of the Rhine, including Freiburg im Breisgau after 1368. Also ruled from the Habsburg residence in Ensisheim near Mühlhausen were numerous scattered territories stretching from Upper Swabia to the Allgäu region in the east, the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laufenburg (district)
Laufenburg District is a district of the canton of Aargau, Switzerland, essentially consisting of the upper Fricktal valley in the Aargau Jura south of the Rhine. Its capital is the town of Laufenburg. It has a population of (as of ). Geography The Laufenburg district has an area, , of . Of this area, or 49.2% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 39.2% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 10.4% is settled (buildings or roads). Demographics The Laufenburg district has a population () of . , 15.6% of the population are foreign nationals.Statistical Department of Canton Aargau -Bereich 01 -Bevölkerung accessed 20 January 2010 Economy there were 13,183 workers who lived in the district. Of these, 9,714 or about 73.7% of the residents worked outside the district whi ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheinfelden (district)
Rheinfelden District lies in the northwest of the canton of Aargau in Switzerland, in the Fricktal region. Its capital is Rheinfelden. Around 88% of the population live in the conurbation of Basel. There are 14 municipalities, with a population of (as of ) living in an area of 112.09 km2. The population density is around 355 persons per square kilometre. Geography The Rheinfelden district has an area, , of . Of this area, or 44.0% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 39.7% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 13.4% is settled (buildings or roads). Demographics Rheinfelden district has a population () of . , 21.3% of the population are foreign nationals.Statistical Department of Canton Aargau -Bereich 01 -Bevölkerung accessed 20 January 2010 Economy there we ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laufenburg, Switzerland
Laufenburg is a municipality in the Swiss canton of Aargau. It is the seat of the district of the same name. On 1 January 2010 the municipality Sulz merged into Laufenburg. It has approximately 2000 inhabitants. On the other side of the Rhine River lies Laufenburg (Baden), Germany. The same name is not by accident, as the two used to be the same city. In the early 19th century Napoleon divided the city. Two bridges now link both cities. In 1985, Laufenburg received the Wakker Prize for the development and preservation of its architectural heritage. History A high point along the Rhine river with a rapids section about from Säckingen Abbey was chosen as a place for a strategic bridge over the river. The '' Kastvogtei'' (a feudal land holder appointed by the Abbey) transferred his loyalty to the Habsburgs in 1173. Laufenburg is first mentioned in 1207 as ''Loufenberc''. In this 1207 document, the rights of the Abbey to parts of the village were secured while the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland In The Napoleonic Period
During the French Revolutionary Wars, the revolutionary armies marched eastward, enveloping Switzerland in their battles against Austria. In 1798, Switzerland was completely overrun by the French and was renamed the Helvetic Republic. The Helvetic Republic encountered severe economic and political problems. In 1798 the country became a battlefield of the Revolutionary Wars, culminating in the Battles of Zürich in 1799. In 1803 Napoleon's Act of Mediation reestablished a Swiss Confederation that partially restored the sovereignty of the cantons, and the former tributary and allied territories of Aargau, Thurgau, Graubünden, St. Gallen, Vaud and Ticino became cantons with equal rights. The Congress of Vienna of 1815 fully re-established Swiss independence and the European powers agreed to permanently recognise Swiss neutrality. At this time, the territory of Switzerland was increased for the last time, by the new cantons of Valais, Neuchâtel and Geneva. The Restoration, the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese , neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS), Saint-Louis (FR-68), Weil am Rhein (DE-BW) , twintowns = Shanghai, Miami Beach , website = www.bs.ch Basel ( , ), also known as Basle ( ),french: Bâle ; it, Basilea ; rm, label= Sutsilvan, Basileia; other rm, Basilea . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine. Basel is Switzerland's third-most-populous city (after Zürich and Geneva) with about 175,000 inhabitants. The official language of Basel is (the Swiss variety of Standard) German, but the main spoken language is the local Basel German dialect. Basel is commonly considered to be the cultural capital of Switzerland and the city is famous for its many museums, including the Kunstmuseum, which is the first collection of art accessibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Rhine
The High Rhine (german: Hochrhein) is the name used for the part of the Rhine that flows westbound from Lake Constance to Basel. The High Rhine begins at the outflow of the Rhine from the Untersee in Stein am Rhein and turns into the Upper Rhine in Basel. In contrast to the Alpine Rhine and Upper Rhine, the High Rhine flows mostly to the west. The section is marked by Rhine-kilometers 0 to 165, measurements beginning at the outflow of the Obersee at the Old Rhine Bridge in Constance. It is the first of four sections (High Rhine, Upper Rhine, Middle Rhine, Lower Rhine) of the Rhine between Lake Constance and the North Sea. In the western part, the Rhine marks the border between Germany and Switzerland, while in the eastern part, Switzerland owns areas north of the Rhine and surrounds the popular German holiday resort of Büsingen am Hochrhein. The term ''High Rhine'' was introduced by scientists in the 19th century. Above all geologists tried to differentiate the High Rhine () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Zähringen
The House of Zähringen (german: Zähringer) was a dynasty of Swabian nobility. The family's name derived from Zähringen Castle near Freiburg im Breisgau. The Zähringer in the 12th century used the title of Duke of Zähringen, in compensation for having conceded the title of Duke of Swabia to the Staufer in 1098. The Zähringer were granted the special title of Rector of Burgundy in 1127, and they continued to use both titles until the extinction of the ducal line in 1218. The territories and fiefs held by the Zähringer were known as the 'Duchy of Zähringen' (), but it was not seen as a duchy in equal standing with the old stem duchies. The Zähringer attempted to expand their territories in Swabia and Burgundy into a fully recognized duchy, but their expansion was halted in the 1130s due to their feud with the Welfs. Pursuing their territorial ambitions, the Zähringer founded numerous cities and monasteries on either side of the Black Forest, as well as in the western S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Swabia
The Dukes of Swabia were the rulers of the Duchy of Swabia during the Middle Ages. Swabia was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German kingdom, and its dukes were thus among the most powerful magnates of Germany. The most notable family to rule Swabia was the Hohenstaufen family, who held it, with a brief interruption, from 1079 until 1268. For much of this period, the Hohenstaufen were also Holy Roman Emperors. With the death of Conradin, the last Hohenstaufen duke, the duchy itself disintegrated, although King Rudolf I attempted to revive it for his Habsburg family in the late-13th century. Dukes of Swabia (909–1268) Early dukes * Burchard I Hunfriding (d. 911), mentioned as ''marchio'' (margrave) in 903 and ''dux'' (duke) in 909 * Erchanger Ahalolfing, dominant count in Alemannia after the execution of Burchard I, declared duke in 915, exiled September 916, executed January 917. * Burchard II (917–926, Hunfriding), recognized Henry the Fowler as king of German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |