|
Frenštát Pod Radhoštěm
Frenštát pod Radhoštěm (; german: Frankstadt (unter dem Radhoscht)) is a town in Nový Jičín District in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 11,000 inhabitants. The historic town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument zone. Administrative parts Frenštát pod Radhoštěm is made up of one administrative part. Geography Frenštát pod Radhoštěm lies at the confluence of the Lomná and Lubina rivers. The town is located in the Moravian-Silesian Foothills and extends into the Moravian-Silesian Beskids at the western tip. The mountain of Radhošť, contained in the name of the town, is located south of the town outside the municipal territory. History The first written mention of Frenštát is from 1382. It was probably founded during the colonization between 1293 and 1316. In 1473, tt was first referred to as a market town. In the 16th century, it became a prosperous market town with developed trade and handicr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obec
Obec (plural: ''obce'') is the Czech and Slovak word for a municipality (in the Czech Republic, in Slovakia and abroad). The literal meaning of the word is " commune" or "community". It is the smallest administrative unit that is governed by elected representatives. Cities and towns are also municipalities. Definition Legal definition (according to the Czech code of law with similar definition in the Slovak code of law) is: ''"The municipality is a basic territorial self-governing community of citizens; it forms a territorial unit, which is defined by the boundary of the municipality."'' Every municipality is composed of one or more cadastral areas. Every municipality is composed of one or more administrative parts, usually called town parts or villages. A municipality can have its own flag and coat of arms. Czech Republic Almost whole area of the republic is divided into municipalities, with the only exception being military training areas. The smaller municipalities consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire was a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region during the 17th and early 18th centuries ( sv, Stormaktstiden, "the Era of Great Power"). The beginning of the empire is usually taken as the reign of Gustavus Adolphus, who ascended the throne in 1611, and its end as the loss of territories in 1721 following the Great Northern War. After the death of Gustavus Adolphus in 1632, the empire was controlled for lengthy periods by part of the high nobility, such as the Oxenstierna family, acting as regents for minor monarchs. The interests of the high nobility contrasted with the uniformity policy (i.e., upholding the traditional equality in status of the Swedish estates favoured by the kings and peasantry). In territories acquired during the periods of ''de facto'' noble rule, serfdom was not abolished, and there was also a trend to set up respective estates in Sweden proper. The Great Reduction of 1680 put an end to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albin Polasek
Albin Polasek (February 14, 1879 – May 19, 1965) was a Czech-American sculptor and educator. He created more than 400 works during his career, 200 of which are displayed in the Albin Polasek Museum & Sculpture Gardens in Winter Park, Florida. Career Born as Albín Polášek in Frenštát, Moravia, part of the Austria-Hungary (now in the Czech Republic), Polasek apprenticed as a wood carver in Vienna. At the age of 22, he emigrated to the United States and began formal art training at age 25 under Charles Grafly at the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts in Philadelphia. As a student, he first produced ''Man Carving His Own Destiny'' (1907) and ''Eternal Moment'' (1909). In 1909, Polasek became an American citizen; in 1910, he won the Rome Prize competition; in 1913, he received honorable mention at the Paris Salon for "The Sower;" in 1915, he took the Widener Gold Medal from the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts for his sculpture "Aspiration." At age 37, after peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radegast (god)
Radogost is, according to medieval chroniclers, the god of the Polabian Slavs, whose temple was located in Rethra. In modern scientific literature, however, the dominant view is that ''Radogost'' is a local nickname or a local alternative name of the solar god Svarozhits, who, according to earlier sources, was the chief god of Rethra. Some researchers also believe that the name of the town, where Svarozhits was the main deity, was mistakenly taken for a theonym. A popular local legend in the Czech Republic is related to Radogost. Sources The first source mentioning this theonym is the ''Gesta Hammaburgensis ecclesiae pontificum'' by Adam of Bremen: The elderly Bishop John, captured with other Christians in the city of Mecklenburg, was kept alive to be exhibited in triumph. And consequently, lashed with whips for having confessed to Christ, he was then paraded in each of the cities of the Slavs to be mocked, as he could not be forced to renounce the name of Christ, his hands a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association Football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is to score more goals than the opposition by moving the ball beyond the goal line into a rectangular framed goal defended by the opposing side. Traditionally, the game has been played over two 45 minute halves, for a total match time of 90 minutes. With an estimated 250 million players active in over 200 countries, it is considered the world's most popular sport. The game of association football is played in accordance with the Laws of the Game, a set of rules that has been in effect since 1863 with the International Football Association Board (IFAB) maintaining them since 1886. The game is played with a football that is in circumference. The two teams compete to get the ball into the other team's goal (between the posts and under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ski Jumping Hill
A ski jumping hill is a sports venue used for ski jumping. They vary in size from temporary handmade snow structures to permanent competition venues. At the top is an in-run where the jumper runs down to generate sufficient speed, before reaching the jump. The skier is then airborne until landing on the landing slope. The last part of the hill is the out-run, which may be either flat or even uphill, allowing the jumper to stop. The steepest point of the hill is the construction point, which is used to determine the score of a particular length. The size of a hill is measured in the hill size. Hills with a hill size exceeding HS185 are designated ski flying hills; there are five such hills in the world. Structure The top of the hill is the start. This allows the jury to regulate the speed of the jumpers in varying wind conditions, by shortening or lengthening the distance along the in-run. The platform has a bar across it, which the jumper sits on. By leaning forward, the jumper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were Nazi Germany, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Empire of Japan. The Axis were united in their opposition to the Allies, but otherwise lacked comparable coordination and ideological cohesion. The Axis grew out of successive diplomatic efforts by Germany, Italy, and Japan to secure their own specific expansionist interests in the mid-1930s. The first step was the protocol signed by Germany and Italy in October 1936, after which Italian leader Benito Mussolini declared that all other European countries would thereafter rotate on the Rome–Berlin axis, thus creating the term "Axis". The following November saw the ratification of the Anti-Comintern Pact, an anti-communist treaty between Germany and Japan; Italy joined the Pact in 1937, follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bentwood
Bentwood objects are those made by wetting wood (either by soaking or by steaming), then bending it and letting it harden into curved shapes and patterns. In furniture making this method is often used in the production of rocking chairs, cafe chairs, and other light furniture. The iconic No. 14 chair by Thonet is a well-known design based on the technique. The process is in widespread use for making casual and informal furniture of all types, particularly seating and table forms. It is also a popular technique in the worldwide production of furniture with frames made of heavy cane, which is commonly imported into European and Western shops. Bentwood boxes are a traditional item made by the First Nations people of the North American west coast including the Haida, Gitxsan, Tlingit, Tsimshian, Sugpiaq, Unangax, Yup'ik, Inupiaq and Coast Salish. These boxes are generally made out of one piece of wood that is steamed and bent to form a box. Traditional uses of the boxes was v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hosiery
Hosiery, also referred to as legwear, describes garments worn directly on the feet and legs. The term originated as the collective term for products of which a maker or seller is termed a hosier; and those products are also known generically as hose. The term is also used for all types of knitted fabric, and its thickness and weight is defined by denier or opacity. Lower denier measurements of 5 to 15 describe a hose which may be sheer in appearance, whereas styles of 40 and above are dense, with little to no light able to come through on 100 denier items. Etymology The word hosiery is a morphological derivation of the Anglo Saxon word ''hosa'', which meant a woven garment for the lower body and legs. Overview The first references to hosiery can be found in works of Hesiod, where Romans are said to have used leather or cloth in forms of strips to cover their lower body parts. Even the Egyptians are speculated to have used hosiery, as socks have been found in certain tombs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyeing
Dyeing is the application of dyes or pigments on textile materials such as fibers, yarns, and fabrics with the goal of achieving color with desired color fastness. Dyeing is normally done in a special solution containing dyes and particular chemical material. Dye molecules are fixed to the fiber by absorption, diffusion, or bonding with temperature and time being key controlling factors. The bond between dye molecule and fiber may be strong or weak, depending on the dye used. Dyeing and printing are different applications; in printing, color is applied to a localized area with desired patterns. In dyeing, it is applied to the entire textile. The primary source of dye, historically, has been nature, with the dyes being extracted from animals or plants. Since the mid-19th century, however, humans have produced artificial dyes to achieve a broader range of colors and to render the dyes more stable to washing and general use. Different classes of dyes are used for different types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
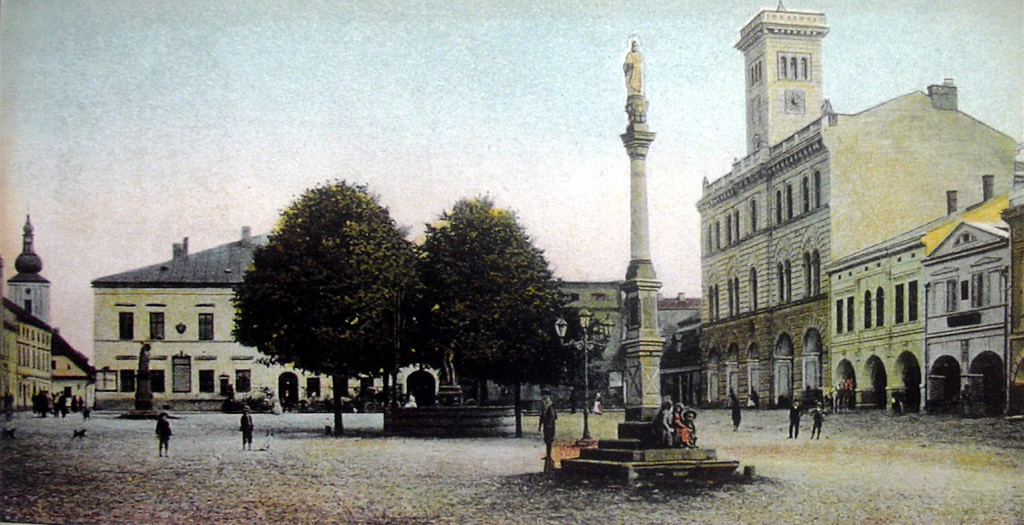






.jpg)